What is IC50?
[I] that gives 50% inhibition or antagonism under
defined experimental conditions.
Name 3 potential outcomes of untreated hypertension?
CKD, Retinopathy, Stroke, Angina, MI, Heart Failure, coronary heart disease.
List 3 common comorbidities of hypertension.
smoking, obesity, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and CKD
What is the defining characteristic that separates HTN urgency from HTN emergency?
end organ damage
what fatty acids are essential fatty acids?
omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
What is ASCVD? What are the diseases/events under this umbrella?
Athersclerotic cardiovascular disease which includes: Acute coronary syndrome (myocardial infarction, unstable or stable angina), coronary/arterial revascularization, Stroke/TIA, and peripheral artery disease.
What is the triglyceride cutoff where LDL can no longer be measured?
>400
A patient presents with CKD, a deadbeat father, a blood pressure of 145/90, and an ASCVD risk of 7.2%. What is the treatment?
two first line antihypertensive agents
What functional group present on this molecule decreased Losartan's IC50 by 10 fold from previous attempts to create an ARB? Point to the functional group.
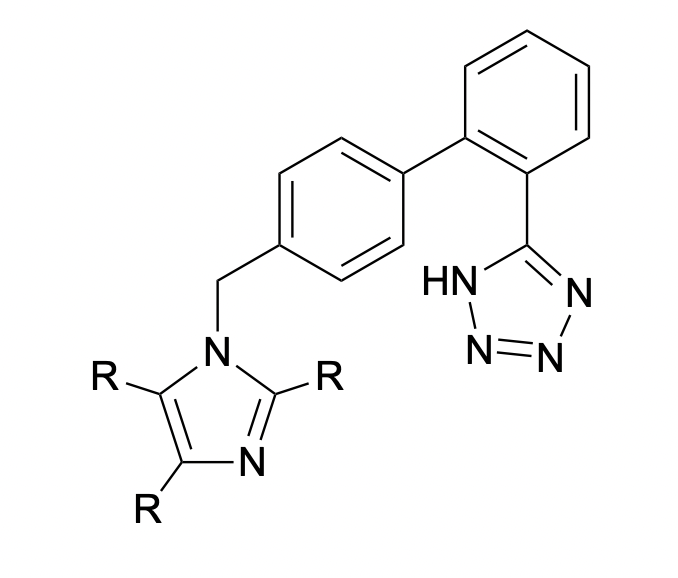
Tetrazole.
Name the 4 diuretic drugs?
Thiazide, loop, potassium sparing, and MRA
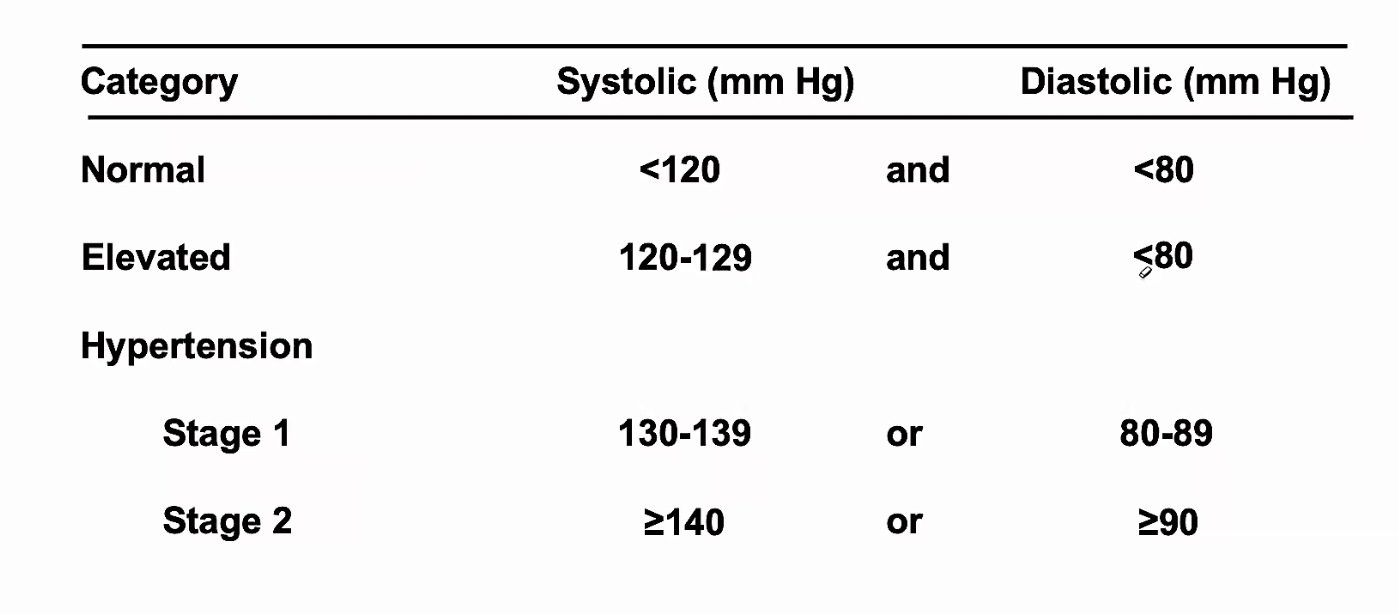
Fill in the chart
What are the blood pressure lowering goals for patients experiencing HTN urgency?
lower BP by 20-30% in the first few hours, then normalize under 140/90 in the following days
order the lipoproteins from least protein content to the most protein content.
chylomicrons<VLDL<IDL<LDL<HDL
risk factors/causes for dyslipidemia?
primary/hereditary, diet, drugs, disorders (nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, biliary obstruction, pregnancy, advanced age), diseases (hypothyroidism, obesity, PCOS, DM, HTN, liver disease, CKD)
When is follow up visit for persistent triglyceridemia?
4-12 weeks
A patient presents with a blood pressure of 134/87 with a 10 year ASCVD risk of 6.7% and no prior history of MI, HF, stroke, or CKD. What is the recommended treatment plan?
3-6months of lifestyle interventions followed by initiation of anti-hypertensive agent, if lifestyle interventions do not work.
Losartan's metabolite has a lower IC50 than Losartan does. Does this make it a prodrug? why or why not?
No, because a prodrug has no effect prior to metabolism. Losartan is still active prior to metabolism, it just so happens that it has a lower IC50.
What is the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics in the treatment of hypertension?
initially, diuresis the patient to lower overall blood volume and decrease BP that way. However, initial diuresis effect will wane, and chronic use will decrease peripheral vascular resistance through unknown mechanism.
name 3 non-pharm interventions for decreasing HTN.
DASH diet, reduce sodium intake, enhance potassium intake, physical activity, reduce stress, reduce alcohol consumption
Treatment options for previously untreated HTN urgency pts?
amlodipine, HCTZ, or chlorthalidone, though combination agent may be more appropriate.
What enzyme is responsible for the conversion of 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonic acid?
HMG CoA reductase
What are the two high intensity statins, their LDL lowering %, and their dosing ranges?
Atorvastatin (40-80mg), Rosuvastatin (20-40mg), can lower LDL by 50% or more.
Number 1 treatment goal for patients with triglycerides above 500
prevent pancreatitis
PT presents with home BP of 128/79 and an office BP of 129/79 and is on lisinopril, amlodipine, HCTZ, and propranolol. They have no known drug allergies or contraindications to therapy. How would you alter their therapy?
add an MRA
Angiotensin converting enzyme uses what metal for proteolytic activity?
Zinc
important and common ADRs with ACEi?
hyperkalemia, AKI, angioedema, persistent dry cough, and orthostatic hypotension.
What other things do we need to know before initiating a pharmaceutical intervention for a patient whose systolic blood pressure is above 130 mmHg or their diastolic is above 80 mmHg?
Their ASCVD risk and whether or not they have already had a CVD event like coronary heart disease, stroke, or HF.
What are 3 signs of end organ damage?
kidney injury or failure, shortness of breath, aortic dissection, hypertensive encephalopathy, MI, LV dysfunction, intracranial bleeding, etc.
Name all the drugs used for cholesterol and lipid management?
Statins (HMG CoA reductase inhibitors), PCSK9 inhibitors, bempedoic acid, fibrates, ezetimibe, niacin, bile acid sequestrants
What is the reason that Simvastatin and Lovastatin are associated with more side effects?
they are lipophilic and can pass deeper into membranes
name 3 non-pharm recommendations for HTG pts?
weight loss, aerobic exercise, diet, restrict alcohol, refer to nutritionist/dietician
PT has a BP of 210/100. PT states no symptoms. You decide to run a metabolic panel and urinalysis. You see that his Scr is 2.5 and BUN is 57 with protein present in his urine. What is your diagnosis and treatment plan?
hypertensive emergency due to presence of end organ damage. 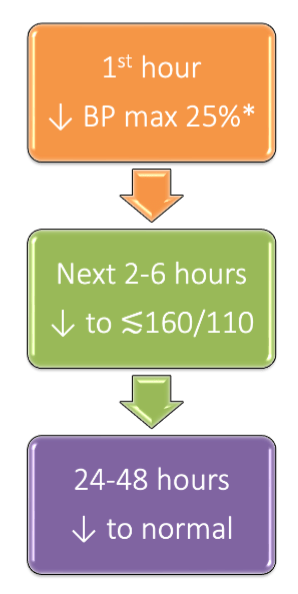
Enalapril is a prodrug metabolized by what kind of enzyme to give enalaprilat?
esterase
Contraindication of non-DHPCCBs? why?
Heart Failure. Cardiac conduction abnormalities like bradycardia and/or AT block.
What is the threshold value for ASCVD risk from the PREVENT calculator needed to assess a patient's need for blood pressure lowering medication?
7.5%
Draw out either the BP or MAP roadmap for hypertensive emergency.
BP roadmap: 1st hour lower BP max 25% → next 2-6 hours lower to around or below 160/110 → next 24-48 hours lower to normal and transition back to PO meds
MAP roadmap: 1st hour lower MAP 10-20% → next 2-6 hours lower MAP an additional 5-15% → next 24-48 hours lower to normal MAP (normal is 70-100)
What does PCSK9 do?
binds to LDL receptors and marks them for degradation. Fewer LDL receptors leads to higher LDL blood concentrations.
What are the three options we have for a patient who had a statin associated myalgia, and has already completed a drug holiday.
2. switch to a lower risk statin
3. discontinue statin
What are all the pharmacological interventions for hypertriglyceridemia?
fatty acids, fibrates, niacin
What is the BP goal for a patient who arrives to the ER with a stroke and is not a candidate for tenecteplase?
<220/120
Calcium channel blockers all bind ___sterically?
allo-
MOA of calcium channel blockers in the treatment of HTN?
block calcium across cell membrane --> lowered muscle contraction --> coronary and peripheral vasodilation
Which catecholamine receptor agonist drugs are avoided in older adult populations?
central alpha agonists
Drugs of choice for most hypertensive emergencies?
labetalol, nicardipine or clevidipine.
Which drug should not be combined with alirocumab?
inclisiran (leqvio)
What is the difference in therapy considerations for a patient with a triglyceride value between 500-1000 vs a patient with a triglyceride value over 1000?
Consideration of ASCVD. a patient with a TG between 500-1000 should have their ASCVD assessed, and whether their ASCVD risk is above or below 5% will determine therapy.
27 YO♀now 37-week gestation
presents to L&D triage with BP
176/92mmHg and tonic/clonic seizures
• Lab abnormalities
– uACR 50g/mg
– Platelets 89k/μL (normal 150-450k/μL)
What is the treatment?
IV labetalol, IV hydralazine, and magnesium sulfate
What kind of calcium channel blocker is this drug? how do you know that?
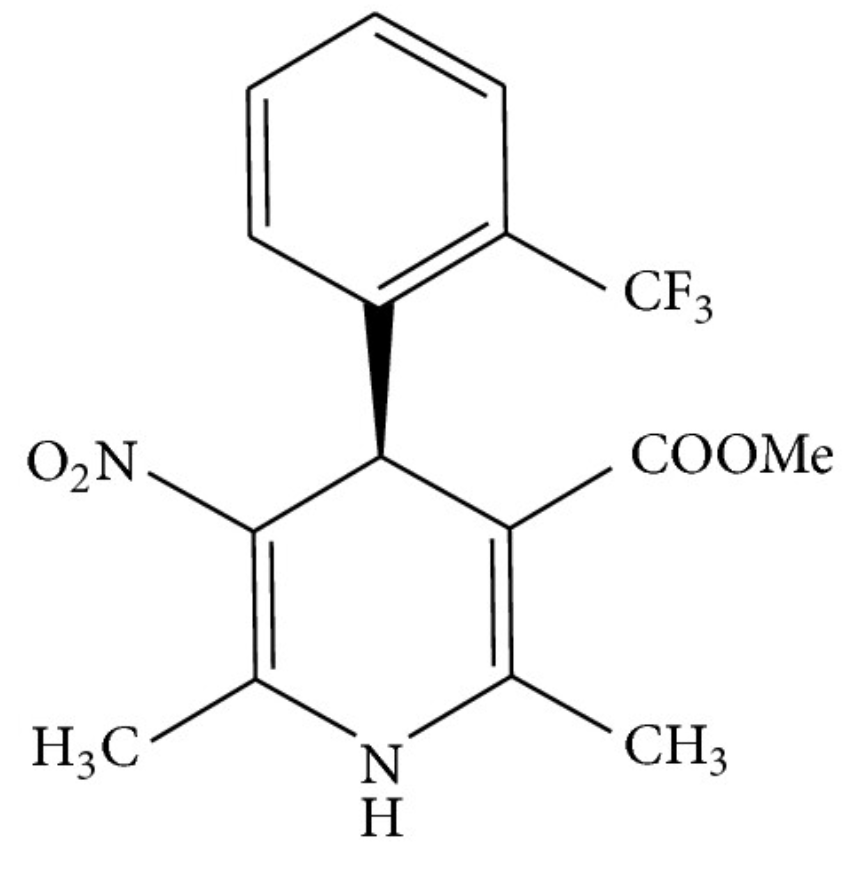
1,4-Dihydropyridine CCB, Because it has hydrogens at the 1 and 4 positions of the pyridine ring
ADRs of DHPCCBs
reflex tachycardia, angina, MI, dizziness, flushing, headache, and peripheral edema
Pregnant women with hypertension receive what medications for hypertension? (according to karboski)
Labetalol and extended release nifedipine.
What is one thing you need to know before initiating IV clevidipine?
Soy allergy
What is the dyslipidemia treatment and goal LDL for patients with clinical ASCVD with very high risk?
high intensity statin with an LDL goal under 55
55 yo patient with LDL of 145 an ASCVD risk of 6.5% and DM comes to clinic. What drug and dose do you recommend?
high intensity statin, atorvastatin 40-80, or rosuvastatin 20-40.
What is this drug? How many chiral centers does it have? Where is the chiral center? point to it. What is the mechanism of inhibition for this calcium channel blocker?
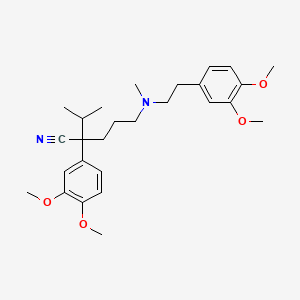
Verapamil. 1 chiral center. Carbon bonded to nitrile functional group. Physically blocks the open pore of calcium channel to prevent calcium entering the cell.
What makes Labetalol and Carvedilol different from other beta-blockers?
They also have alpha blocking activity
Patients with Diabetes and/or CKD are especially recommended to be on what hypertension medication?
ACEi or ARB
treatment for pheochromocytoma? what is a pheochromocytoma? what are the signs and symptoms of a pheochromocytoma?
phenoxybenzamine or selective alpha blockers (doxazosin, prazosin, etc). tumor which is secreting epinephrine or norepinephrine. palpitations, headache, and episodic sweating.
What statin benefit groups receives a moderate intensity statin?
age between 40-75, LDL between 70-100, with diabetes and has an ASCVD under 7.5% OR age between 40-75, LDL 70-189 without DM and an ASCVD risk between 7.5-19.9%
Sulley has a history of obesity and dyslipidemia
His BP is 102/60 mmHg
His fasting lipid panel (FLP) 1 year ago revealed
Tchol 238, LDL UNABLE TO CALC, HDL 38,
TG 888
He was started on atorvastatin 40 mg 1 year ago
and has been active scaring people.
New FLP Tchol – 200, LDL 80, HDL 41, TG 799
What medication management would you
recommend?
ASCVD risk is 15%
What is your treatment plan?
increase statin
What are the three groups of beta-blockers? Name one drug that would fall in each category.
1. Cardioselective beta-blockers - Metoprolol, Atenolol, Nebivolol, Bisoprolol, Betaxolol, Esmolol
2. Non-selective - labetalol, carvedilol, nadolol, propranolol, timolol
3. Beta-blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity - Acebutolol, pindolol, penbutolol
What differentiates eclampsia from preeclampsia? what is the treatment for preeclampsia? what is the additional treatment for eclampsia?
tonic/clonic seizures. IV labetalol and IV hydralazine. Magnesium sulfate.
Name 2 peripheral alpha blockers, their mechanism of action, and at least one ADR.
prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin.
Selective alpha-1 receptor antagonists in the peripheral vasculature results in vasodilation and BP lowering
first dose effects - dizziness, fainting, syncope within 1-3 hours after first dose.
Take first dose before bed. Can also occur if non-adherent or big dose increases.
Sustained orthostatic hypotension, CNS effect like lassitude, vivid dreams, and depression. Also can cause priapism.
goal BP for stroke patients who are candidates for tPA?
<185/110