Deoxygenated blood from the upper body returns to the right atrium through this large blood vessel.

What is the superior vena cava?
What are veins?
Plasma is made up of 91% of this element.

What is water?
Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium)
What is myocarditis?
abnormally rapid resting heart rate (above 100 bpm)
What is tachycardia?
What is -emia?
This heart chamber receives oxygenated blood from the lungs

What is the left atrium?
The 2 chambers of the heart that are considered to be "pumping chambers".
What are the ventricles?
Makes up 45% of our blood and consists of: erythrocytes, thrombocytes, and leukocytes.
What are the formed elements?
A condition in which there is narrowing, thickening or blockage of one or more of the valves of the heart
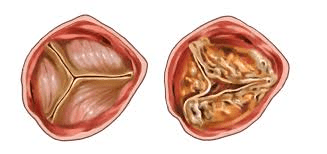
What is valvular stenosis?
Occurs when the heart abruptly stops or has an abnormal arrhythmia that prevents it from pumping blood.

What is cardiac arrest?
What are veins?
What is the aortic valve?
Separates the heart into left and right... also a popular type of nasal piercing.

What is the septum?
Blood pressure remaining when the ventricles are relaxed, in between heartbeats. (Bottom number of BP reading)
What is diastolic pressure?
A person living with A-fib is at risk for developing this side effect, which could cause a stroke or PE
What are blood clots (thrombi)?
occurs when the normal rhythmic contractions of the atria are replaced by irregular twitching and shaking.
What is "A-fib"?
Root word meaning plaque or fatty substance
What is ather/o?
Deoxygenated blood is pumped away from the heart and to the lungs via this vessel.
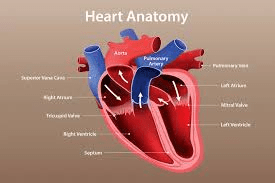
What is the pulmonary artery?
Interior vascular structures that allow blood to flow in only one direction.
What are valves?
Blood pressure created when the ventricles contract. (Top number of BP reading)
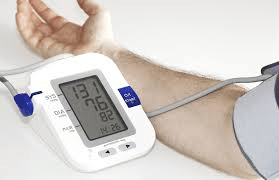
What is systolic pressure?
The abbreviation for a chronic heart condition where the heart is unable to pump out all of the blood it receives, causing fluid build-up in either the lungs, neck, or lower extremities
What is CHF?
This adverse event occurs with the occlusion of one or more coronary arteries due to plaque build-up. (a.k.a "heart attack")
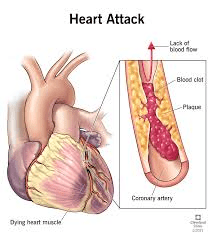
What is a myocardial infarction?
Root word meaning "clot".
What is thromb/o?
What blood being pumped through the pulmonary artery is considered (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
What is deoxygenated?
The smallest blood vessels (one cell wall thick) that perform oxygen/nutrient and waste exchange from the cells of tissues.
What are the capillaries?
Type of medication your patient with A-fib will be prescribed.

What are blood thinners?
An abnormal sound heard when auscultating the heart that could either be harmless or indicate a defect in a valve or chamber.
What is a heart murmur?
Pounding or racing heart with or without dysrhythmia. (Also, what your heart does when you see your crush in the hallway)

What is heart palpitation?
Root word meaning "vessel".
What is vas/o?
Name of the valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle.
What is the bicuspid?
Smooth layer that lines the inside of the heart
What is the endocardium?
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils are all types of WBCs, aka....
What are leukocytes?
A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) can form in the lower leg, and if dislodged will travel to the heart and out to the lungs, causing this condition.
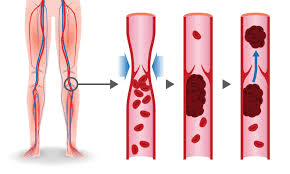
What is a pulmonary embolism (PE)?
A deadly heart arrhythmia where the ventricles are essentially shaking and not effectively contracting to pump blood.
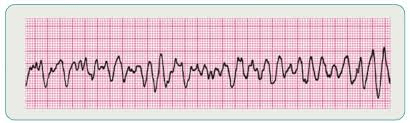
What is "V-fib"?
The meaning of the suffix in the term: Dyscrasia

What is mixture or blending?