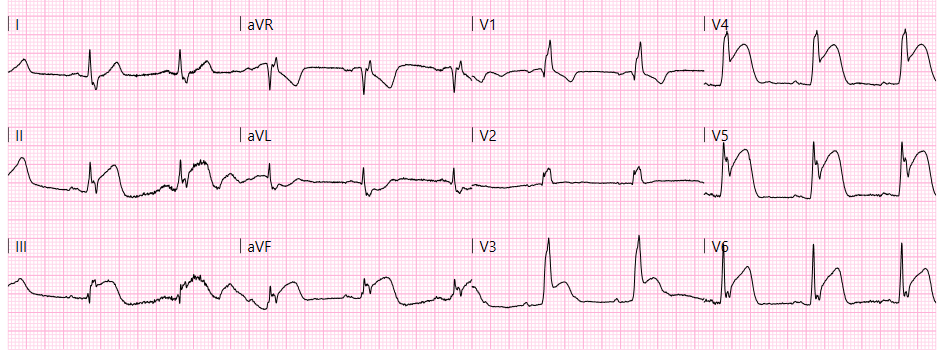
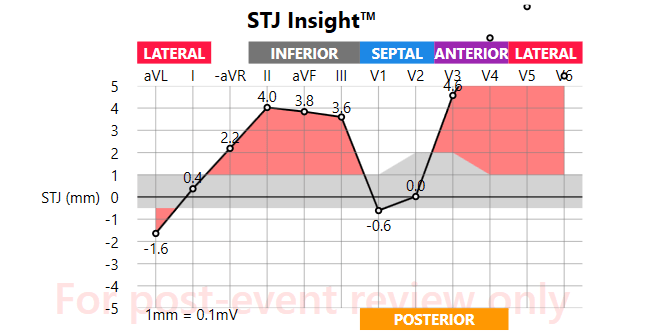
STEMI
During CPR, how long should pulse checks last?
The duration should be a minimum of 5 seconds and a maximum of 10 seconds.
What is the dosage for ASA in an adult patient?
324mg
What structure is known as the heart's natural pacemaker?
SA Node
What is the recommended depth of chest compressions for adult and infant patients?
For adults: 2 inches
For infants: 1.5 inches
What is the STEMI activation criteria for GEMS?
≥1 mm ST elevation in two contiguous leads (or the 12-lead device flags 'STEMI') and the patient is symptomatic
Treatment for this patient...
Pace immediately
You arrive at the scene of a 56-year-old man who is not breathing. Your initial assessment reveals that the patient is pulseless and apneic. The patient's wife tells you that her husband suddenly grabbed his chest and then passed out. After successfully resuscitating the patient, you provide immediate transport. While en route to the hospital, the patient goes back into cardiac arrest. Your next step should be
A. Tell your partner to stop the ambulance.
B. Begin CPR and proceed to the hospital
C. Contact medical control for further advice.
D. analyze the patient's rhythm with the AED.
B. Begin CPR and proceed to the hospital
Aspirin: ASA What is the Drug action
Inhibits platelet aggregation
Anti - inflammatory
What is the flow of blood through the heart chambers only.
Right Atrium, Right Ventricle -> Left Atrium to Left Ventricle
The compression rate must be between ___ and ___, no less and no more.
100 - 120
ST elevation is measured from...
The J Point
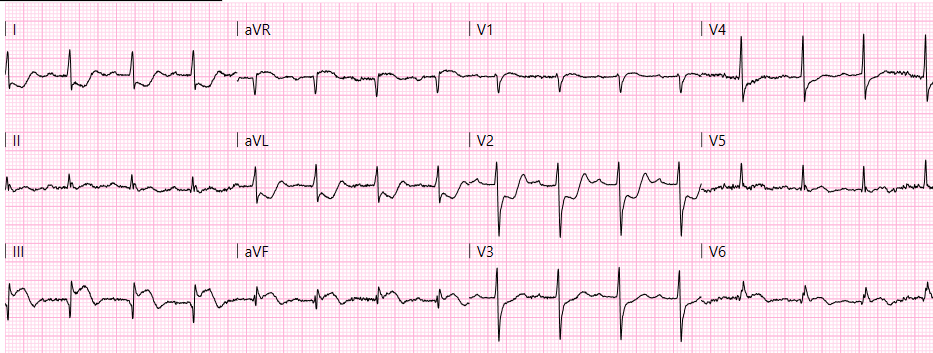
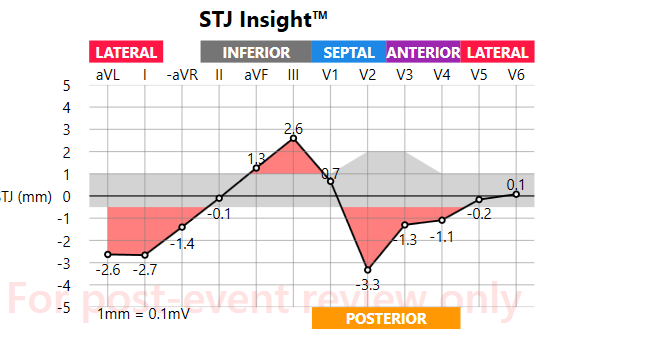
Cardiac arrest in the adult population most often is the result of
A. myocardial infarction
B. respiratory failure
C. a cardiac arrhythmia
D. accidental electrocution
C. a cardiac arrhythmia
What is the dosage and indication for NTG?
0.4mg SL, repeat every 5 min for 15 min
chest pain of cardiac origin, angina, acute CHFAdminister 0.4 mg sublingually, repeat every 5 minutes for 15 minutes for chest pain of cardiac origin, angina, or acute congestive heart failure.
A thrombus which has broken loose, moving with blood flow, is called
Embolism
Pulseless rhythms that are shockable
V-Fib & V-Tach
Artifact or not?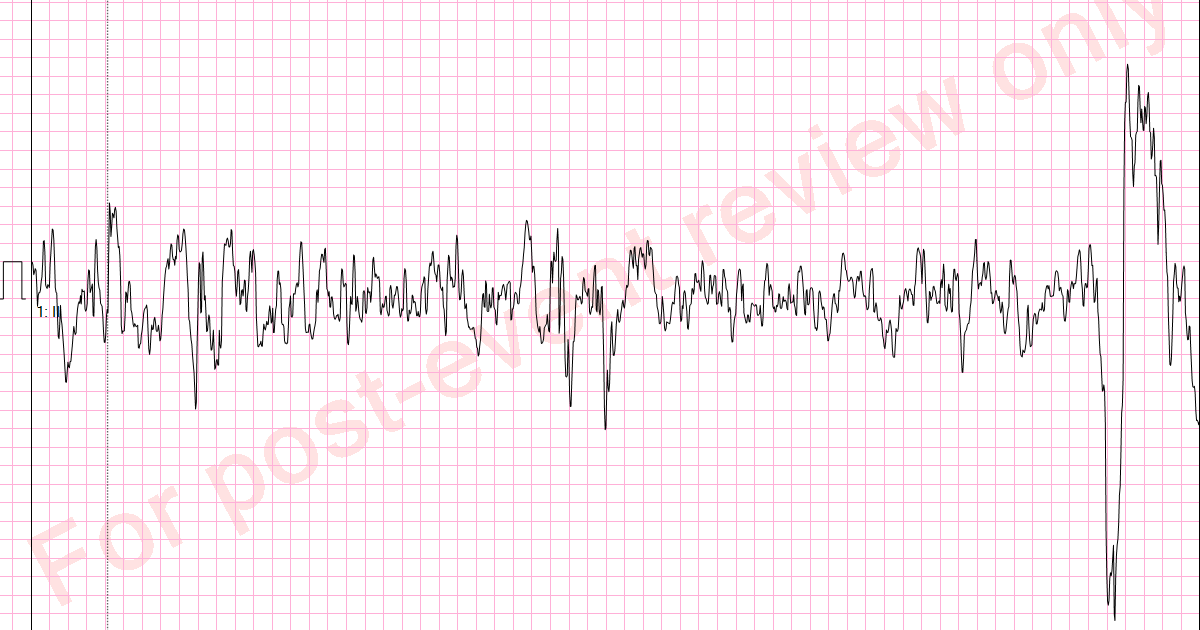
Artifact
Check the patient
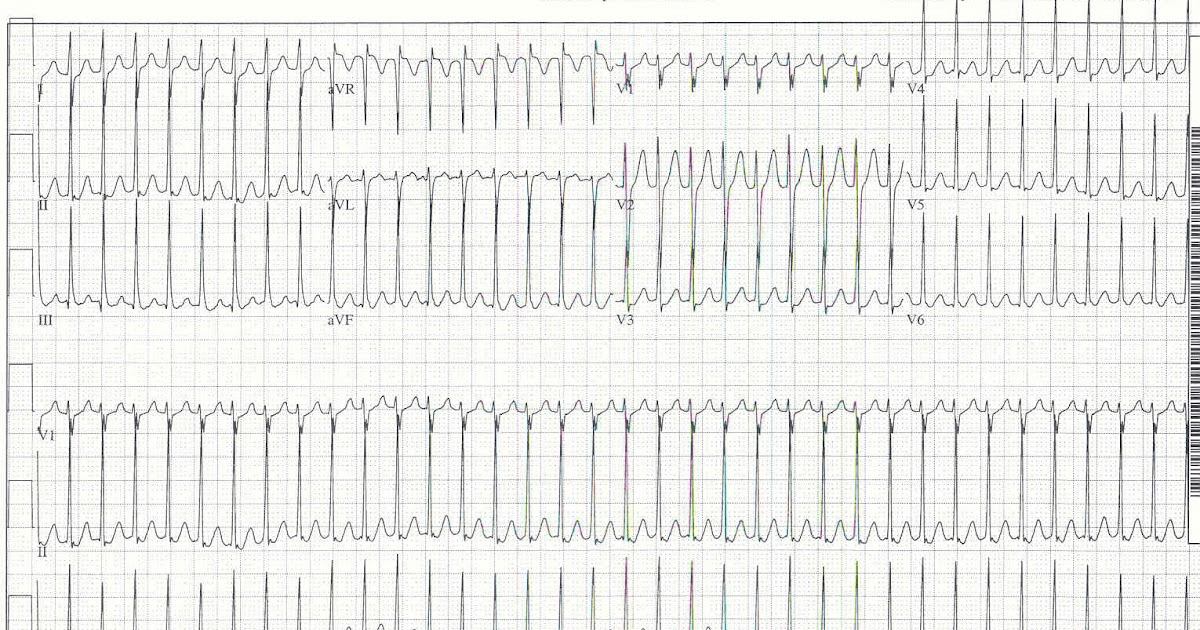
SVT
During CPR, how often do you check for a pulse?
Every 2 minutes or 5 cycles
Nitroglycerin- contraindications
hypotension, head injury, ED medication
What are the normal vital sign ranges for respiratory rate and heart rate in adults?
**Breathing Rate:** 12 to 20 breaths per minute
**Heart Rate:** 60 to 100 beats per minute
When the AED is analyzing a patient for a shockable rhythm, the EMT should:
ensure that no one is touching the patient.
Pace or not?
Unconscious patient with an SBP of 60...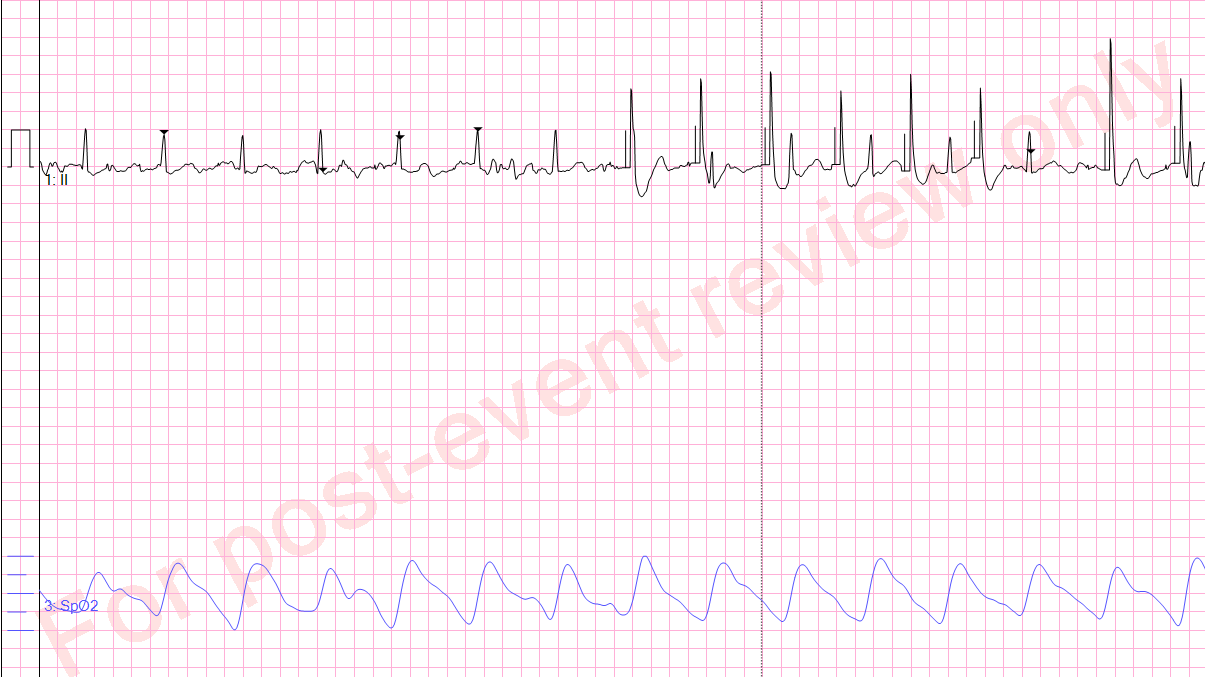
No pacing.
HR is in the 70's
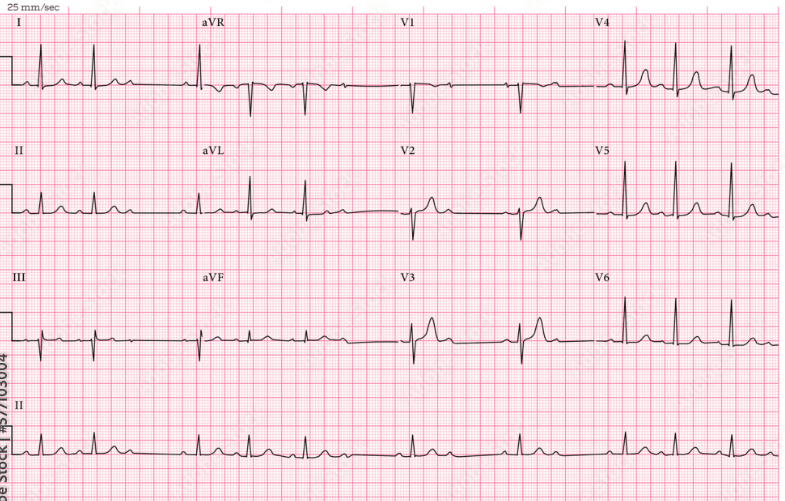
2nd degree type II
Bradycardia, tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation can all lead to ______ in a cardiac patient.
A. an occlusion
B. shooting arm and leg pain
C. diminished lung sounds
D. loss of consciousness
loss of consciousness
What is the minimum SBP for Nitro?
100
Excessive ventilation can cause?
increases intrathoracic pressure, decreases venous return to the heart, and decreases cardiac output
In addition to defibrillation, what other intervention should be performed for a patient in cardiac arrest?
Chest compressions
What are the three GEMS STEMI destinations?
CaroMont Regional Medical Center - Gastonia
Atrium - CMC Main
Novant - Main
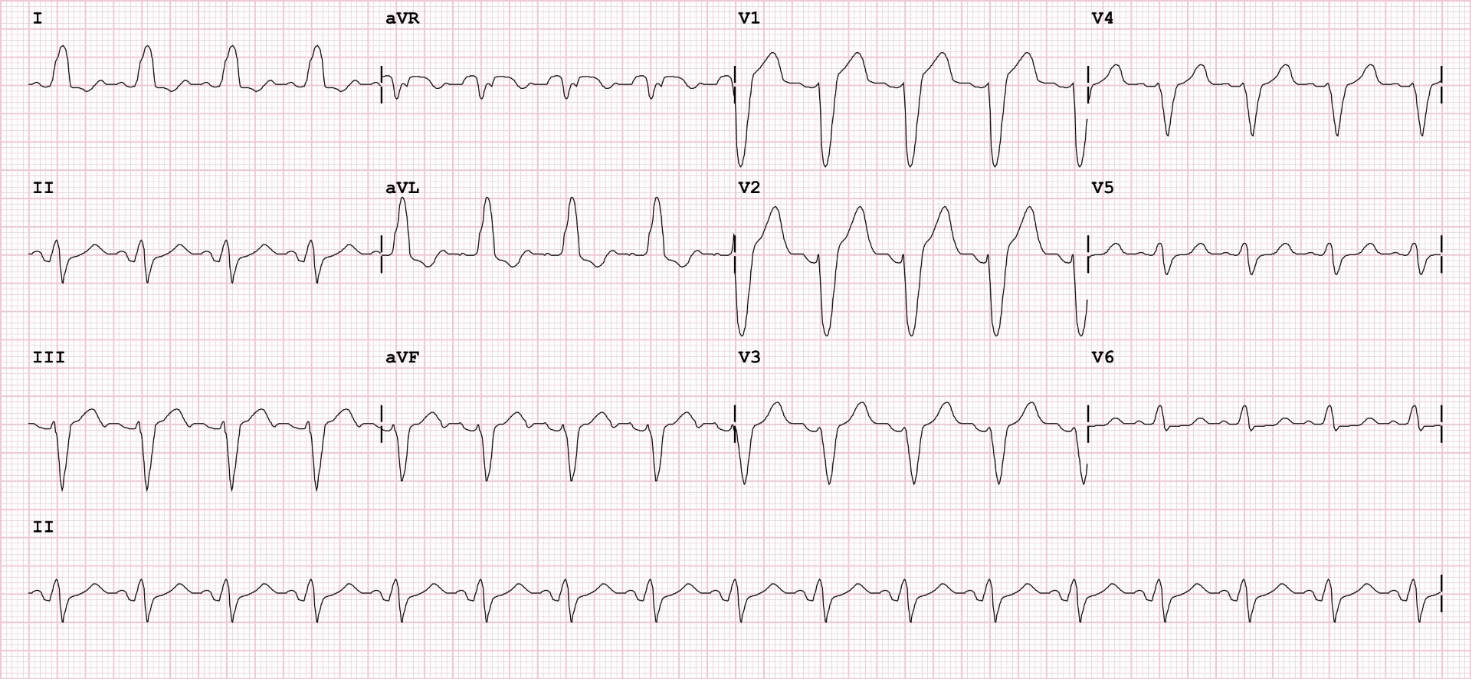
LBBB
Three criteria for the NUE Rule...
Non-Shockable
80 years or older
Unwitnessed arrest
Dosage for Amiodarone for V-Tach with a pulse
150 mg over 10 minutes using an IV pump.
What is the purpose of the EleGARD?
To increase the patient's CPP and decrease ICP.
Airway device for ramping.
What intervention is started after ROSC, it helps protect the brain and other organs?
Initiate target temperature management
Skin prepping steps before applying electrodes?
(3 common steps)
Remove any hair
Clean oily/dirty skin with an alcohol wipe
Replace old/dried electrodes with fresh pads