What does 'x->0^-' mean?
x approaches 0 from the left.
If f(x)=x^2-5x, then f'(x)=
f'(x)=2x-5
d/dx(e^x)=
e^x
If f'(x)<0 forall x on interval (a,b) , then what conclusion can we make about f(x)?
The function is decreasing on interval
(a,b)
int(x^2+sec^2(x))dx=
1/3x^3+tan(x)+C
A vertical asymptote is an example of _______ discontinuity.
infinite
The function y=root(3)(x) is not differentiable at x=0 since...
...there is a vertical tangent at
x=0
If y =
ln(x/4)
, then what is the derivative at x = 1?
asdf
The area, A, of a triangle is changing with respect to time. What equation describes how the area of the triangle is changing?
(dA)/dt=1/2((db)/dtcdoth+bcdot(dh)/dt)
What is the limit as x approaches 2 from the left?
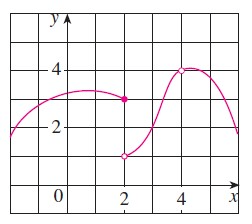
3
In terms of differentiation formulas, what is the quotient rule?
(f'(x)g(x)-f(x)g'(x))/[g(x)]^2
If y=3^(cos(x) , then dy/dx=
3^(cos(x))cdotln(3)cdot(-sin(x))
Newton's Method is an iterative process, which states that xn+1 =
xn - [f(xn) / f'(xn)]
If the area
asdf
If f(x) is continuous on [a,b] , and f(a)<N<f(b) , then by the _________ ______ theorem, there must exist some 'c' on (a,b) , such that ______.
Intermediate Value;
f(c)=N
If y=sqrtxtan(2x) , then dy/dx=
1/(2sqrtx)tan(2x)+sqrtxsec^2(2x)cdot2
If f(x)=sin^-1(x), then state the value(s) of x for which the function is non-differentiable.
Non-differentiable at
x=-1,1
If f is a function that is continuous on [a, b], differentiable on (a, b), and f(a) = f(b), then by ______ theorem, there is a number c in (a, b) such that ________.
Rolle's; f'(c) = 0
Evaluate the limit:
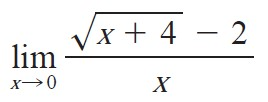
1/4
If y^3=xy-2x^2+8 , then find dy/dx at (1, 2)
Change!
If f(x)=tan^-1(x^2) , then find f'(x).
(2x)/(1+x^4)
If a snowball melts so that its surface area decreases at a rate of 1 cm2/min, find the rate at which the diameter decrease when the diameter is 10 cm.
The diameter is decreasing by
1/(20pi)(cm)/min