Myocardial infarction is diagnosed by....
Congestive Heart Failure is diagnosed by....
Troponin levels (elevated)
BNP levels (elevated)
What is a pacemaker used for?
Implants designed to deliver a battery
supplied electrical stimulus through leads
attached to electrodes in contact with
heart, used for:
– bradycardia
– heart block
– refractory tachycardia
Obstructive: Decreased FEV1/a pulmonary function test percentage below 80%
Restrictive: a pulmonary function test percentage above 80%
What are the stages of lung abcess?
Lung abscesses are a localized area of pus formed lesion associated with necrosis.
Stage 1: Inflammatory infiltration of lung tissue
Stage 2: Formation of a cavity filled with pus
Stage 3: Occurs obliteration of the cavity with the formation of the area of pneumosclerosis
Describe Sarcoidosis
• Systemic disease of unknown cause that can affect many organs (Most common lung and lymph)
• Growth of granulomas (small collection of inflammatory cells)
• General symptoms: fatigue, weight loss, swollen lymph nodes, painful joints
• Pulmonary : dry cough, SOB, chest pain
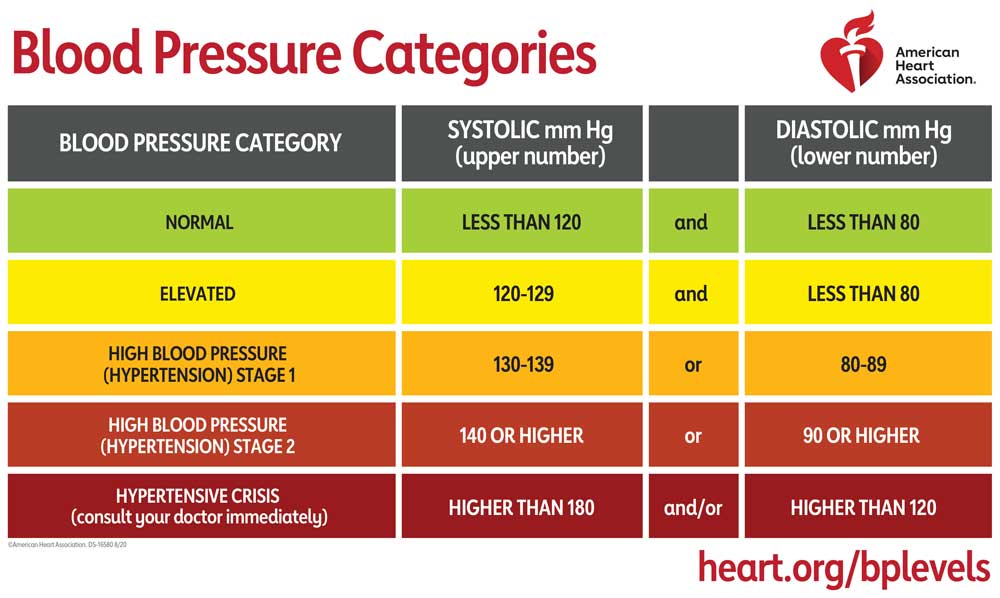
Hypertension is defined as...?
What are the different stages and their BP values?
BP of 140/90 on at least 2 separate days
A Baceterial infection of the endocardium as a result of growths on damaged valves .
High risk for IV drug users, prosthetic valves, past heart sugery patients
Infective Endocarditis
What are the major types of Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases?
Cystic Fibrosis
Chronic Bronchitis
Bronchiectasis
Asthma
Emphysema
An infectious, inflammatory, systemic disease that affects the lungs, lymph nodes, and other organs. It is transmitted by inhalation of airborne particles and requires an N95 mask. It is characterized by granulomas, caseous necrosis, and cavity formation.
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Describe Atelectasis
• Complete or partial collapse of lung tissue that had previously been expanded.
• Can involve:
• Smallest portion of lung unit (alveoli)
• Lobe
• Entire lung (pneumothorax)
• One of the most common pulmonary complications of medical/surgical patients
#1 thing PT should do post op is work with pt ob deep breathing and making them cough
Metabolic Syndrome is characterized by...?
(You must have 3/5 of these to be considered)
Obesity
Decreased HDL levels (Men <40, Women <50)
Fasting glucose >100
Elevated triglyceridea >150
Hypertension
Form of endocarditis caused by bacterial infection by strep A (if untreated). It can cause damage to valves or heart muscle
Rheumatic Heart Disease
What is the difference between Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases and Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases?
Give a brief explanation for both.
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases involves the restriction of lung expansion. Due to the decrease in lung expansion, the vol of air moving in and out of the lungs is decreased. Decreased compliance of the lungs; low chest compliance limits thoracic expansion and lung inflation even if lung tissue is normal. Can be due to trauma, surgery, Neuromuscular/ musculoskeletal conditions.
Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases are diseases of the respiratory system that causes obstruction of airflow. It is hard to exhale all the air from the lungs due to narrowed airways.
Describe Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis? (Interstitial Lung Disease)
• Pathology: fibroblasts distort and shrink the lung at the alveolar level causing decreased compliance
• Etiology unknown may be due to viral, genetic, or immune system abnormalities.
• Treatment: corticosteroids in exacerbation stage. Supportive measures in the fibrotic stage.
What is the #1 way to diagnose Atelectasis?
Chest X-ray and check for tracheal deviation.
Trachea will deviate to area of lower pressure (to the side the atelectasis is taking place)
If R sided lung collapse--R sided atelectasis--the trachea shifts to the R
What are the 4 abnormalities that are apart of the Tetralogy of fallot?
Needs immediate surgery at birth
Pulmonary artery stenosis
Ventricular Septal Defect
Dextroposition of the Aorta
R Ventricular Hypertrophy
What is an aneurysm and what are the two types?
An aneurysm is abnormal stretching or dilation in the walls of an artery, vein, or the heart.
Dissecting: lengthwise splitting of arterial wall creating a false vessel
False Aneurysm: wall of blood vessel ruptures and blood escapes to surrounding tissue and forms a clot
Describe the abnormalities in fetal development? (3)
Agenesis: arrest of lung tissue in development. bronchial tree, lung tissue, and pulmonary vasculature do not develop
Aplasia: Incomplete development of lung parenchyma supplies by a rudimentary bronchus
Hypoplasia: underdeveloped lungs, most often secondary to other congenital abnormalities
Describe Systemic Sclerosis Lung Disease? (Scleroderma)
• Autoimmune disease of connective tissue
(Excessive collagen)
• Restrictive lung disease with inflammation and fibrosis
• Systemic disease that affects many organs-mainly lungs
• Signs and symptoms; Dyspnea on exertion and Dry cough
What is a pneumothorax and how is it diagnosed?
Accumulation of air or gas in the pleural space. Can be traumatic or spontaneous. (young, thin, tall males or GSW/stabbing)
In an X-ray the trachea deviates away from the affected side. (accumulation of air pushes trachea away)
R sided pneumothorax--Trachea shifts to L
Acute Coronary Syndrome is?
What is STEMI vs NSTEMI and what are defining characteristics used to diagnose both?
ACS- Any condition that causes a sudden drop in blood flow to the heart.
STEMI: damage to the entire heart muscle
Diagnosed with ST segment changes, elevated T waves, Q waves appear
NSTEMI: damge to only the inner layer of heart muscle
ST segments remain
Is caused by Rheumatic heart disease and is a heart condition where the aortic valve doesn't close properly, allowing blood to leak back into the heart's left ventricle.
Aortic Regurgitation
An acute lung injury; inflammation of lung parenchyma, infection of the lower respiratory tract.
S&S: Fever, Productive foul smelling cough, SOB
Diagnosis: Chest X-ray (area of radiopacity in involved area), Elevated WBC, breath sounds (Rhonchi or Crackles)
What is the specific classification?
Restrictive
Classified as pneumoconiosis (lung-dust)1`
What is the difference between Pleurisy and Pleural Effusion?
Pleurisy is inflammation of the pleura.
3 classifications:
Dry: no change in fluid content
Wet: increase in fluid content/pleural effusion
Purulent pleurisy: infection with pus formation (called pleural empyema)
Pleural effusion is when the normal balance between pleural fluid formation and reabsorption is disrupted and fluid accumulates in pleural space. (Restricts lung expansion)
Diagnosed: Blunting of the costophrenic angles