These are the two functional groups in a sugar
What is a carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone) and a hydroxyl group?
This is the term for when an enzyme is activated or inactivated by the addition of a phosphate group
What is phosphorylation?
This means a reaction does NOT need oxygen
What is anaerobic?
This is the term for two molecules that differ only in chirality
What is "stereoisomers"
This is the term for a sugar combined with another type of molecule
What is glycoconjugate?
This process turns glucose into glycogen
What is glycogenesis?
Name this sugar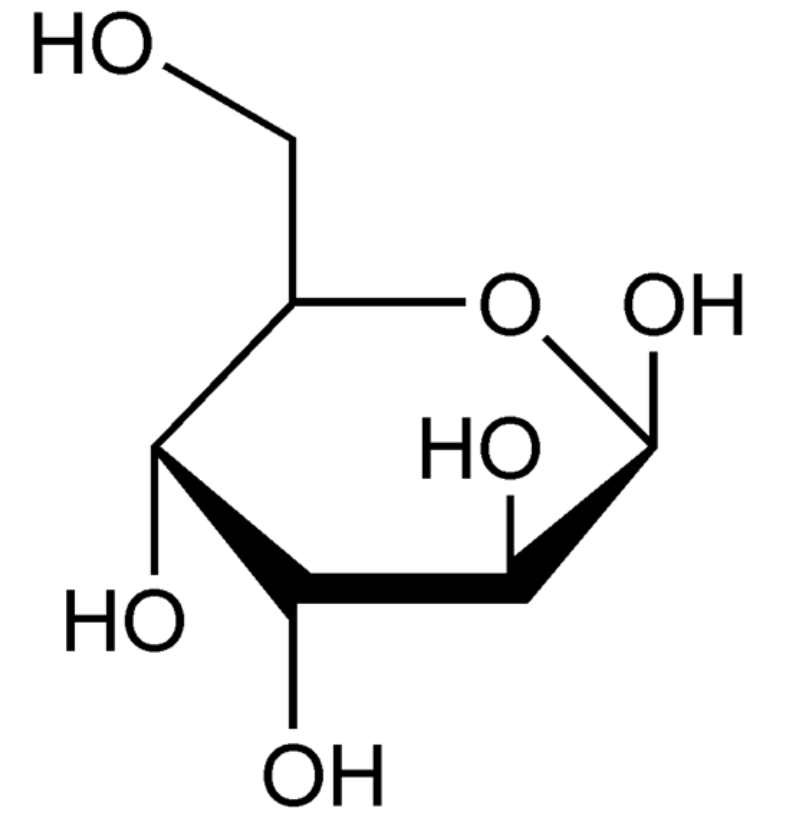
What is ß-D-attrose?
If an enzyme is turned off when a group is added to a location that is not the active site, it is this type of inhibition
What is Allosteric inhibition?
This is the number of times MORE ATP is made in the tricarboxylic acid cycle than is made in glycolysis
What is ~15 times more? (16 also acceptable)
This is the chirality of almost all naturally occurring sugars
What are D sugars
This macromolecule makes up cell walls in bacteria, and is a frequent target of antibiotics
What is peptidoglycan?
Gluconeogenesis is to fructobisphosphatese-1 as glycogenesis is to _________________
Glycogen Synthase
These are the tops of glycosidic linkages found in glycogen
What are alpha (1-->4) linkages, with branching alpha (1-->6) every 8-12 carbons?
Turning on or off this _______ enzyme is the primary method of controlling glycolysis.
Turning on or off this ________ enzyme is the primary method of controlling gluconeogenesis.
What are PFK-1 and fbpase-1, respectively?
The anaerobic fates of pyruvate differ by organism. Which organisms do what?
In anaerobic conditions, humans and animals do the lactic acid fermentation. Yeasts do ethanol fermentation
A molecule with 3 chiral centers would have this number of different stereoisomers
What is 8?
This is the type of enzyme that adds a phosphate group from an ATP
What is a kinase?
Glycolysis occurs particularly quickly in these type of cells, which can show up on a PET scan
What are cancerous cells?
This is the type of reaction that turns a straight chain hexose into a ring
What is a hemiacetal reaction?
Insulin will activate the ___________________ pathway, while inhibiting the __________________ pathway
What is ..
Insulin will activate the _glycolysis (or glycogenesis)_ pathway, while inhibiting the _gluconeogenesis (or glycogenolysis)_ pathway
This is the (biochemical) reason we need to breath
The kreb's cycle/tricarboxylic acid cycle/Citric Acid cycle is aerobic, requiring oxygen. This produces a majority of the ATP/energy we use to survive
The (alpha/beta) conformation is more common in glucose because __________________
What is beta, because this places the hydroxyl group in the more stable equatorial position, limiting sterics interactions?
This pathway is used to make ribose and other sugars found in such useful molecules as DNA, NADH, ATP, and more
What is the pentose phosphate pathway?
These two enzymes control the metabolism of glucose to glycogen, and vice versa
What are glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase?
This is the common name for alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-beta-D-fructofuranoside
What is sucrose?
Epinephrine or glucagon will signal for the addition of a phosphate group, allosterically adding onto the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme. This switches from the less active b form to the more active a form, speeding up the breakdown of glycogen
This is the reason that the lactic acid cycle results in increased energy
The lactic acid cycle replenishes the NAD+ needed for glycolysis, allowing the glycolysis reactions to run, producing more ATP
Draw (R,S) 2,4-dichlorohexane
do it do it do it
Describe the Cori cycle in detail
Glycogen stored in the muscles is broken down into glucose, which then undergoes glycolysis. When working out, a lack of sufficient oxygen causes the pyruvate to go through the lactic acid cycle. This lactate is shuttled to the liver, where it undergoes gluconeogenesis, building it back up to glucose. This glucose is then sent back to the muscles to rebuild glycogen
This is why it is important that glycogen is branched
The glycogen phosphorylase acts on the non-reducing end of the sugar. By branching, there are many non-reducing ends, and glucose can be released more quickly from multiple ends simultaneously