describe how to name carbohydrates with this 
-aldehyde: name by aldo(# of carbon)+ose
what are cyclic carbohydrates called
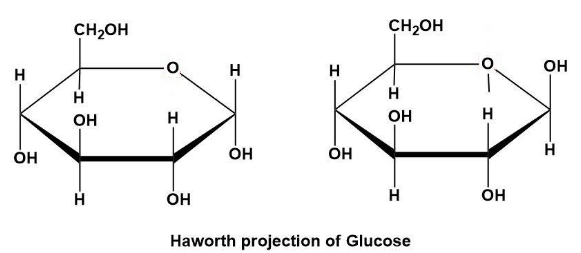
haworth structures
Oxidation is...
increasing C-O bonds, decreasing C-H bonds
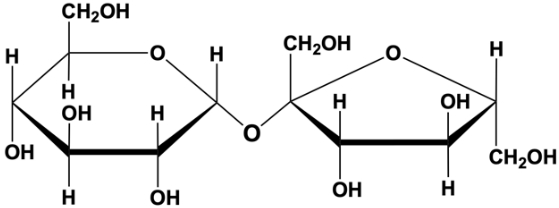
what is the most common glycosidic bond
1,4
Which of the following is only found in plants,
cellulose, starch, and glycogen
cellulose
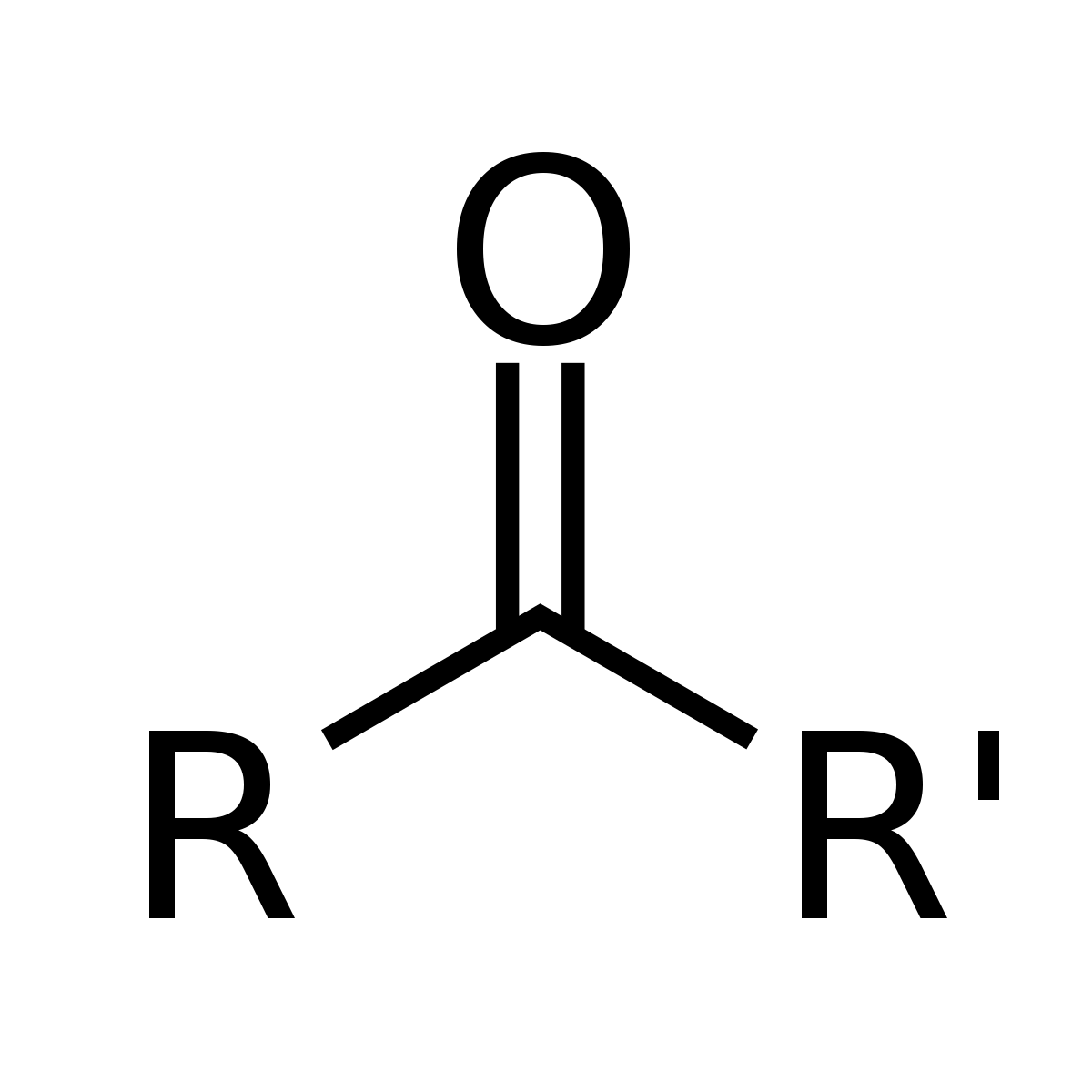 how do you name a carbohydrate with this functional group
how do you name a carbohydrate with this functional group
ketone: name by keto(# of carbon)+ose
from what carbon do you start counting
start counting counterclockwise from the O in the ring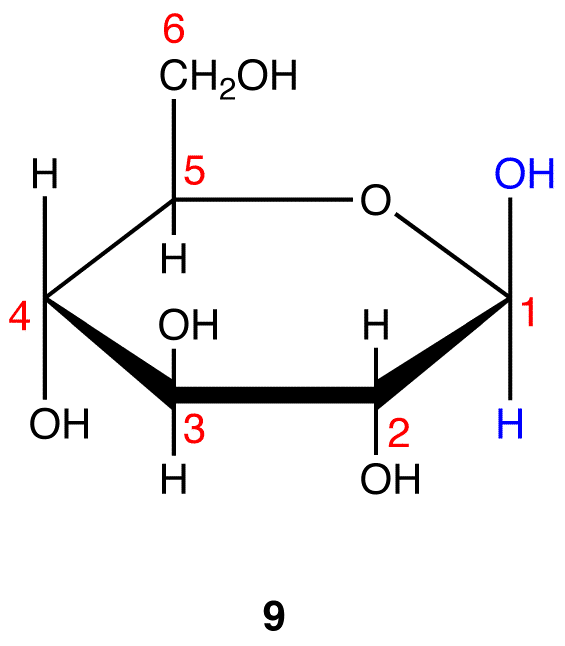
Reduction is
decreasing C-O bonds, increasing C-H bonds
what makes a glycosidic bond alpha
the original left monosaccharide was alpha (O will come down off of the first carbon )

why can't humans digest cellulose
humans cannot break the beta 1,4 glycosidic linkages (humans can’t gain nutritional value from it)
How many chiral carbons are in this structure

4
a monosaccharide will have ___ ring(s)
a disaccharide will have ___ ring(s)
a polysaccharide will have ___ ring(s)
1,2,2+
oxidation of an aldehyde will result in
carboxylic acid
what makes a glycosidic bond beta
the original left monosaccharide was beta (O will come up off of the first carbon )

if starch is made by plants, why can humans digest it?
it has alpha 1,4 glycosidic linkages
What does it mean if a fischer projection is L
OH on the left for the 1st chiral carbon from the bottom
What does it mean if a haworth structure is alpha
OH is on bottom of carbon 1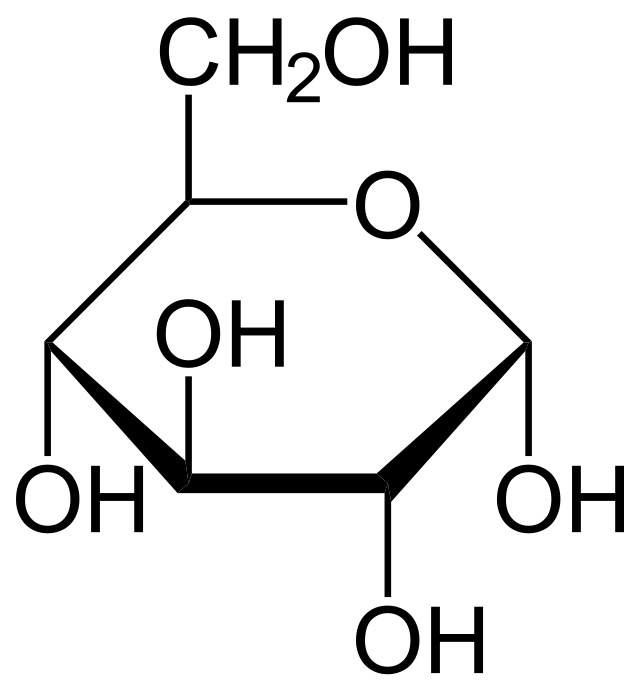
reduction of aldehyde
results in primary alcohol

what process forms a glycosidic bond

dehydration synthesis(pull out water)
how do we store polysaccharides and what type of glycosidic bonds are they
glycogen, 1,4 alpha glycosidic bonds
What does it mean if a fishcer projection is D
OH on the right for the 1st chiral carbon from the bottom

What does it mean if a haworth structure is beta
Is OH is on top for Carbon 1

what will happen during the oxidation AND reduction of a ketone
Oxidation: nothing (already at max C-O bonds)
reduction: secondary alcohol
hydrolysis of a disaccharide will break the ____ and form 2 ______
1,4 glycosidic bond
monosaccharides
give me the 2 examples of starch that vonderheide gave us and describe the difference
→amylose is what makes up starch, alpha 1,4 glycosidic bonds (long chain)
→amylopectin, same thing but more branched, still with alpha 1,4 glycosidic