Define the Term "Viscosity" and provide an example.
A fluids resistance to flow and thickness
Define the Term "Density" and provide an example.
The amount of mass in a given volume.
Define the Term "Solution"
A homogenous mixture
Define The Term "The Particle Model of Matter"
The particle model of matter is a scientific theory that describes the behavior of matter as being composed of tiny, discrete particles that are in constant motion. These particles can be atoms, molecules, or ions, depending on the type of matter being considered. The particle model is used to explain the properties and behavior of matter, such as its density, viscosity, and heat capacity, as well as the changes that can occur when matter is subjected to different conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical reactions. The particle model helps scientists understand the fundamental nature of matter and how it interacts with other matter and energy in the universe.
What are the different states of matter and how do they relate to the particle model? Provide examples.
Solids, gas, liquids, and plasma
Why do we divide mass by volume to get density?
Density is the measure of how much mass is in a given volume.
Define the term "Buoyancy"
Buoyancy is an upwards force which allows an object to float, in opposition to gravity.
What is happening within particles that is making a substance more viscous?
Friction, and adhesive attraction.
Density = Mass divide Volume
When a solution cannot dissolve more solutes, it's considered a...
Saturated Solution
Define the term "Mixture"
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically combined but not chemically combined.
Describe the movements of particles within a solid.
Minimal movement and vibrations, very tightly compacted.
A box 5 cm long, 4 cm wide and 6 cm high would have what volume?
120 cm/3
According to Archimedes' principle, what is the rule for the amount of water displaced?
The force exerted up (buoyancy) is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
When we heat up a fluid, it likely becomes less viscous because...
Particles expand, less attraction, causing less friction and particle collisions
The scientific term that describes the connection between particles is
Cohesive Attraction!
Name three different methods for separating solutes and solvents
Evaporation, filtration, funnel, reverse osmosis, Chromatography, distillation, etc
Define both "volume" and "mass"
I do not have a definite volume. I can be easily compressed. What am I?
Gas
Which one is more dense?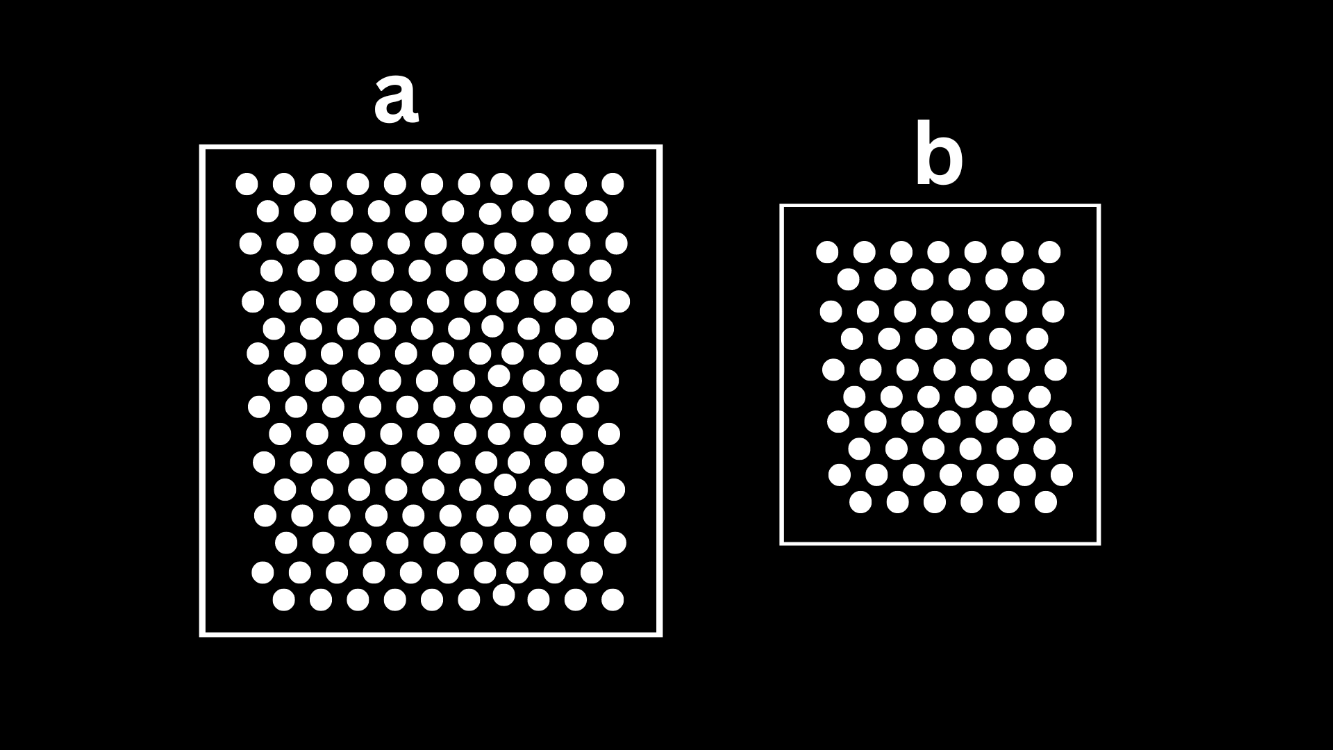
They are the same density!
How can we tell if an object will float or sink?
Comparing the ratio of the object to the liquid, and seeing which is more dense
What are some common methods for measuring the viscosity of a substance?
Viscometer, pouring it down a tray, rheometer, etc
Most times, solids are denser than their liquid state. Give me an example of when this is false.
Water and ice, sulfur, etc
What are some factors that impact solubility? Name at least 3.
Temperature and thermal energy, agitation and stirring, pressure, chemical components of our solvent, and surface area
Define "Suspension" and provide an example.
A suspension is a mixture in which the particles of the solute are large and do not dissolve in the solvent, but instead remain suspended in the mixture.
Name an example of how we can identify a mixture and a pure substance.
Boiling point, pH levels, and characteristics, etc
A solid is 5 cm tall, 3 cm wide and 2 cm thick. It has a mass of 129 g. What is its density? Round to the nearest one if needed.
4.3 grams per cubic centimeter / 4
How do Archimedes' principles of buoyancy relate to real-world applications, such as the design of ships and submarines?
Ships must displace enough water through its hull to balance out the weight of the ship
Sort the following from least to most viscous - water, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium, molasses, syrup, honey, oxygen, pitch, and molten lava
Helium, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, syrup, molasses, honey, pitch, and molten lava
If a substance is very dense, how can we make it less dense?
Dilution, thermal energy, reducing pressure, and physically changing the states
How can we form a super-saturated solution?
Increasing thermal energy to dissolve more solutes that is beyond what is capable of doing.
Define "Plasma", and provide an example.
Plasma is a gaslike state which contains both positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons. An example of this is FIRE.
How does the particle model explain the behavior of gases?
Gases have no defined volume, larger spaces between particles, more collisions, and more kinetic energy
Will an object with a density of 0.97 g/ml float or sink in water? Explain.
The object will float because anything less than 1 is less dense than water, with the density level of around 1 g/mL at room temperature.
How is the concept of buoyancy related to density?
An object will float if it is less dense than the fluid it is placed in, and it will sink if it is more dense. The density determines the buoyant force exerting within an object.
What are some common applications of viscosity measurements in industry and science? Explain and provide examples for how its used.
Food industry, petroleum industry, automotive industry, biomedical field, and environmental field
You have a different rock with a volume of 30cm3 and a mass of 60g. What is its density?
2.0g/cm3
A mixture where you cannot see the different parts and solutes is called a...
Homogenous Mixture
Define the term "Dispersion" (hint, its related to diffusion)
Dispersion is the process by which a solute is evenly distributed throughout a solvent to form a homogeneous mixture.
The transition from a solid to gas state (directly) is called...
Sublimation
What is the volume of this triangular prism?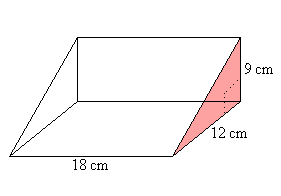
972 CM/3
Why does a piece of metal, but a huge metal ship can float?
Using the equation flow rate = volume divided by time, calculate the flow rate of a substance that takes 14 seconds for 500mL to flow.
35.7
What is the density of an object with a mass of 48 grams and a volume of 3 ml?
16 grams/ml.
How do the properties of a mixture compare to the properties of its individual components?
Density, viscosity, saturation, compounds, etc
An element is a substance that can no longer be broken down into smaller parts.
What are some common applications of the particle model in science and technology?
Biomedicine and flow of blood, geology and behavior of rocks, chemistry and behavior of atoms and interactions, engineering and understanding engines and pumps, etc
A cat has volume of 0.0040 m^33 and density of 980980 kg/m^33. Calculate the mass of the cat. (hint: 980 times 0.004)
3.92 kg
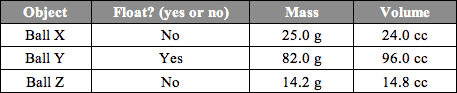
Three balls were measured and placed in a liquid. Based on the following data, what could be the density of the liquid? Round if needed.
0.9 g / mL