A general term for the inadequacy of the heart to pump blood throughout the body, causing insufficient perfusion of body tissues with vital nutrients and oxygen.
heart failure (HF)
Enlargement of the heart.
cardiomegaly
The major types of heart failure are:
• Left-sided heart failure
• Right-sided heart failure
• High-output failure
A client with heart failure reports increasing shortness of breath when lying flat and a cough productive of pink, frothy sputum. Which type of heart failure is most likely?
A. Right-sided heart failure
B. Left-sided heart failure
C. Both right- and left-sided heart failure
D. High-output heart failure
Correct Answer: B. Left-sided heart failure

Which assessment finding in a client with left-sided heart failure requires immediate action by the nurse?
A. Crackles in both lung bases
B. Jugular vein distention
C. Dependent edema
D. Weight gain of 2 pounds in 2 days
Answer: A. Crackles in both lung bases
Rationale:
- Crackles in both lung bases indicate pulmonary congestion and fluid overload, which can quickly progress to pulmonary edema—a life-threatening complication.
Accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space.
pericardial effusion
Narrowing of the aortic valve orifice and obstruction of left ventricular outflow during systole.
aortic stenosis
was formerly referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF). - cardiac output (CO) is diminished, leading to impaired tissue perfusion, anaerobic metabolism, and unusual fatigue.
Left-sided heart failure
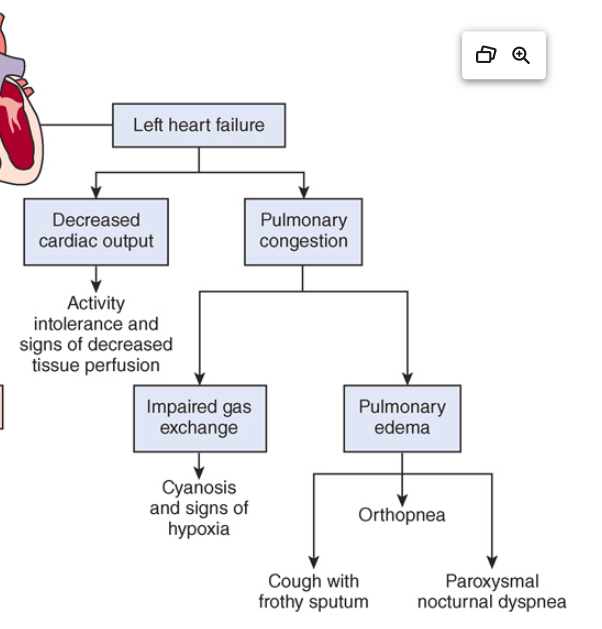
A nurse is assessing a client with a history of heart failure. Which finding is most indicative of left-sided heart failure?
A. Jugular venous distention
B. Crackles in the lung bases
C. Peripheral edema
D. Hepatomegaly
Correct Answer: B. Crackles in the lung bases
Rationale:
- Crackles are caused by fluid backing up into the lungs, a hallmark of left-sided heart failure.
- JVD, peripheral edema, and hepatomegaly are more commonly associated with right-sided heart failure.
The nurse is teaching a client with heart failure about dietary restrictions. Which food should the client avoid?
A. Fresh fruit
B. Canned soup
C. Baked chicken
D. Steamed vegetables
Answer: B. Canned soup
Rationale:
- Canned soup is typically high in sodium, which can worsen fluid retention in heart failure.
Sensitivity response that develops after an upper respiratory tract infection with group A beta-hemolytic streptococci that can damage the heart valves.
rheumatic carditis
Enlargement of the cardiac muscle.
myocardial hypertrophy
may be caused by left ventricular failure, right ventricular myocardial infarction (MI), cardiomyopathies, pulmonic valvular disease, or pulmonary hypertension. In this type of heart failure (HF), the right ventricle cannot empty completely. Increased volume and pressure develop in the venous system, and peripheral edema results.
Right-sided heart (ventricular) failure
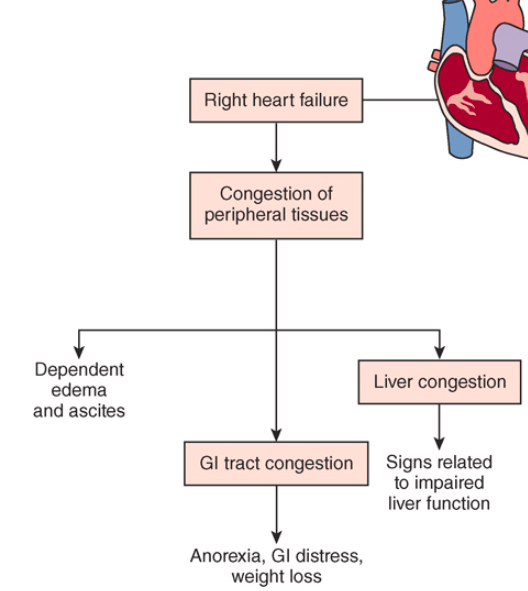
The nurse is caring for a client with right-sided heart failure. Which assessment finding should the nurse expect?
A. Orthopnea
B. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
C. Ascites
D. Pulmonary crackles
Correct Answer: C. Ascites
Rationale:
- Ascites (abdominal swelling from fluid accumulation) is a classic sign of right-sided heart failure.
- Orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and pulmonary crackles are more typical of left-sided heart failure.
A client with heart failure is prescribed furosemide (Lasix). Which laboratory value should the nurse monitor most closely?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Calcium
D. Glucose
Answer: B. Potassium
Rationale:
- Furosemide is a loop diuretic that can cause significant potassium loss, leading to hypokalemia.
An inflammation or alteration of the pericardium, the membranous sac that encloses the heart; may be fibrous, serous, hemorrhagic, purulent, or neoplastic.
acute pericarditis
Thickening of the mitral valve due to fibrosis and calcification. The valve leaflets fuse and become stiff, and the valve opening narrows, which prevents normal blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
mitral stenosis
can occur when cardiac output remains normal or above normal, is caused by increased metabolic needs or hyperkinetic conditions, such as septicemia, high fever, anemia, and hyperthyroidism. This type of heart failure is not as common as other types.
High-output heart failure
A client with left-sided heart failure is at greatest risk for which complication?
A. Pulmonary edema
B. Deep vein thrombosis
C. Hepatomegaly
D. Dependent edema
Correct Answer: A. Pulmonary edema
Rationale:
- Pulmonary edema results from fluid backing up into the lungs due to left-sided heart failure.
- DVT, hepatomegaly, and dependent edema are more associated with right-sided heart failure.
Which statement by a client with heart failure indicates a need for further teaching?
A. "I will weigh myself every morning."
B. "I will call my provider if I gain more than 2 pounds in a day."
C. "I will take my medication even if I feel better."
D. "I will drink at least 3 liters of fluid every day."
Answer: D. "I will drink at least 3 liters of fluid every day."
Rationale:
- Clients with heart failure are usually on fluid restrictions to prevent fluid overload. Drinking 3 liters daily is excessive and could worsen heart failure.
- The other statements reflect appropriate self-care behaviors.
Compression of the myocardium by fluid that has accumulated around the heart; this compresses the atria and the ventricles, prevents them from filling adequately, and reduces cardiac output.
cardiac tamponade
The flow of blood from the aorta back into the left ventricle during diastole; occurs when the valve leaflets do not close properly during diastole and the annulus (the valve ring that attaches to the leaflets) is dilated or deformed.
aortic regurgitation
A client with a history of heart failure presents to the emergency department with severe shortness of breath, pink frothy sputum, and crackles in both lung bases. Which action should the nurse take first?
A. Place the client in high Fowler’s position
B. Administer IV morphine
C. Obtain a 12-lead ECG
D. Insert a Foley catheter
Correct Answer: A. Place the client in high Fowler’s position
Rationale:
- Positioning the client upright improves lung expansion and reduces venous return to the heart, helping to relieve pulmonary congestion immediately.
- The other interventions are important but do not address the immediate need to improve oxygenation and reduce respiratory distress.
Which statement by a client indicates understanding of the difference between left-sided and right-sided heart failure?
A. "If my legs swell, it means my left heart is failing."
B. "Shortness of breath at night is a sign of right-sided heart failure."
C. "If I have trouble breathing and cough up pink sputum, my left heart is not working well."
D. "Right-sided heart failure causes fluid to build up in my lungs."
Correct Answer: C. "If I have trouble breathing and cough up pink sputum, my left heart is not working well."
Rationale:
- Shortness of breath and pink, frothy sputum are classic signs of left-sided heart failure.
- Leg swelling and fluid in the lungs are more associated with right- and left-sided heart failure, respectively, but the statement in option C is the most accurate.
The nurse is caring for a client with acute decompensated heart failure. Which order should the nurse implement first?
A. Administer IV furosemide
B. Insert a Foley catheter
C. Place the client on a low-sodium diet
D. Obtain daily weights
Answer: A. Administer IV furosemide
Rationale:
- IV furosemide will help rapidly remove excess fluid, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications.
- The other interventions are important but not as urgent as addressing fluid overload.