In the arm, this artery bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries.
What is the brachial artery?
These structures house the capillary bed for exchange of CO2 and O2.
What are alveoli?
Name the two atrioventricular valves
What are the tricuspid and mitral valves?
The difference between a Grade III/VI and a Grade IV/VI murmur is the presence of this physical finding.
What is a palpable thrill?
Normal breathing should be associated with this sound while standing next to the patient.
What is silent or quiet breathing?
In the lower extremities, this a prominent vein runs along the medial aspect of the lower leg anterior to the medial malleolus and is used as a graft in coronary artery bypass surgery.
What is the saphenous vein?
This lung has 3 lobes.
What is the RIGHT lung?
Aortic stenosis (AS) is a reduction in the surface area of the aortic valve resulting in turbulent and decreased flow across the valve. This can best be heard as a murmur at this surface anatomical location.
What is the 2nd intercostal space, right sternal border?
The name of this state is usually used to describe the pattern of cardiac sounds associated with an S3 gallop.
What is the state of Kentucky?
To best hear stridorous breath sounds, it is best to place your stethoscope in this location.
What is over the neck or supraclavicular area? (since these sounds are from upper airway obstruction)
What is the common iliac artery?
The trachea branches into the LEFT and RIGHT mainstem bronchi. This bronchus has an acute angle and supplies the upper, middle, and lower lobes.
What is the RIGHT mainstem bronchus?
The mitral valve is known to occasionally have a structural abnormality known as Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP). When the valve prolapses, into which chamber does the mitral valve prolapse?
What is the LEFT atrium?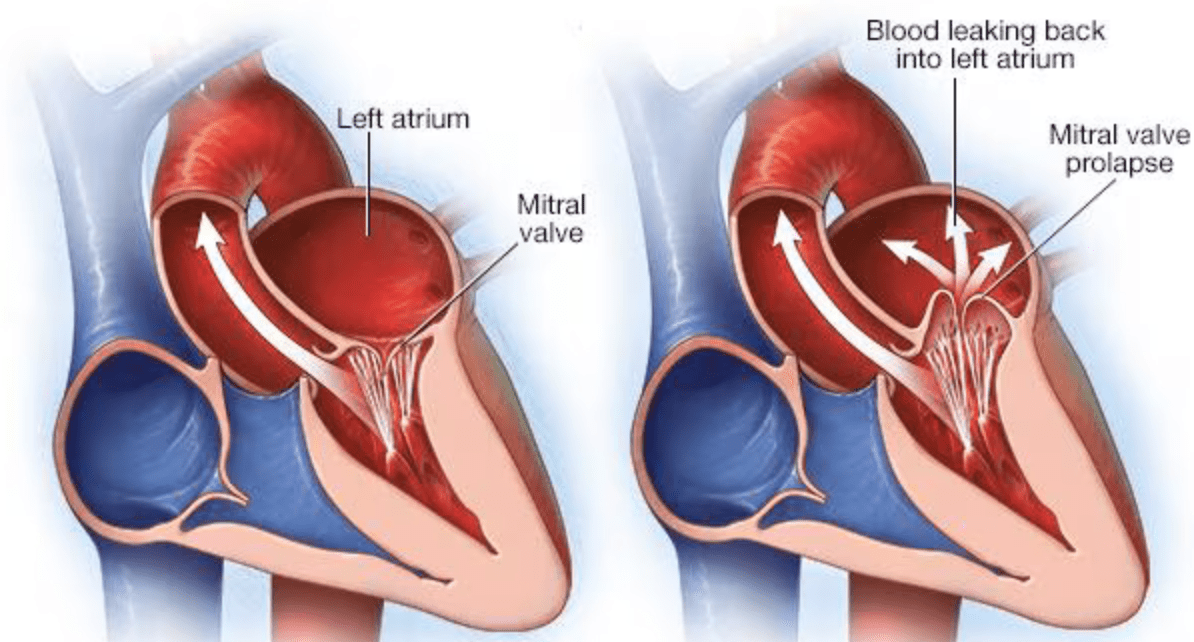
The S1 sounds is created by the nearly simultaneous closing of these two cardiac valves.
What are the mitral and tricuspid valves?
These lung sounds produce a crackle-like sounds on deep inspiration, but resolve after a few breaths.
What are atelectatic crackles?
As blood flows out of the left ventricle of the heart, the first 3 branches off of the aortic arch are which vessels (in order)?
What are the innominate artery (also known as the brachiocephalic artery), the left common carotid artery (CCA) the left subclavian artery.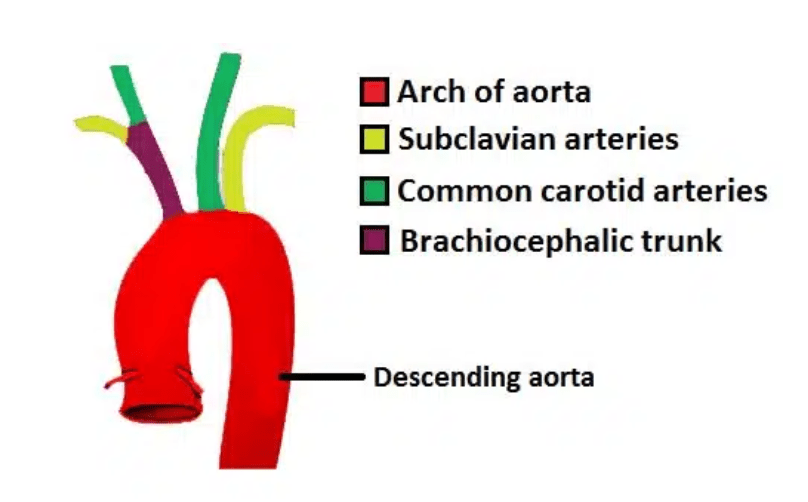
This pleural lining covers the outside of the lungs.
What is the visceral pleura?
This is the most common genetic cardiac valve abnormality.
What is bicuspid aortic valve? 2% of the population has a BAV.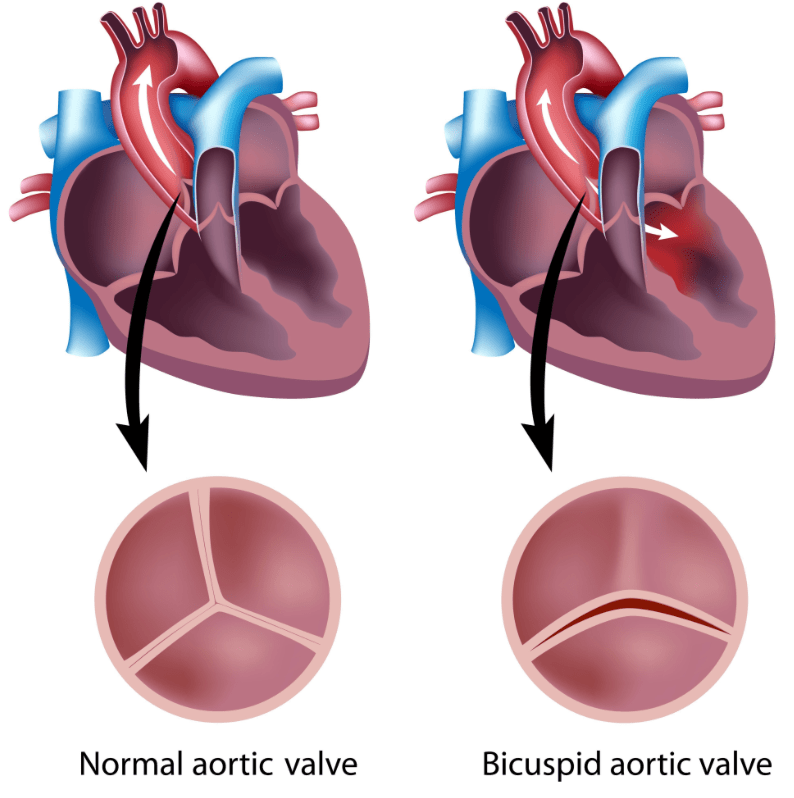
This cardiac disease state may be associated with muffled heart sounds and a friction rub.
What is pericarditis?
What is the opening of alveolar structures that have excess fluid causing their collapse?
This vessel gives rise to the RIGHT common carotid artery.
What is the innominate or brachiocephalic artery?
In the midaxillary plane, the lungs extend down to the level of these ribs
What are the 7th or 8th rib?
Typical systolic murmurs are usually caused by which valvular pathology.
What is aortic stenosis/sclerosis and mitral regurgitation?
This sound originating from a heart valve may be mistaken for a bruit in the carotid arteries.
The wheezing lung sounds of an chronic emphysema are best heard in this phase of the respiratory cycle.
What is expiration? since this is a disease of air trapping and expiratory dysfunction