List the monosaccharides:
glucose
fructose
galactose
Macronutrient
Starch is what kind of carbohydrate and what is its structure?
Polysaccharide
Long chain of glucose molecules joined together
Example of a sugar crystal
What kind of heat creates dextrinisation?
dry heat / cooking
List the disaccharides
Lactose
Sucrose
Maltose
Category of carbohydrates are soluble
monosaccharides + disaccharides / simple sugars
The two different types of starch
Amylose and amylopectin
Increases how much sugar can be dissolved in solution
Temperature
Name of oligosaccharide that breaks off from the starch chain in the process of dextrinisation
dextrins
List the polysaccharides
Fibre
Glycogen
Starch
Anatomy of a whole grain
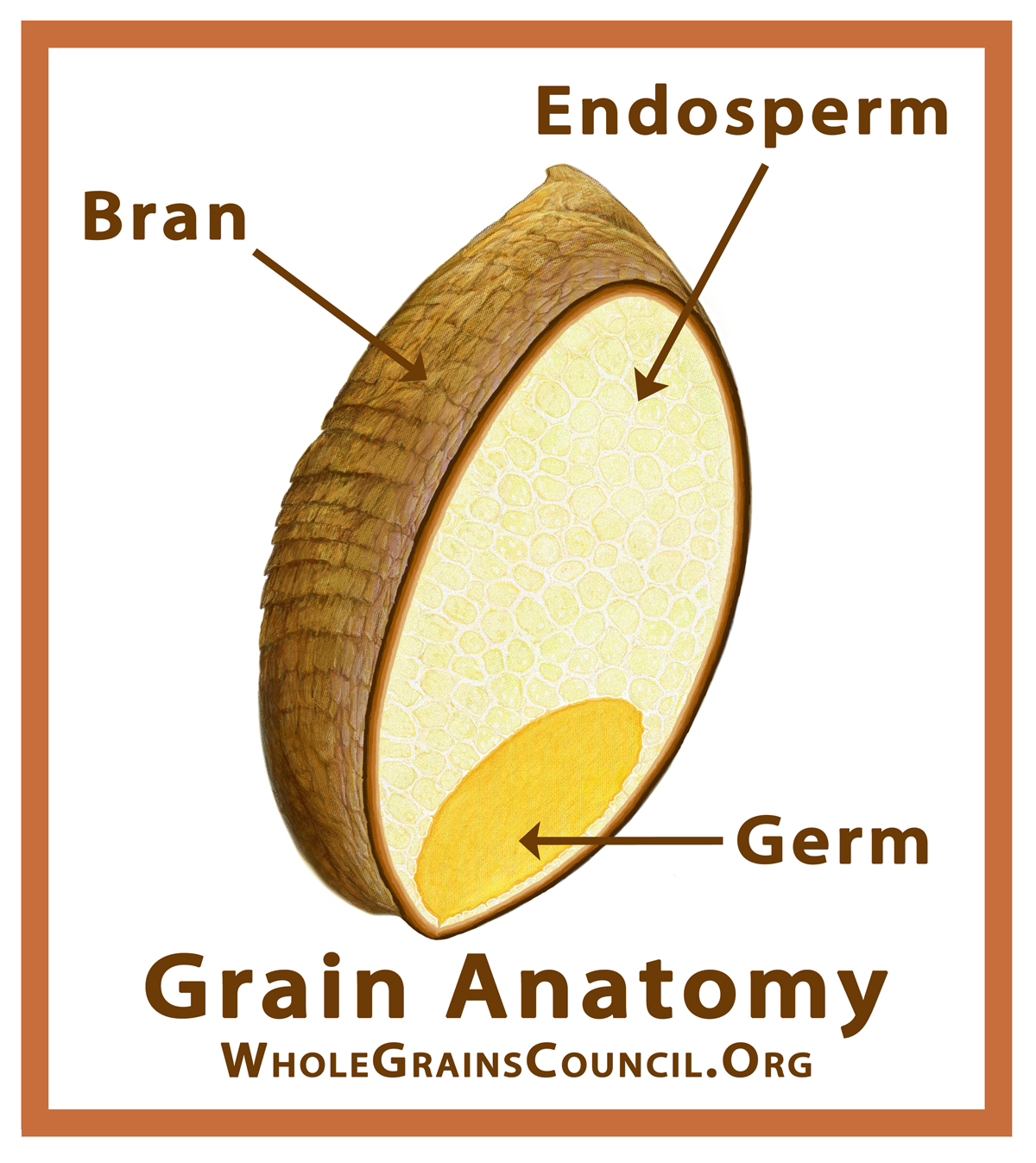
starch granules are bonded together by what?
hydrogen bonds
Fudge is creamy, not grainy, what cooking technique is used to prevent sugar crystals forming early?
Do not stir too early. Stirring encourages sugar crystals aggregating together forming larger crystals in solution.
By stirring too early, while the sweet solution is still warm, only a few seeds will form, and the rest will continue to float around in the warm solution. Then they will grab onto the already formed sugar crystals, and grow into large crystals, like rock candy.
The sweet solution will then have small chunks of sugar in it, rather than being smooth, with tiny sugar crystals in it making a sweet and creamy solution! Like ice cream and fudge
Colour of dextrins
brown / golden brown
The formula of glucose
C6 H12 O6
Nutrient consistent in carbohydrate-based foods
Fibre
What happens to the starch granules when a solution of starch and water heats up?
Hydrogen bonds break in hot water and the amylose and amylopectin interacts with the water molecules instead, further separating the starch chains, thickening the solution.
How caramel is made
Cooking sugar on very high heat with added fat / oil.
When a saturated solution of liquid and sugar begins to cool, these sugar crystals form. However, when fat is added to this solution, the fat molecules bind to the sugar molecules also and prevent them from sticking together, therefore preventing them from forming large sugar crystals. Therefore the solution stays semi liquid / soft / "gooey".
What happens to the starch molecules in a piece of toast due to the heat?
Heat breaks the glycosidic bond of starch forming dextrins, making the toast a golden brown colour as it cooks.
Name:
The bond connecting glucose molecules
The reaction separating glucose molecules
The reaction joining glucose molecules
Glycosidic linkage
hydrolysis
dehydration / condensation
State the source, bond, and branched for:
cellulose, starch (amylose + amylopectin), and glycogen
Cellulose: plant, beta bond, not branched
Amylose: plant, alpha bond, not branched
Amylopectin: plant, alpha bond, branched
Glycogen: animal, alpha, branched
Affects the thickening of a starch and water solution
Sugar, as it is soluble and competes for interaction with the water molecules
Describe the relationship between sucrose concentration and temperatures in a sugar solution
As the water continues to boil, the water changes its state of matter.
From liquid > gas i.e., water vapour / steam
Meaning the solution of water and sugar is becoming more and more concentrated as the temperature increases. And, as the temperature increases more and more, more sugar can be dissolved in the solution also.
Describe what happens to the carbohydrate molecules when toast burns.
Bonds in the glucose molecule break due to the heat. The hydrogen and oxygen bond together forming water / water vapour / steam, and the carbons bond together forming the black on the toast.