Trauma
What are the main indications for jet ventilation in ENT surgery?
Procedures that need an unobstructed surgical view of the larynx, subglottis or trachea
This kind of ETT has a spiral wire reinforcement to prevent kinking when the tube is bent or compressed.
Reinforced (armored) endotracheal tube

What is the primary airway concern in midface trauma?
Airway obstruction from bleeding, swelling, or fractures.
What must be done before using electrocautery near oxygen delivery devices?
Reduce FiO₂ to the lowest safe level to prevent airway fire.
Which of the following would MOST INCREASE the risk of intraoperative airway fire?
A. Allowing FiO2 to peak at 30%
B. Activation of jet ventilation during laser use
C. Use of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose eye drops near the surgical field
D. Use of a stainless steel endotracheal tube
B.
Metal endotracheal tubes can reduce the risk of airway fires. Saline should be immediately available, use the lowest possible concentration of oxygen, and activate jet ventilation between laser use (not during).
Name 2 complications of jet ventilation.
Barotrauma (pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema). Hypoventilation/Hypercarbia - especially with low driving pressure, high airway resistance, or obstructed outflow. Hypoxemia, device failure.
For oral or nasal surgery, _ tubes can help route the tube away from the surgical field.
Preformed (RAE) tube?
In a patient with severe midface trauma, the safest initial airway is?
Awake tracheostomy or cricothyrotomy
During jet ventilation in ENT procedures, this type of anesthesia is required because inhalational agents are not feasible.
TIVA (intravenous anesthetics)
Elective subglottic jet ventilation for laryngeal papilloma resection is initiated in an otherwise healthy patient. Which of the following is the MOST likely complication associated with this airway management technique?
A. Hypercarbia
B. Impaired venous return
C. Pneumothorax
A.
One of the most common complications of transtracheal or subglottic jet ventilation is hypercarbia. Other important complications include impaired respiratory ciliary function, hypoxia, and loss of the airway. Rarely, subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, and pneumomediastinum can result from barotrauma while necrotizing tracheobronchitis can occur from prolonged use.
Contraindications to transtracheal jet ventilation are?
Upper airway obstruction or any disruption of the airway
Designed for laryngeal and tracheal surgery, this narrow-diameter endotracheal tube is used to maximize surgical access to the glottis.
Microlaryngeal tube (MLT)
You attempt oral intubation in midface trauma; airway obscured by blood. What’s your action?
Suction aggressively, consider video/fiberoptic, call for surgical airway backup
In ENT cases, what is the most feared intraoperative fire triad?
Oxidizer (O₂/N₂O), ignition source (laser/cautery), and fuel (ETT/surgical drapes).
A 32-year-old construction worker requires emergency neck exploration after a section of sheet metal struck his head and neck. He has dysphonia, hoarseness, and a Le Fort I fracture. No major vascular injury was identified. The patient tolerated flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy by an ENT surgeon in the emergency department which showed a hypopharyngeal hematoma and laryngeal cartilage disruption. Which of the above injuries is MOST likely a contraindication for endotracheal intubation?
A. Laryngeal cartilage disruption
B. Hypopharyngeal hematoma
C. Dysphonia and hoarseness
D. Le Fort I fracture
A.
Endotracheal intubation is generally contraindicated in the setting of laryngeal cartilage disruption or laryngotracheal separation. Awake surgical tracheostomy is the preferred method for airway control.
During jet ventilation, monitoring includes observing this as a sign of effective gas exchange, since capnography may be limited.
Chest rise and fall.
Consider transcutaneous CO₂ monitoring for longer cases or patients with limited reserve.
Intraoperative nerve monitoring is utilized by surgeons in anterior neck operations to help preserve the superior laryngeal, recurrent laryngeal, and vagus nerves. What type of tube is preferred for this procedure?
NIM (Neural Integrity Monitor) endotracheal tube
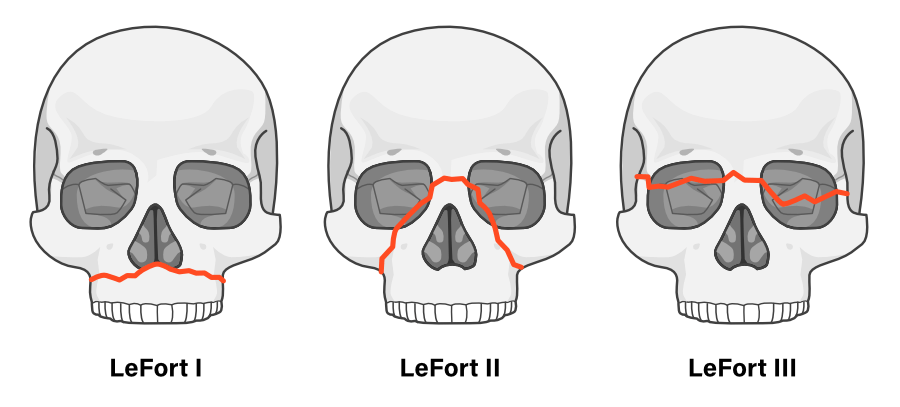
Which facial fracture type contraindicates nasotracheal intubation?
LeFort II or III fracture (basilar skull fracture risk), Naso-orbito-ethmoid (NOE) fractures.
Due to risk of ETT entering the cranial vault.
This is the most important first step when you see subcutaneous emphysema and sudden desaturation during jet ventilation.
Disconnect the jet ventilator and assess for pneumothorax or barotrauma, followed by preparation for emergency airway access if oxygenation cannot be restored.
A physician is deciding whether to use a 5.0 microlaryngeal tracheal tube (MLT) or a 5.0 standard endotracheal tube (ETT) for an otolaryngology procedure in an adult. Which of the following is the BEST reason to use an MLT instead of a standard ETT of the same internal diameter?
A. Increased length
B. Low-volume cuff
C. More flexibility
A.
Microlaryngeal tracheal tubes are designed with a smaller internal diameter but with a length and cuff size appropriate for the adult airway.
Which law of physics primarily explains gas delivery in jet ventilation?
Venturi effect/Bernoulli’s principle.
When a gas or liquid flows through a constricted region, its speed increases and its pressure drops. In jet ventilation, a high-pressure jet of oxygen entrains surrounding air due to the pressure drop, delivering a mix of oxygen and surrounding room air.
You are using an MLT tube, and ventilation pressures are high. What’s the likely cause?
Narrow lumen increases resistance; consider suction, ensure no kinking.
Smaller diameter = higher resistance (Poiseuille’s Law: resistance ∝ 1/r⁴)
In facial trauma, this fracture classification system describes levels of maxillary involvement.
LeFort fractures.
A 50yo M has a paroxysm of coughing in the PACU while awakening following uneventful endoscopic sinus surgery. Immediately afterward, his respirations seem labored with a loud inspiratory stridor. What is the differential diagnosis of inspiratory stridor?
Laryngospasm, laryngeal edema, foreign body aspiration, or vocal cord dysfunction.
Laryngospasm, an involuntary spasm of the laryngeal musculature, may be triggered by blood or secretions stimulating the superior laryngeal nerve. Laryngeal edema may be caused by an allergic drug reaction, hereditary or iatrogenic angioedema, or a traumatic intubation. Vocal cord dysfunction could be due to residual muscle relaxant effect, hypocalcemic alkalotic tetany, intubation trauma, or paradoxical vocal cord motion.
Intraoperative use of which of the following airway management techniques is MOST associated with an increased risk of tracheobronchial contamination by upper airway debris during airway surgery?
A. Laser-safe endotracheal tube placement and mechanical ventilation
B. Microlaryngeal tube placement and mechanical ventilation
C. Subglottic jet ventilation via a specialized catheter
D. Supraglottic jet ventilation via a rigid broncoscope
D.
Use of supraglottic jet ventilation, in contrast to subglottic jet ventilation and endotracheal intubation, significantly increases the risk of lower airway contamination and results in less reliable control of inspired oxygen concentrations. The primary advantage of supraglottic jet ventilation is lack of obstruction of the operative field by a tube or catheter.
