This patient has persistent ST elevations on EKG on hospital follow up in the office. What is the diagnosis.

Apical anuerysm

What trial showed benefit of eplerenone in post-MI heart failure?
EPHESUS trial
EF <= 40% after MI deserve an MRA
Besides TAA, what aortic abnormality can be seen in approximately 20% of bicuspid aortic valve patients?
Coarctation of aorta
This disease is described is an inherited cardiomyopathy, characterized by fibro-fatty replacement of the right ventricular (RV) myocardium.
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
- can have biventricular enlargement
- no shunt, normal tricuspid valve
Patients taking rivaroxaban can have these three abnormal coagulation assay values. Name 2 of 3.
PT, PTT, antia-Xa
This is the 2017 ACC/AHA recommendation for blood pressure goal in a patient targeting secondary prevention of recurrent CVD events.
130/80
Primary prevention or ASCVD risk score <10% goal <140/90
Posterior mitral leaflet restriction will create a jet in this direction
Prolapse, Flail - opposite
Restriction - same
This attending physician was a DJ in college
Praveen Rao, MD
(He needs better Facebook permissions/security)


What is the trouble?
Secundum ASD
Which trial demonstrated the mortality benefit of sacubitril/valsartan in HFrEF over enalapril?
PARADIGM-HF
Name one of the two most common congenital heart defects in Down syndrome
- atrioventricular septal defects (AVSDs)
- Tetralogy of fallot
50% of patients with down syndrome will have a congenital heart defect
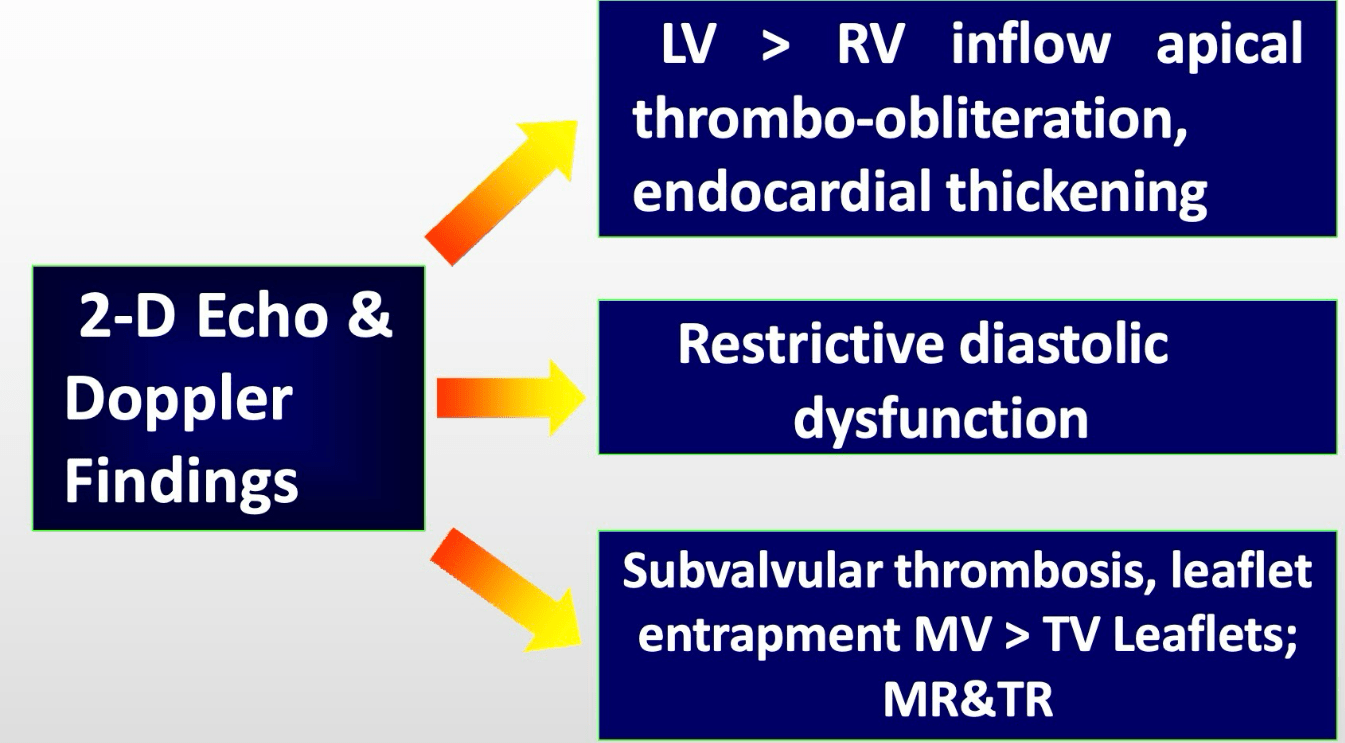
This systemic disease causes a restrictive LV and RV, endomyocardial thrombosis and fibrosis, characterized by LV mural thrombus and subvalvular thrombosis.
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
What are the two missing pieces in the ischemic cascade?
1. ***
2. Diastolic dysfunction
3. Systolic dysfunction by Strain
4. Systolic dysfunction by 2D
5. Hemodynamic abnormalities
6. Abnormal ECG
7. ***
1. Perfusion abnormality
2. Diastolic dysfunction
3. Systolic dysfunction by Strain
4. Systolic dysfunction by 2D
5. Hemodynamic abnormalities
6. Abnormal ECG
7. Chest Pain
Name 3 IV medications you can use for hypertensive emergencies.
Nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Nitroprusside)
CCB (clevidipine, nicardipine)
Beta blockers (Labetalol, Esmolol)
Others (Hydarlazine, Enalaprilat, Phentolamine, Fenoldopam)
Name two causes of false positive stress echocardiograms (decreased specificity)
- Hypertensive response
- Pacemaker
- LBBB
- Cardiomyopathy
- Previous cardiac surgery
- Dynamic RV pressure overload
This attending physician swam in college, making it to second team academic all-american


What is this arrow pointing to and what does it represent?
- The wave between the E and A wave is known as the "L-wave"
- It represents severe diastolic dysfunction and prolonged relaxation lead to LV filling in mid-diastole before atrial contraction.
Name three trials studying NOACs for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
RE-LY, ROCKET AF, ARISTOTLE, ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48
This defect is seen in about 75% of patients with Ebstein anomaly
ASD (sometimes PFO)
Can contribute to cyanosis at birth, improvement due to reduced PVR, then cyanosis in adolescence.
This disease is characterized by massive left ventricular hypertrophy and skeletal myopathy. It is a X-linked dominant disorder caused by mutations in the LAMP2 gene, leading to glycogen storage abnormalities within the myocardium.
Danon disease = LAMP2
What two anticoagulants should be used in cases of heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Argatroban or bivalirudin (direct thrombin inhibitors)
Under normal physiological conditions, PF4 is stored in alpha-granules of the platelets and is released upon platelet activation. PF4 is positively charged and can, therefore, bind to the negatively charged heparan (a heparin-like substance normally present on the endothelial cell surface); PF4 can also bind to exogenous heparin with a much higher affinity than heparan.
PF4 binding to heparin may trigger the formation of IgG, IgA, or IgM antibodies specific to the heparin-PF4 complex. HIT can only occur if IgG, while attached to the heparin-PF4 complex, binds to the FC receptor on the platelet surface and leads to platelet activation. Activated platelets then release pro-thrombotic substances (such as thrombin) and PF4. As IgG activates more platelets, more PF4 is released forming more complexes with heparin, thus activating more platelets. This creates a severely hypercoagulable state and a continuous cycle that can only be broken when heparin is discontinued, and appropriate treatment is initiated.

This "first-in-class" mineralecorticoid receptor antagonist was shown to reduce CKD progression and cardiovascular events when compared to placebo in diabetic patients
Finerenone
- Fidelio-DKD
- Figaro-DKD
Wall stress is directly proportional to these two parameters of a chamber
Wall tension (stress) = pressure x radius/2xthickness
This attending physician played guard on the Wesleyan basketball team. They can no longer dunk.
\

What does this doppler represent, obtained from the aorta?


Coarctation of the Aorta - note the flow does not fall to zero at the end of diastole
What trial in 2001 established the role of dual antiplatelet therapy post-PCI?
CURE Trial
- UA/NSTEMI randomized to ASA + placebo vs ASA + clopidogrel
- Composite of CV mortality, non-fatal MI, or stroke9.3% vs. 11.4% (RR 0.80; 95% CI 0.72-0.90; P<0.001; NNT=48
-Any bleeding: 8.5% vs. 5.0% (RR 1.69; 95% CI 1.48-1.94; P<0.001; NNH=29)
- Major bleeding 3.7% vs. 2.7% (RR 1.38; 95% CI 1.13-1.67; P=0.001)
This is the most common abnormality found with sinus venosus ASD and should always be investigated
Anomalous (right) pulmonary venous connection.

This aortopathy may be accompanied by hypertelorism, bifid uvula, and skin fragility
Loeys-Dietz Syndrome (TGFBR1 or 2)
Aortic surgery may be recommended with aortas 4.0-4.5 cm due to high risk population
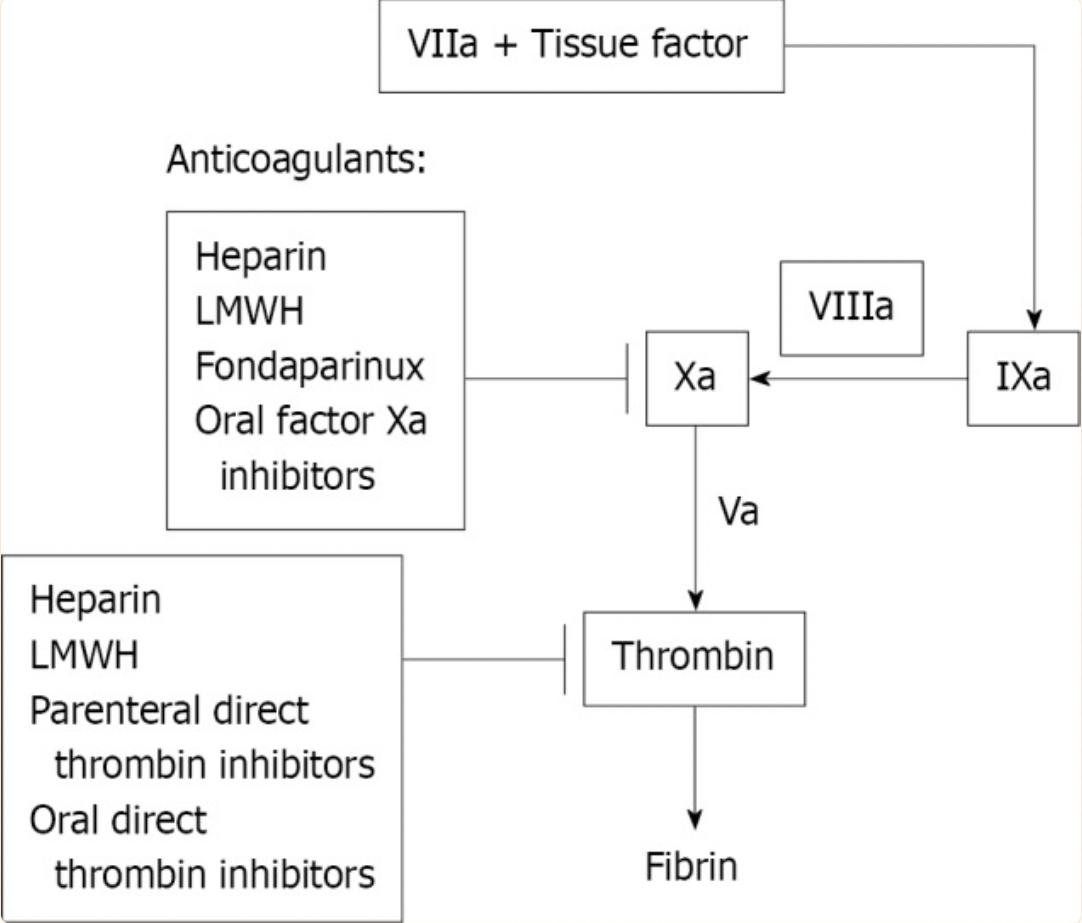
What is the mechanism of action of fondaparinux, and why is it not used as a monotherapy in PCI?
Fondaparinux inhibits factor Xa, but does not inhibit thrombin directly, thus requiring additional antithrombin activityduring PCI to prevent thrombin generation.
Oral minoxidil carries this serious cardiovascular side effect that does not occur with topical use.
Name three absolute contraindications for TEE.
- esophageal disease with known stricture, diverticuli, varices or tumor
- recent esophageal or stomach surgery, perforated viscus
- active upper GI bleed
- uncooperative patient
- Relative contraindications include cervical spine disease, hiatal hernia, coagulopathy, prior chest radiation, or facial or airway trauma.
This attending played soccer at a collegiate level. Her sister was also recruited to the women's US national team
Jessica Meyer MD
Soccer at Texas A&M commerce
Other fun facts:
- Lives in Poetry, Texas
- Ancestors trace back to Jamestown settlement
- Rescues animals
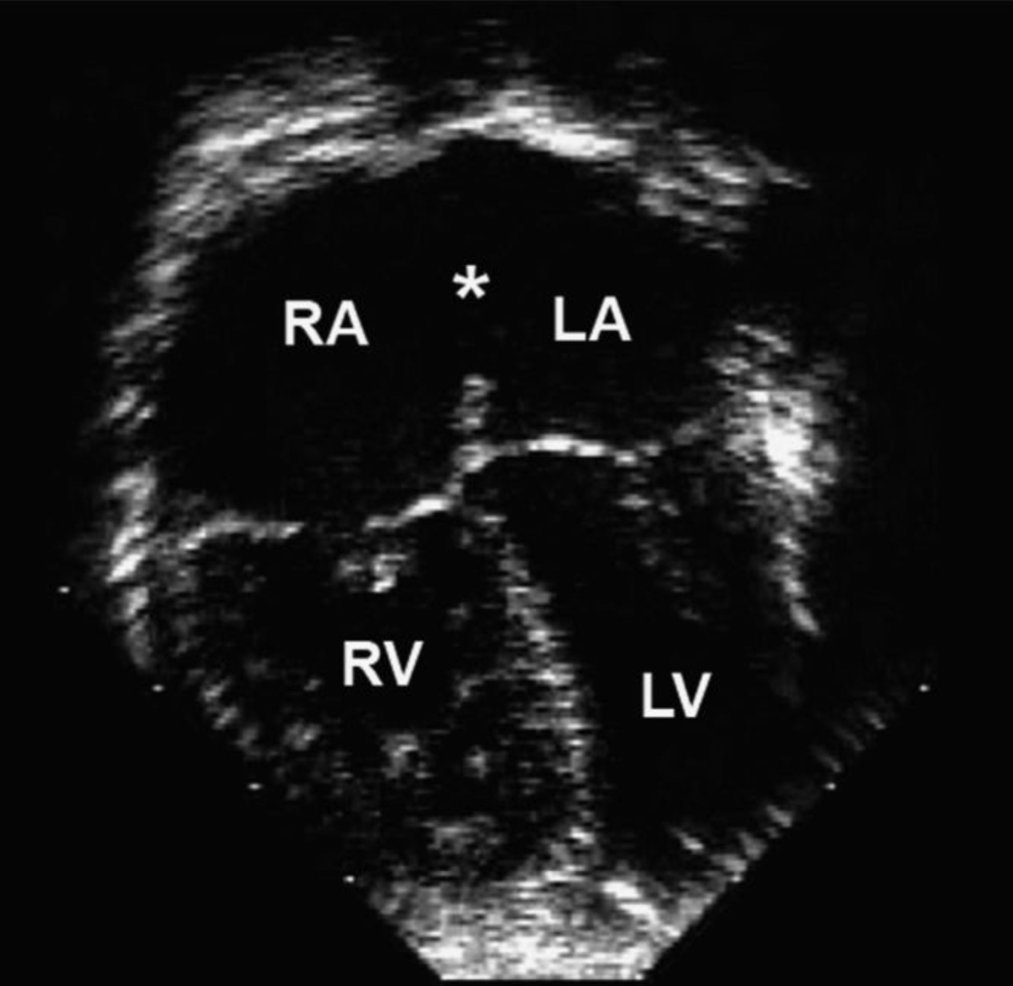
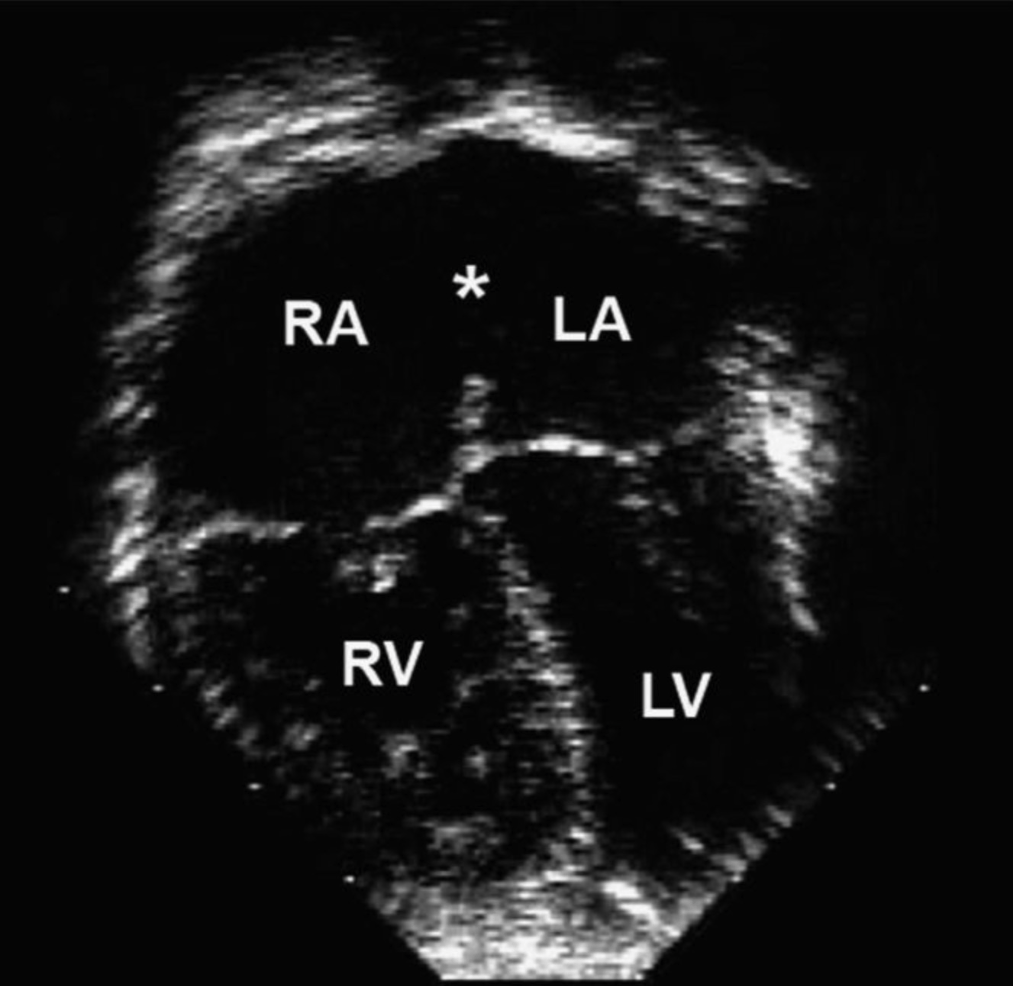
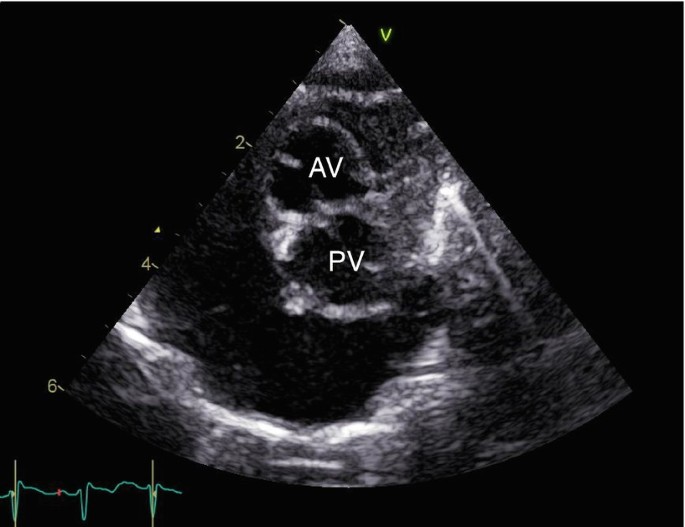
What is the diagnosis?

This trial evaluated the safety of an "ultra-low" LDL target with Evolocumab (PCSK9 inhibitor) in those with known ASCVD.
FOURIER TRIAL
Among patients with clinical atherosclerotic disease and LDL > 70 despite high- or moderate-intensity statin therapy (70% high intensity), the addition of evolocumab resulted in an absolute 1.5% reduction in major cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death, MI, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or coronary revascularization) at median follow-up 26 months,
This autosomal dominant condition has a phenotype of short stature, webbed neck, and triangular facies and should be remembered for the association with pulmonary stenosis
Noonan Syndrome
(sure sounded like Turner syndrome which has coarct and bicuspid valve)
What are the typical echocardiographic findings in Uhl’s anomaly?
Uhl’s anomaly, also known as the "parchment heart," is characterized by severe thinning of the right ventricular wall with the near absence of myocardial tissue, leading to a massively dilated right ventricle and poor systolic function on echocardiography.
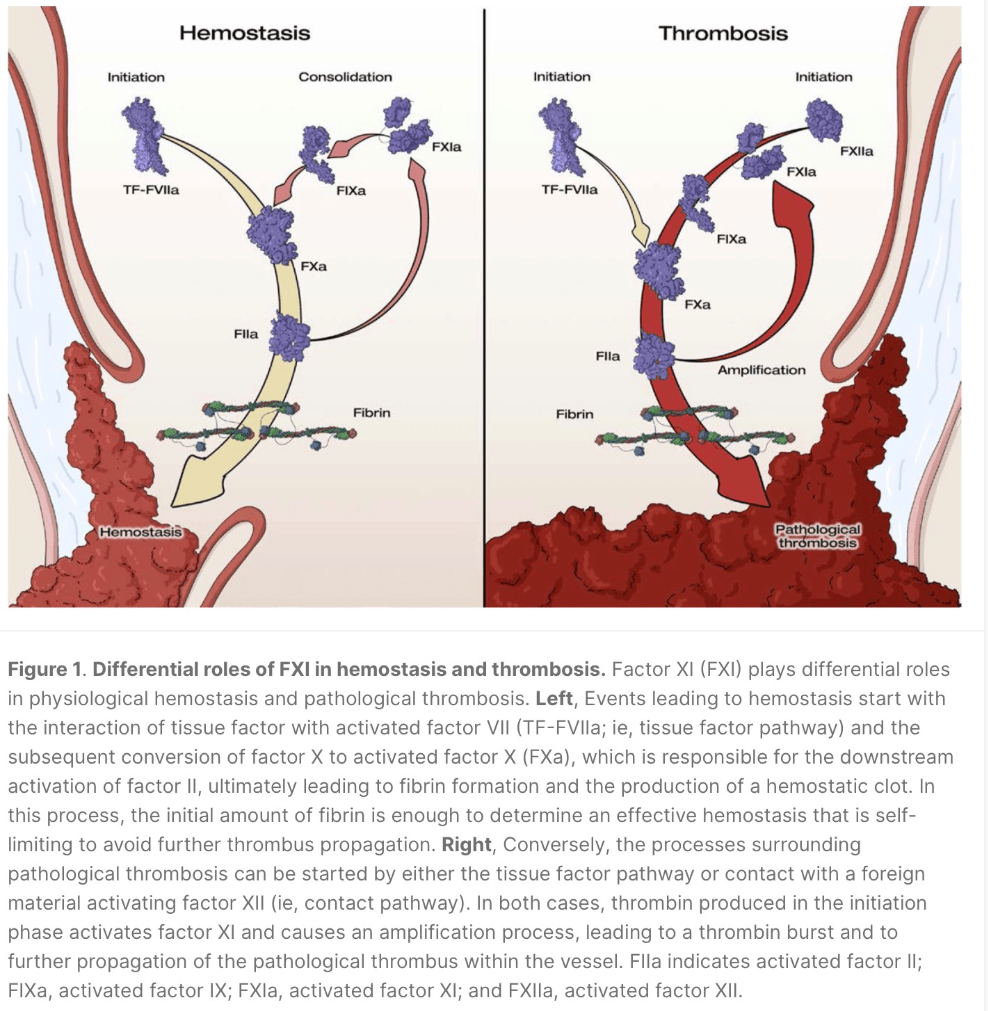
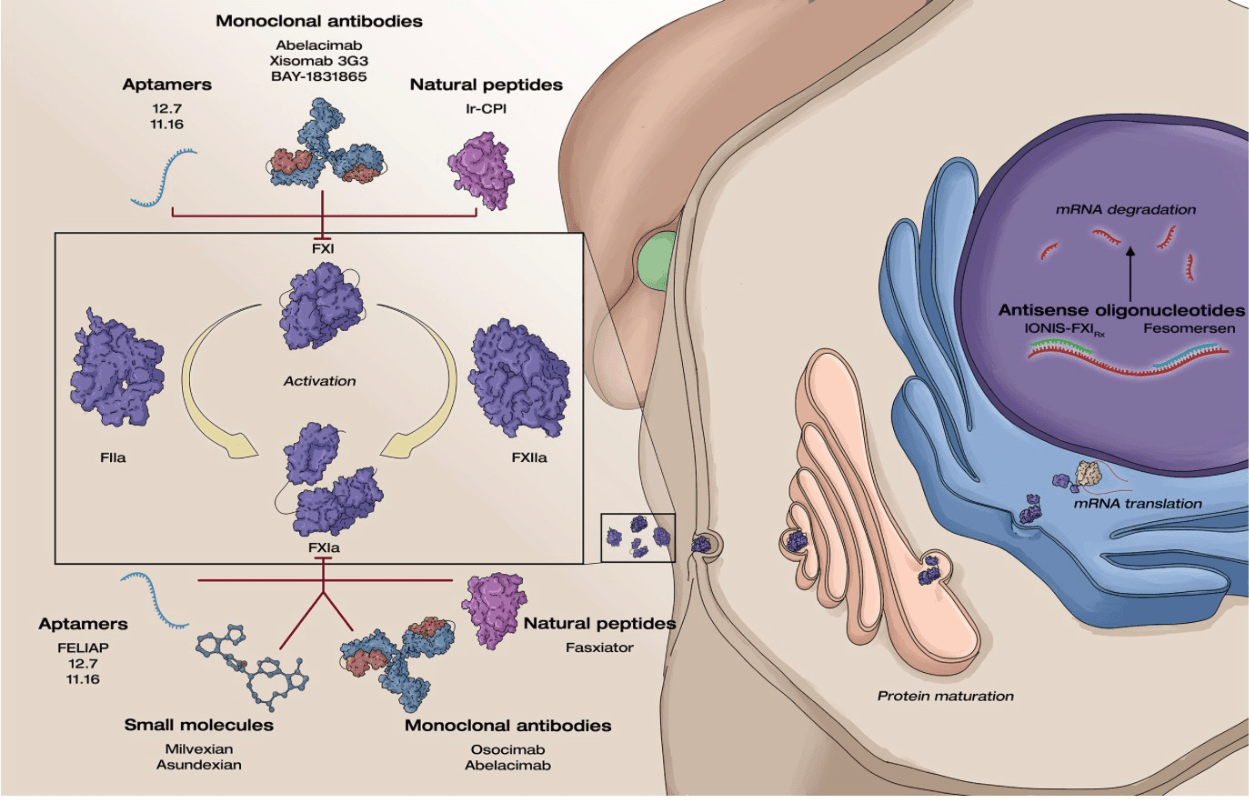
Novel factor XI inhibitors promise less bleeding with similar efficacy due to this effect on the cascade?
"Differential contribution of FXI to thrombus amplification, in which it plays a major role, and hemostasis, in which it plays an ancillary role in final clot consolidation"
What landmark trial demonstrated cardiovascular benefit of intensive BP control (systolic <120) in patients at high risk for ASCVD but without prior CVA or diabetes?
SPRINT Trial
- >50 years of age, nondiabetic, no prior CVA
- Reduction in all-cause mortality (3.3 vs 4.5% NNT 83)
- No difference in serious adverse events but did have more non-orthostatic hypotension, syncope, electrolyte derangements, AKI
Accord (2010) patients with diabetes, target SBP <120 did not improve CV outcomes
1. Pressure recovery phenomenon is most commonly seen with this valve replacement?
2. Will cath or echo overestimate the gradient?
Most commonly seen in bileaflet bioprosthetic valves (St. Jude). Doppler should be obtained from a side orifice rather than the central orifice.
Echo will overestimate

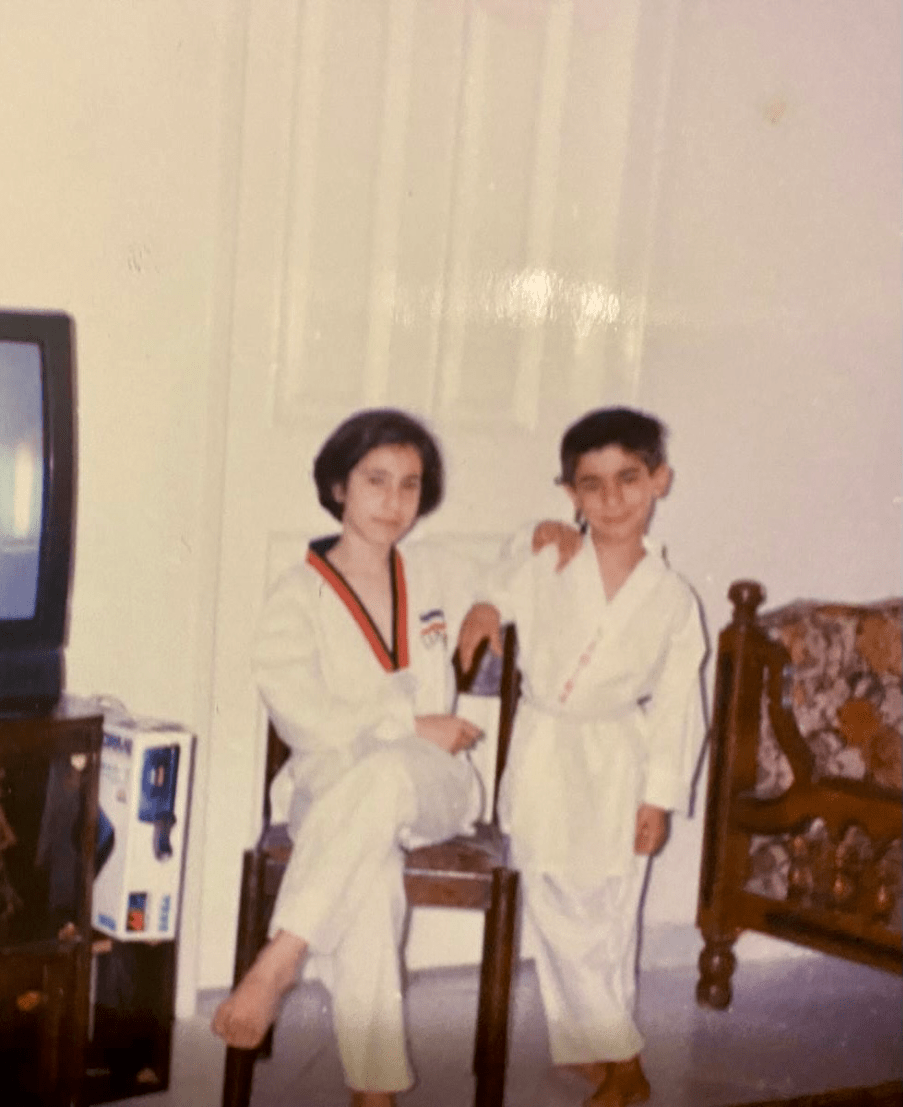
This attending physician has a black belt in Taekwondo....and isn't afraid to use it
Helen Hashemi, MD



