What is a hydroxyl functional group?
OH
What is the fat stored in adipocytes?
Triglycerides
State the type of reaction which converts excess monosaccharides to polysaccharides.
condensation/dehydration/synthesis/anabolic/anabolism ✔
What type of reactions link monomers to form polymers?
Condensation reactions

What type of linkages would I find in Amylose vs Amylopectin?
1,4 vs 1,6 for the branches.
Name the 3 forms of carbohydrates
Mono, disacchariedes, polysaccharides
Which molecule can form 5 covalent bonds.
Phosphorus
What distinguishes cellulose from glycogen and starch?
A. Only cellulose is found in plants.
B. Only cellulose is made up of glucose monomers.
C. Cellulose is far more branched than starch and glycogen.
D. Cellulose has a structural role whereas starch and glycogen function in energy storage.
D. Cellulose has a structural role whereas starch and glycogen function in energy storage.
When digesting carbohydrates into monosaccharides, what is the name of the digesting agents.
Hydrolysing Enzymes in a hydrolysis reaction
Name the monomers of lipids?
Glycerol, 3 fatty acids, inorganic phosphate group.
What is the difference between alpha & beta glucose and why is it important?
 Beta glucose is used in cellulose helping to create hydrogen bonds linking the cellulose chains together.
Beta glucose is used in cellulose helping to create hydrogen bonds linking the cellulose chains together.
Name a molecule that can pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Steroid hormones
What carbon based molecule is this? C4H10
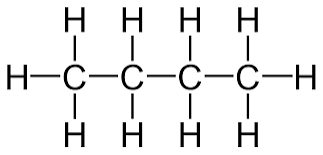
Butane

What is the monomer of hormones?
Cholesterol
What ingredients are necessary to build a DNA
Phosphate group, Pentose sugar, Nitrogenous base,
Using vocabulary from this module explain what happens to a beef taco in your body.
1. Protein is broken down in the digestive system using hydrolysis reactions, resulting in amino acids.
2. Amino acids are absorbed in the blood and taken to body cells.
3. DNA in the body cell directs specific condensation reactions to produce a specific protein from amino acids.
What blood type is the universal donor vs the universal recipient? What molecule is involved in determining the different blood types?
Type O = universal donor
Type AB = universal recipient.
Glycoproteins acting as antigens.
Lipids exist in four forms, what are they?
Triglycerides, phospholipid, cholesterol, steroid hormones.
What type of molecule is this?
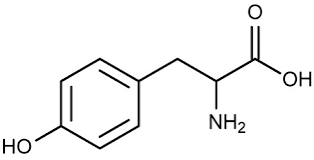

Maltose, lactose, and sucrose are what category of molecule?
Disaccharides
What is chitin and where would I find it?
Polysaccharide, exoskeleton.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-465855494-8474453edef34db88ff14f50818aea82.jpg)
Name 3 of the 4 properties and use of glucose.
1. Molecular Stability
2. High solubility in water
3. Easily transportable
4. Yields a great deal of chemical energy
What type of bonds form between the hydrogen and carbons in a lipid? How does this affect its properties.
Non-polar covalent bonds making fats insoluble in water but will dissolve other non-polar solvents.
How do endotherms maintain body temperature, specifically.
Adipose cells between skin and muscles maintain heat from metabolic processes
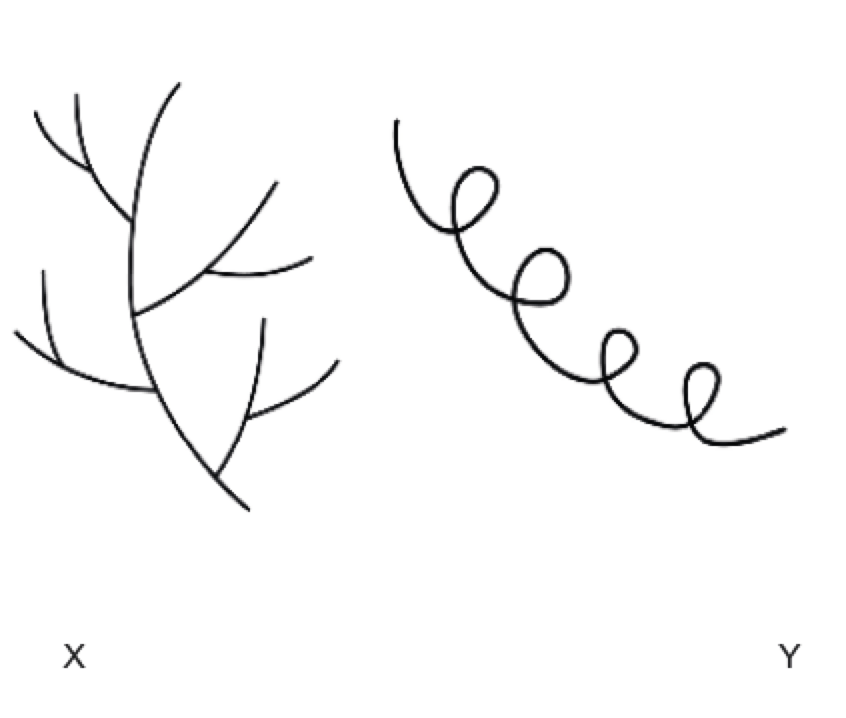
Name X & Y
A
What is the monomer of ATP?
Nucleotides
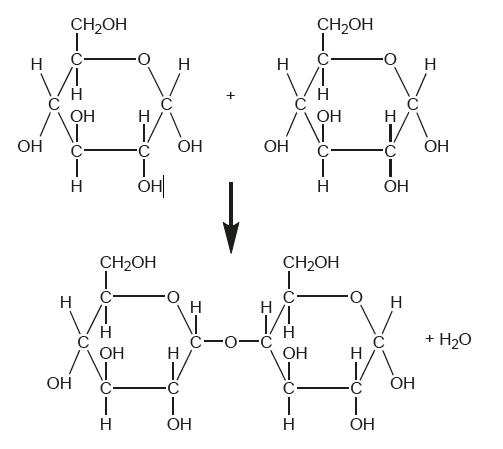 What type of molecule is formed by the chemical reaction shown in the diagram?
What type of molecule is formed by the chemical reaction shown in the diagram?
Disaccharides
When stored glucose's covalent bonds are broken down into high yield energy, what type of reaction is this.
Oxidation Reactions to form ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation.
What type of fat is olive oil? What does that mean?
Monounsaturated
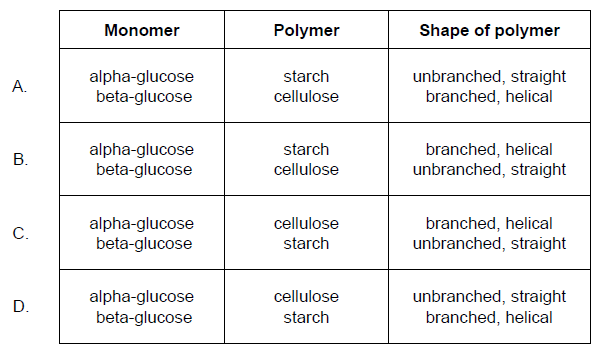
The structure of monomers affects the structure and function of the polymers they form. Which row
describes the structural features of polysaccharides made from alpha-glucose and beta-glucose?
B
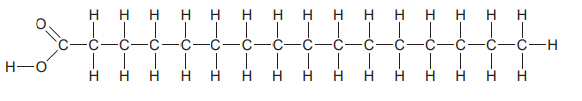 Which molecule is depicted in the diagram?
Which molecule is depicted in the diagram?
A. A saturated fatty acid
B. An unsaturated fatty acid
C. A trans fat
D. A vegetable oil
A. Saturated Fat
What special property of phospholipid molecules explains their ability to spontaneously assemble into a lipid bilayer?
A. They are hydrophobic.
B. They are amphipathic.
C. They are saturated.
D. They are hydrophilic
B. They are amphipathic.
What is a property of water?
A. Water has a low specific heat capacity so large increases in heat energy cause a small temperature change.
B. Water is an excellent solvent for non-polar substances.
C. Covalent bonds between adjacent water molecules are responsible for its unique properties.
D. Water molecules are highly cohesive which is important for transport in xylem.
D. Water molecules are highly cohesive which is important for transport in xylem.