Blood returned from the body to the heart is... Deoxygenated or oxygenated
deoxygenated
What is the pacemaker of the heart?
SA node
What is arteriosclerosis? what causes it?
Hardening/ thickening of artery walls. Caused by build up of plaque/ fatty deposits and calcification.
What is a cardiac catherization?
Cardiac catherization is a diagnostic test used to assess the structure and flow of the heart to see if there is any blockage in any of the vessels.
What is the shape of a platelet and how does it relate to its function?
Platelets are involved with blood clotting so they have small projections to help stick to eachother and clot the damaged area.
what are the smallest forms of arteries and veins?
Arterioles and venules.
What is the back up pacemaker if the SA node is disrupted?
The AV node
What are the treatments for arteriosclerosis?
Lowering blood pressure, lowering cholesterol, dissolving clots. Aspirin also helps decrease chance of clotting around plaque.
What is a balloon angioplasty?
A balloon angioplasty is used when a patient has a blockage in an artery. A catheter is sent to the blocked site and then expands and compresses the plaque to the vessels walls.
Which type of white blood cell makes up 50- 70% of the total WBC count. What does it target?
Neutrophils- targets bacteria and fungi.
Which vein returns blood from the upper body? Which returns to the lower body?
Upper- Superior vena cava
Lower- inferior vena cava
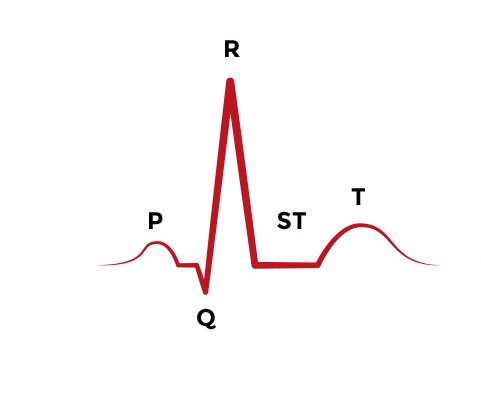
Draw and label a waveform on the board.
Name the risk factors of heart disease.
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking.
Which way do arteries and veins carry blood?
Arteries- away from heart
Veins- towards heart.
What are lymphocytes also known as? What percent do they make out of the total WBC count?
B and T cells/ natural killer cells. 25-35% of cells.
What is systolic and diastolic pressure?
Systolic- the amount of pressure exerted on vessels when heart is contracted.
Diastolic- The amount of pressure exerted on the vessels when the heart is relaxed.
What does P, QRS, and T- wave stand for on an EKG?
P- Contraction of the atria.(Depolarization)
QRS Complex- Contraction of ventricles.(Depolarization)
T- Ventricles relaxing. (Repolarization)
Name the symptoms of a myocardial infarction.
Severe chest pain and fullness, nausea/ vomiting, anxiety, sweating, and pain that extends from chest to jaw, shoulder, and down the left arm.
Describe the flow of blood starting in the right atrium to the left atrium.
right atrium -> tricuspid valve -> right ventricle -> pulmonic valve-> left pulmonary artery to lungs -> left pulmonary veins -> left atrium ->
What do basophils do. What percent do they make up out of total WBC count?
They release histamines and make up .4- 1% of total WBC count.
Name the five main arteries and their location. Which artery is used to take blood pressure?
Carotid- Neck
Brachial- above elbow on pinky side. Used to take BP.
Radial- Wrist; thumb side.
Femoral- Inner thigh
Popliteal- behind knee.
Name the electrical pathway of the heart in order.
SA node, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, then Purkinje network fibers.
Name the symptoms of a cerebrovascular accident and the test used for the disease.
Sudden numbness/ weakness on one side of body, facial droop, confusion, difficulty talking, hearing and seeing, headache, and loss of balance.
The FAST test is used in this situation.
F- Facial drooping
A- Arms. Do they move symmetrically?
S- Speech. Is it slurred?
T- Time to call an ambulance.
Name the pathway a red blood cell would take through the pulmonary and systemic pathway starting at the superior vena cava through the heart and body and back to the superior vena cava.
Superior vena cava-> right atrium -> tricuspid valve -> right ventricle -> pulmonic valve-> left pulmonary artery to lungs -> left pulmonary veins -> left atrium -> bicuspid/ mitral valve -> left ventricle -> aortic valve-> aorta. Blood then travels through body and back to the superior vena cava.
What is an eosinophil? what percent does it make up out of total WBC count?
Targets large parasites and is the body's natural inflammatory response.