(Anatomy/murmurs)
(Anatomy/murmurs)
(Hypertension)
(Heart Failure)
("electrical" related)
The names of the heart valves.
What is Tricuspid, Pulmonic, Mitral and Aortic valves?
According to the 2018 ACC/AHA Hypertension guidelines, normal, or "ideal", BP.
What is 120/80?
Metabolic syndrome is defined as a constellation of 3 or more conditions.
What is -Abdominal obesity, -TG 150 or higher, -HDL < 40 (men) or < 50 (women), -Fasting Glu 110 or higher, - HTN?
Double Jeopardy!! At high risk for heart failure but w/o current or previous S/S of HF & w/o structural/functional heart disease or abnormal biomarkers.
What is Stage A -At-risk for HF
Bonus Question-what type conditions might this include?
“Natural” pacemaker of the heart.
What is the Sinoatrial (SA) node?
Nonpharmacologic therapies for HTN.
What is weight loss, healthy diet (DASH), reduced intake of dietary NA, enhanced intake of dietary K, physical activity, limited ETOH intake?
When the atria contract, which heart valves are open?
What are the mitral and tricuspid valves?
Steps for proper BP measurement.
What is 1) properly prepare the pt (relax, sitting in chair - feet on floor, back supported) for > 5 minutes, no talking, etc. 2) Use proper technique for taking BP (arm supported, proper cuff size, proper placement of cuff, etc.) 3) Take proper measurements for DX/Tx of elevated BP/HTN (first visit, both arms, etc.). 4) document BP readings, 5) Average the readings (avg. 2 or more on 2 or more occasions) 6) provide BP readings to pt.
Which patient types should be treated with statin?
What are Pts. with:
Clinical ASCVD (known dz),
those w/ LDL ≥ 190,
those 40-75 w/ DM (w/o ASCVD) & LDL ≥ 70, &/or
those 40-75 w/o ASCVD/DM but LDL 70-189 & elevated 10-year risk of ASCVD (≥7.5%)?
Double Jeopardy!! Brain natriuretic peptide
What is BNP – hormone assessed to diagnose/prognose HF?
Bonus: when on which HF medication should you use NT-proBNP instead of BNP?
List the electrical pathway of the conduction system ("Point A to E").
What is the SA node to AV node, to BOH, Bundle branches, to Purkinje fibers.
Prosthetic heart valves, including TAVR; previous endocarditis; congenital heart disease w/ repair and residual valve regurgitation; or s/p cardiac transplantation with valve regurgitation due to a structurally abnormal valve.
What are indications for antibiotic prophylaxis prior to dental work/cleaning?
On the Levine Scale, a "thrill" is first noted on exam with this grade murmur.
What is grade IV / VI?
- you should know each of the levels.
95% of most patients have this type of hypertension
What is essential (primary) HTN?
The two common "high-intensity" statins.
What is Atorvastatin (Lipitor) 40 mg or 80 mg or Rosuvastatin 20 mg or 40 mg?
"Approved" Beta-blocker(s) indicated for HF.
What is Carvedilol (Coreg), Metoprolol succinate (Toprol XL) and Bisoprolol (Zebeta)?
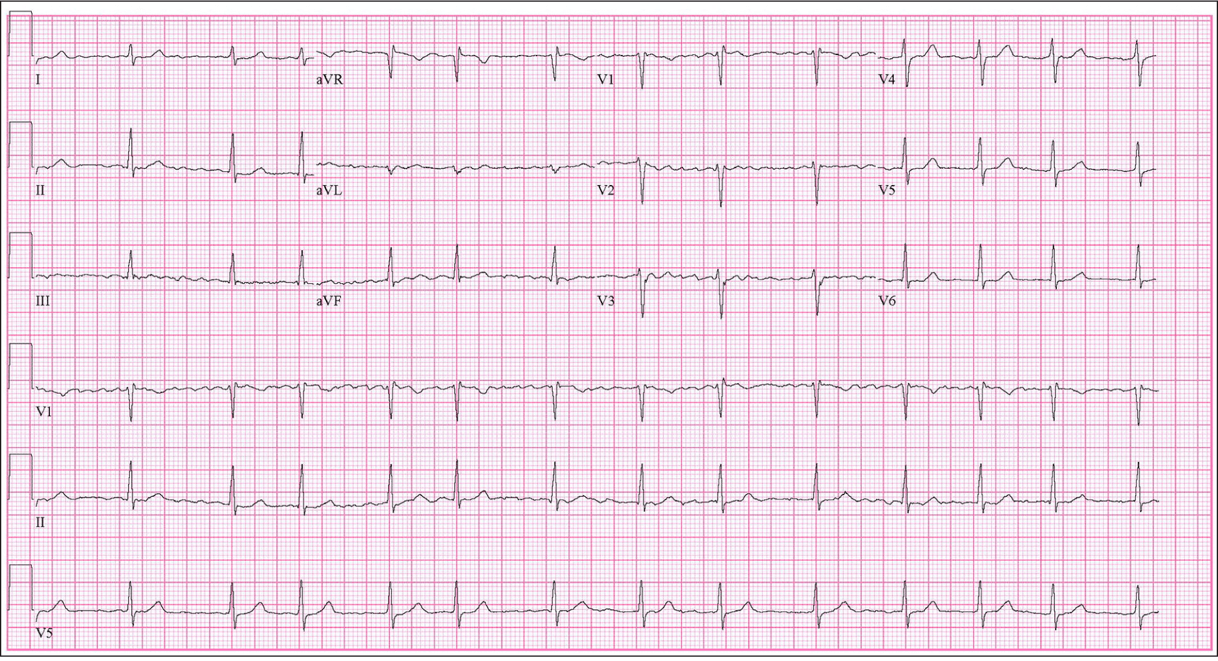
What is atrial fib?
Double Jeopardy!! Cardiac indications for oral anticoagulation.
What are valve replacements and atrial fib?
Bonus Question: Are mechanical valves eligible for NOACS or stick w/ VKAs?
This valvular disorder creates a systolic murmur that typically radiates to the carotids.
What is aortic stenosis?
Initial (basic) labs/diagnostic testing when working up patient with hypertension.
What are - CMP (includes fasting glucose, Cr, NA, K, Calcium), CBC, TSH, UA, and EKG? (optional - ECHO, uric acid, urinary albumin to creatinine ratio)
Indication(s) for coronary artery calcium (CAC) testing.
What is - Pts reluctant to start statin therapy ..., pts concerned about the need to reinstitute statin tx after statin-associated sx, older pts w/ low burden of risk factors who question if would benefit from statin therapy, middle-aged adults w/ 10-yr risk of 5% to < 7.5% w/ factors that increase their ASCVD risk, even though they are in BL risk group?
Uncontrolled hypertension, myocardial infarction, pregnancy, drugs & alcohol, viral, or idiopathic.
What are typical causes of LV dysfunction.
Double Jeopardy!! Clinical Risk tool to calculate need for anticoagulation in someone w/ atrial fib.
What is the CHA2DS2-VACs score?
Bonus – what does CHA2DS2-VACs stand for?
Recommended screening for AAA per USPSTF.
What is men aged 65 to 75 years old who have ever smoked? (per USPSTF 1-time screening for AAA w/ US in this group).
Double Jeopardy!! A 65 yo man with left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is also diagnosed with regurgitation of the valve located at the entrance of the LV. Which valve in this patient is most likely damaged?
What is the mitral valve?
Bonus: Where do murmurs from MV radiate?
First-line pharmacologic therapies for hypertension
What is Thiazide diuretics, ACEi or ARB, and/or CCB?
Double Jeopardy!! Most common statin-associated side effect.
What is Statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS)?
BONUS – what are recommendations w/ SAMS?
Indication(s) for implantable cardioverter defibrillator.
What is LVEF < 35% despite GDMT? or as resynchronization therapy in pts with EF < 35 w/ LBBB (or prolonged QRS duration)?
Irregularly irregular rhythm w/ no discernible P waves.
What is atrial fib?
Describe process for performing an ankle-brachial index (ABI) assessment.
What is - Measure the SBP in both arms (use the higher #), then the SBP in both legs - individually. Divide the SBP in leg by the SBP of the arm (highest # of the two arms) = the ABI. Normal 1.00-1.40; abnormal (and need referral) ≤0.90.