Structure that longitudinally divides atria
Interatrial Septum
What structure is #1 in the image below?
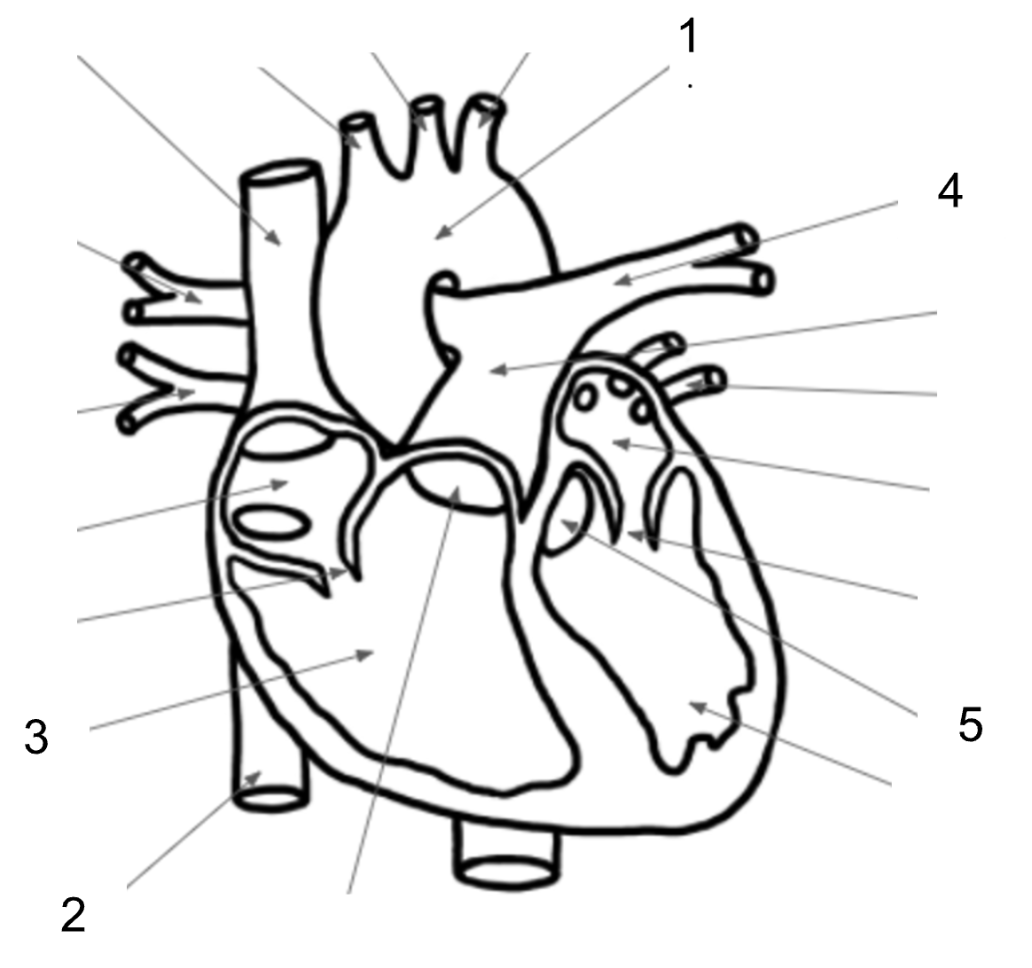
Aorta
Describe the difference between veins and arteries in terms of the direction in which blood flows.
Vein - Towards heart
Artery - Away from heart
The condition describing an individual with a rapid heart rate
Tachycardia
A non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart over time
Electrocardiogram
What is the nonliving component of blood?
Plasma
Describe the locations of the apex and base of the heart.
Apex - The tip of your heart that points forward, downward, and to the left
Base - Widest part of the heart
What structure is #2 in the image below?
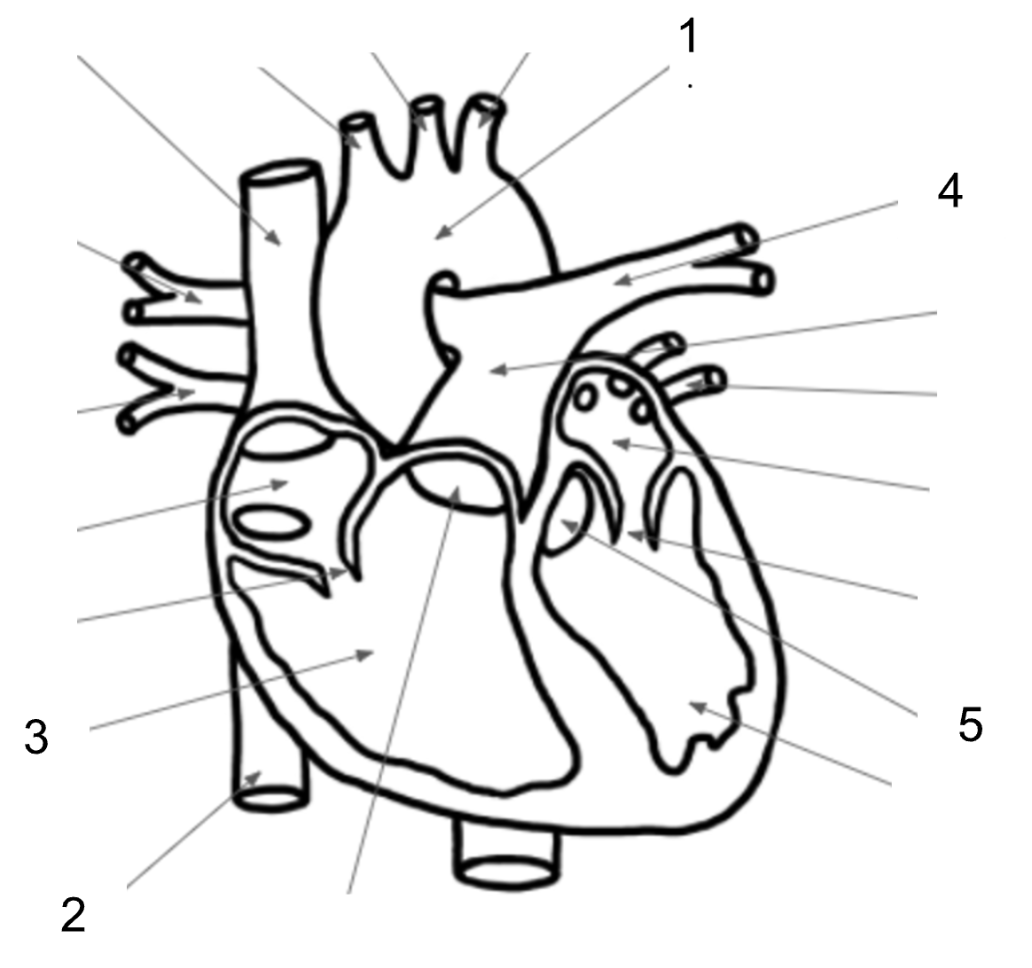
Inferior Vena Cava
What is the other name for the mitral valve? What is unique about this valve?
Bicuspid - Only valve with two cusps
Which side of the heart is oxygenated? Which is deoxygenated?
Oxygenated - Left
Deoxygenated - Right
Scientific name for a "heart attack"
Myocardial infarction
What type of blood cell is irregular shaped (fragments of cells) and needed for clotting?
Thrombocytes (Platelets)
What is the largest artery of the body and carries blood from the heart to the blood vessels?
Aorta
What structure is #3 in the image below?
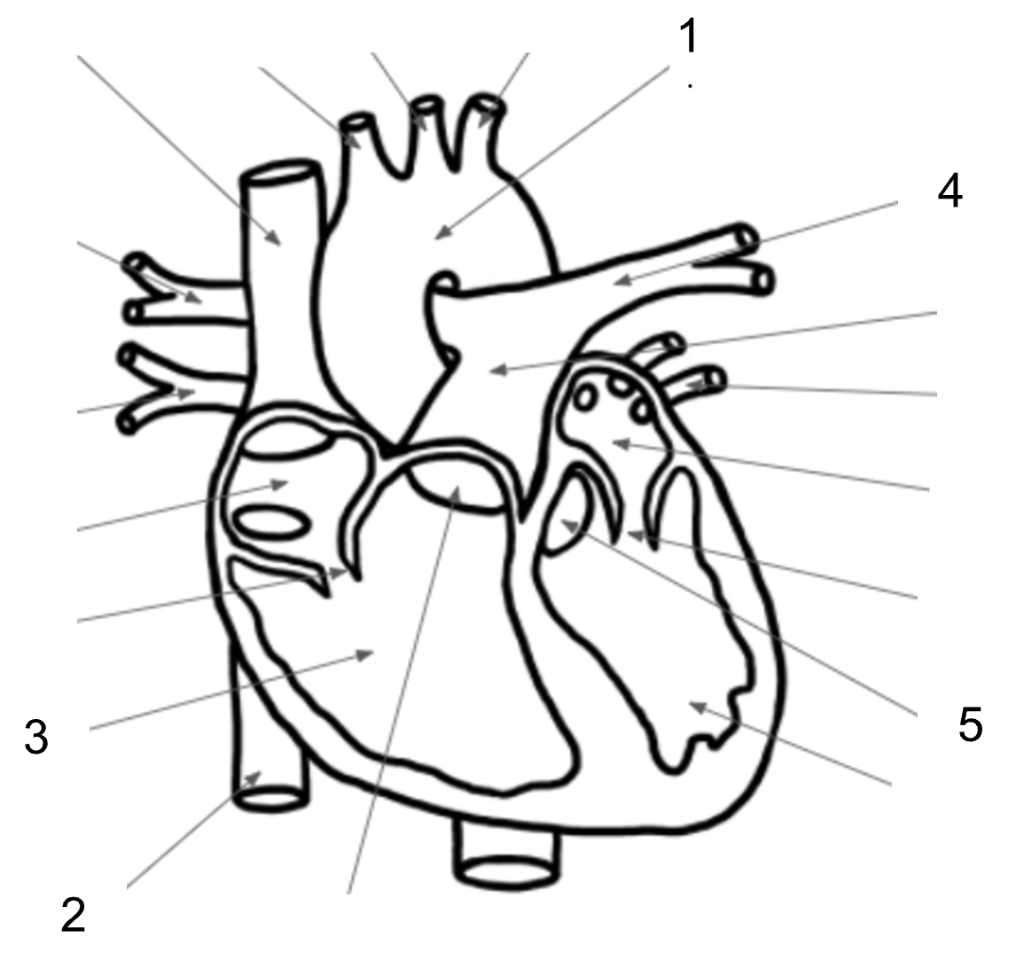
Right Ventricle
_______________ are the exception to the general flow of arteries.
Coronary Arteries
Explain the terms "systole" and "diastole."
Systole - Period of contraction
Diastole - Period of relaxation
The condition where there is rapid, irregular contraction of the heart muscle
Fibrillation
What is considered a normal heart rate?
75-100 bpm
What are the three layers that make up the heart (in order from most inner to outer)?
Endocardium, Myocardium, Epicardium
What structure is #4 in the image below?
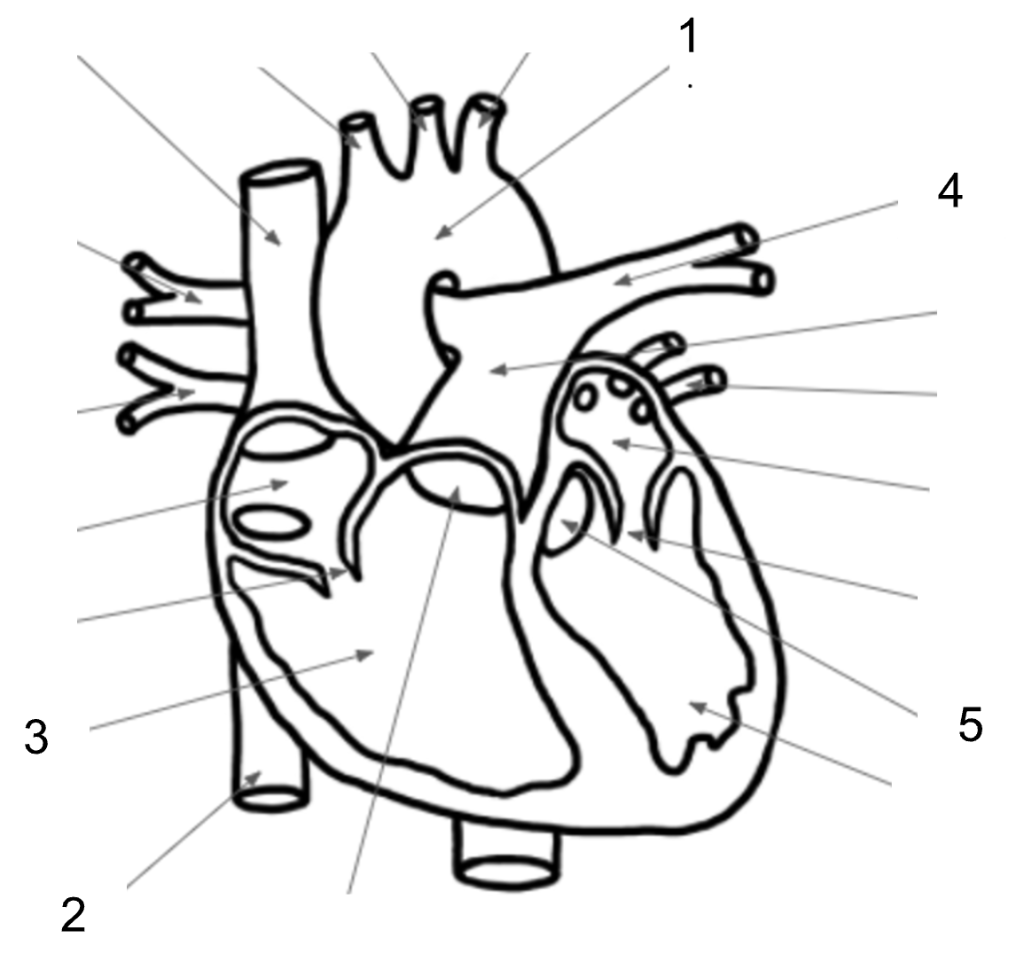
Pulmonary Artery
Out of the three tunics (layers) seen in arteries and veins, capillaries are only made up of one. Which one is it?
Tunica intima
Heart sound that is heard when set of AV valves close
Lub
Condition where cardiac output does not equal venous return
Congestive Heart Failure
What are the four vital signs?
Body Temperature, Blood Pressure, Respiratory Rate, Arterial Pulse
Explain how the heart acts as a "double pump." Describe the pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation in your answer.
Your heart is considered a "double pump" because of the two circulatory circuits within the organ. The pulmonary circulation is the circuit in which blood from the right side of the heart is carried out to the lungs and returned back to the left side of the heart. The systemic circulation is the circuit in which blood from the left side of the heart goes through the body tissues and returns back to the right side of the heart.
What structure is #5 in the image below?
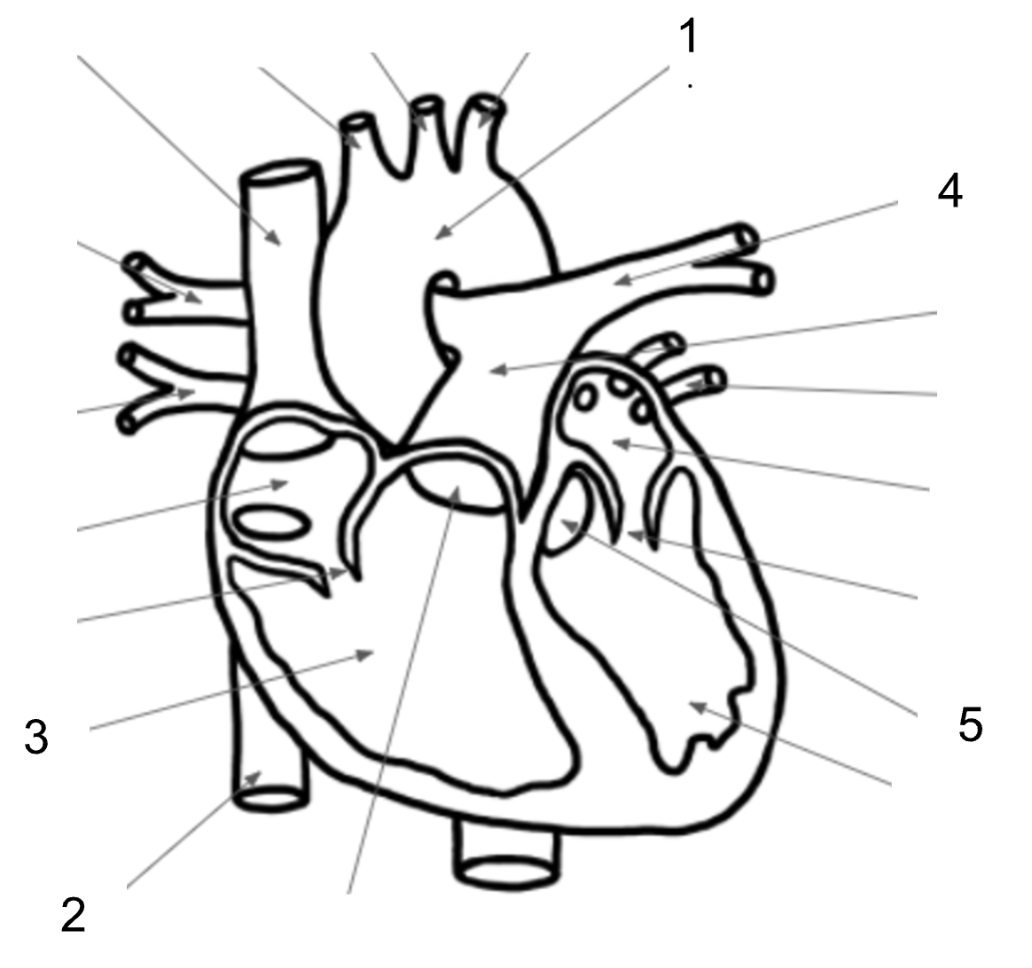
Aortic Valve
What are the atrioventricular (AV) valves of the heart? What are the semilunar (SL) valves?
AV - Mitral (Bicuspid) and Tricuspid
SL - Pulmonary and Aortic
After the blood travels to the lungs, what structure does it go to next?
Pulmonary Veins
Label the components of the EKG below.
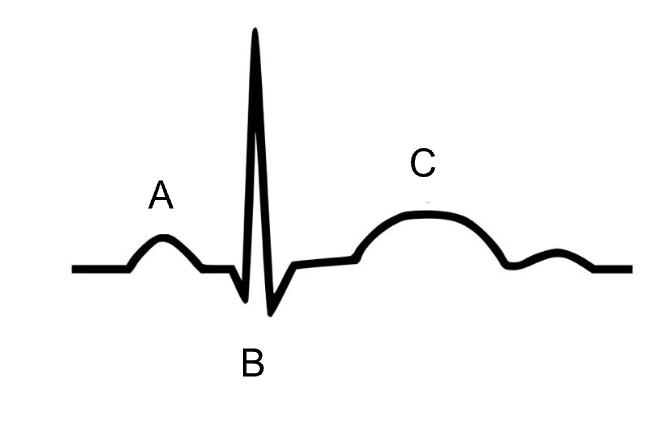
A - P Wave
B - QRS Complec
C - T Wave
Trace the path of blood flow within the vascular system by placing the following terms in order: Arteries, Arterioles, Venules, Veins, Capillary beds
Arteries, Arterioles, Capillary Beds, Venules, Veins