poikilothermy
coolness of the skin related to decreased perfusion
Which medication(s) are used to treat fluid volume overload secondary to heart failure?
diuretics
Which laboratory test would the nurse expect for a client with a suspected myocardial infarction? (There are three total, but only one needed to get points)
Troponin I, CK-MB, myoglobin
PQRST (sometimes U)
Identify the rhythm
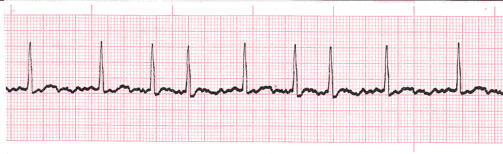
Atrial Fibrillation (Afib)
cardiomyopathy
enlargement of the heart muscle
Tell me about coumadin/warfarin
anticoagulant
requires PT/INR monitoring
Target PT/INR is 2.0-3.0 during therapy
Bleeding precautions
Anecdote is Vitamin K
patient teaching!! (specific to vitamin K)
A client in right sided heart failure has been started on IV furosemide (Lasix), which laboratory value(s) would the nurse monitor?
electrolytes (potassium, sodium, etc.)
A client diagnosed with atrial fibrillation is at risk for which potentially fatal complication?
blood clots/DVT/PE/Stroke
Which condition causes the complex shown?
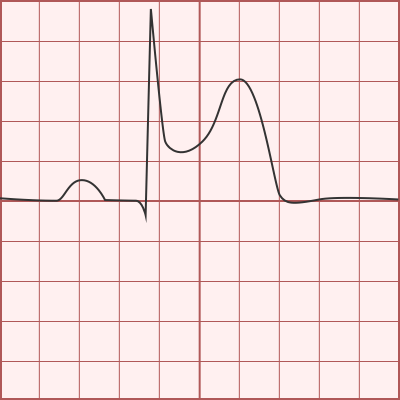
STEMI (ST- elevated MI)
atherosclerosis
plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries
Name that medication
Medication action: Increases force and contraction of myocardium, which increases cardiac output. Slow heart rate to reduce workload of heart
digoxin (class: inotropes)
Which diagnostic test would the nurse anticipate for a client with suspected infective endocarditis?
ECG, echocardiogram, CT, MRI (will take any and all for correct)
WBC would be laboratory value, but correct!
A client has a WBC count of 20,000, hyperthermia, osler's nodes, and petechiae to their skin. Which condition would the nurse suspect?
infective endocarditis
Identify the rhythm shown
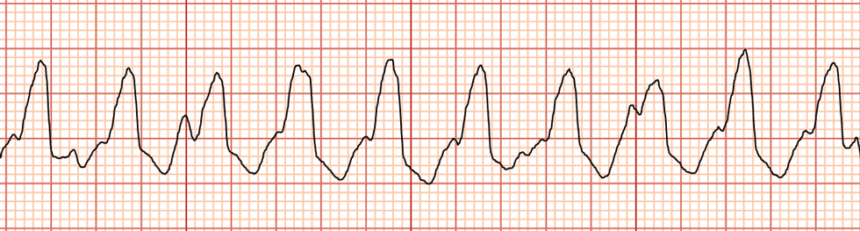
Ventricular tachycardia (VTACH)
intermittent claudication
pain in the lower extremities associated with movement or activity
A client is experiencing atrial fibrillation with a heart rate of 144 beats per minute. What medication would the nurse anticipate, that would reduce the client's heart rate?
beta blockers OR calcium channel blockers OR digitalis
(will accept any of these for points)
Which precautions should the nurse implement on a client after a cardiac catheterization?
(at least 2 for points)
-lay flat for 4-6 hours
-assess groin site q15 minutes
-assess distal pulse q15 minutes
-monitor ECG
-assess vital signs q15 minutes
-educate on symptoms of internal bleeding
-apply pressure to groin site if experiencing bleeding
Myocardial infarction (MI)
You are watching the ECG monitor for your client, and see this rhythm appear. What is your initial action?
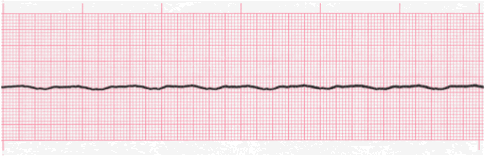
Verify the rhythm (check the patient).
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
sudden shortness of breath that occurs after lying flat for a time
Which medications can be prescribed to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction in a high risk client?
lipid lowering agents
beta blockers
calcium channel blockers
ACE/ARBs
*depends on what makes the client high risk*
A client is diagnosed with CHF. Which diagnostic test would the nurse anticipate to evaluate the function of the left ventricle?
ejection fraction, usually obtained via echocardiogram
What is the difference between defibrillation and cardioversion?
cardioversion: machine is synced to the R wave on the ECG and a low voltage shock is delivered at a VERY specific time during the QRS complex (used for Vtach with a pulse, and other dysrhythmias non-responsive to medical treatment), patient is sedated for the procedure
Defibrillation: used in pulseless vtach and vfib, done in emergency setting. higher voltage than cardioversion. life saving intervention, doesn't matter when the shock is delivered (no R wave to sync to)
What is your INITIAL intervention for the rhythm strip shown (after verifying that the client is truly in this rhythm)?
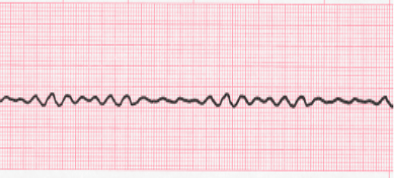
CPR!!! Cardiopulmonary resuscitation...
What comes after that?