This class of medications are the first line therapy to relieve stable anginal symptoms by reducing heart rate and contractility.
What are beta blockers?
Name the four pillars of GDMT.
What are ACEi/ARBs, BBs, MRAs, and SGLT2i?
This medication is the first line intervention for those with symptomatic bradycardia.
What is atropine?
1mg doses, max dose 3mg
This systolic murmur is classically heard at the cardiac apex and demonstrates a mid-systolic click followed by a rumble.
What is mitral valve prolapse?
Ms Beam presents to the ER with crushing substernal chest pain. Her ECG is shown below. What class of medications is contraindicated which would normally be used for post-ACS care?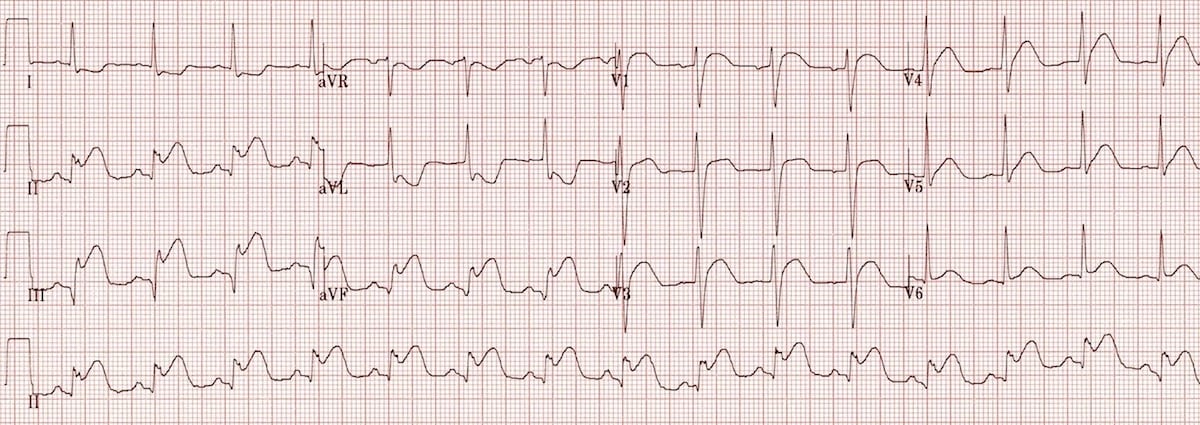
Nitrates
Decreased preload -> collapse of the RV
If a patient presents to a non-PCI capable hospital with a STEMI, if transfer to another hospital and performance of a PCI is not possible within ____ minutes, a fibrinolytic strategy should be pursued instead.
What is 120 minutes?
Door-to-PCI time goal <90 minutes at PCI capable hospitals, <120 minutes at non-PCI hospitals including transfer time. If they cannot get to a PCI capable hospital in 120 minutes, then fibrinolysis should be performed within 30 minutes.
A 2004 study found that in Blacks with HFrEF, the combination of these two medications reduces mortality.
What are hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate?
The other subgroups had no mortality change
This medication is the preferred oral anticoagulant in patients with atrial fibrillation and moderate or severe mitral stenosis.
What is warfarin?
Patients with afib and rheumatic valve disease were demonstrated to have a reduced composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, MI or death compared to rivaroxaban.
Mr Rodgers presents with increased wall thickness on TTE, a low voltage ECG, bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome and progressive leg swelling. He recently was found to have an elevated M spike on labwork. What underlying process is driving his cardiomyopathy?
What is Amyloidosis? (specifically AL Amyloidosis)
This American aviator, who completed one of the first transatlantic flights in history, is credited with inventing an perfusion pump for supplying blood to hearts outside the body.
Who is Charles Lindbergh?/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/db/ff/dbffc39f-6738-41df-8fee-d46f5af0cab1/rws201204787web.jpg)
Per the 2025 ACC guidelines, in a patient treated for ACS who has a separate indication for an oral anticoagulant, _____ (medication) should be discontinued after ______ (timeframe) and _____ (2 medications) should be continued.
Aspirin should be stopped after 1-4 weeks, and continued use of P2Y12 with the oral anticoagulant
Ms Bee is a 46F who presents with acute-onset substernal chest discomfort with associated dyspnea, an elevated cardiac troponin level and ST elevation in the anterior precordial leads and TTE demonstrating EF 35% (previously normal) with preserved basal left ventricular function with apical and mid-ventricular hypokinesis. LHC shows normal coronaries. What is her diagnosis?
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Name the arrythmia
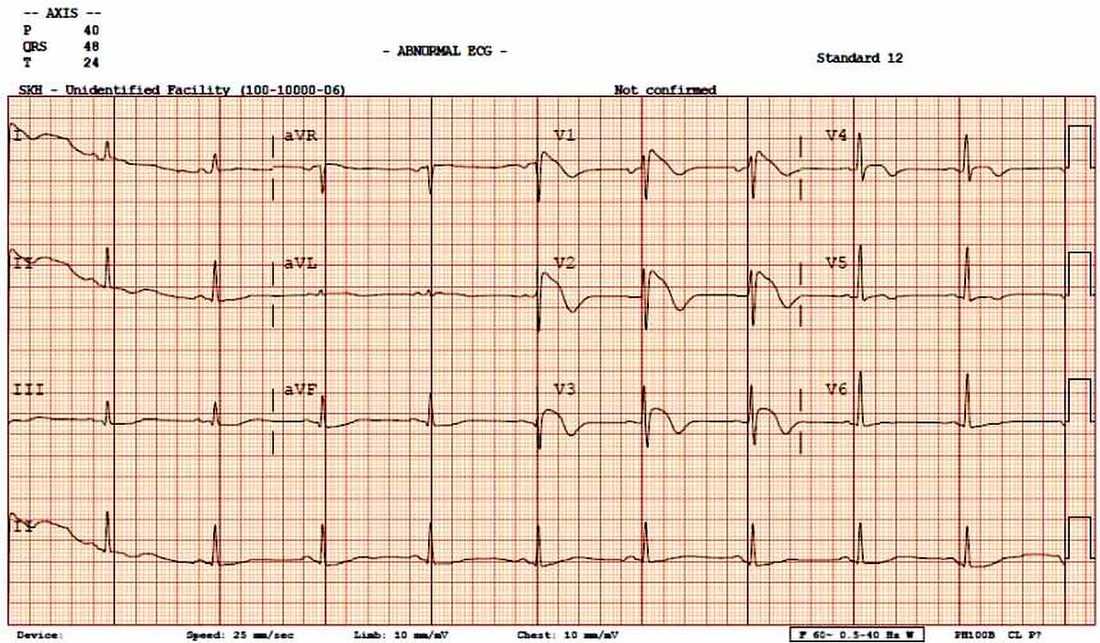
What is Brugada syndrome?
- Coved ST segment elevation >2mm in >1 of V1-V3 followed by a negative T wave.
Due to a Na channelopathy, can lead to VT, VFib, and sudden cardiac death. These patients need an ICD
On exam, Mr John has a systolic ejection murmur best heard at the left upper sternal border that increases during valsalva, decreases with squatting and decreases with handgrip. What cardiac pathology does he have?
What is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)?

In patients with an EF of 35% or less who have tolerated 3 months of maximal GDMT and still have NYHA class II or III symptoms, this non-medical therapy should be considered to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death.
What is Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator therapy?
Arrhythmias are a common cause of death, and ICD improves survival both in primary and secondary prevention of sudden cardiac death.
Mr Jones underwent PCI for a large RCA STEMI 5 days ago. He had been recovering appropriately, however this morning he suddenly became hypoxic, hypotensive, and cold. A CXR demonstrates severe bilateral pulmonary infiltrates. POCUS does not show any pericardial effusion, otherwise windows are poor. What post-MI complication is he likely suffering from?
Posterior papillary muscle rupture leading to acute mitral regurgitation.
(Half point for just saying mitral regurg)
Name the characteristics of two of the groups that have a mortality benefit in CRT placement.
Class I: EF < 36%, Sinus with LBBB morphology, QRS >149ms, NYHA II, III or IV on optimal medical therapy
Class IIA: EF < 36%, Sinus with LBBB morphology, QRS 120 to 149ms, NYHA II, III or IV on optimal medical therapy
Class IIA: EF < 36%, Sinus with non-LBBB morphology, QRS >149ms, NYHA III or IV on optimal medical therapy
Class IIA: EF < 36%, AFib, rate control that requires ventricular pacing, on optimal medical therapy
Class IIB: EF < 36%, Sinus with non-LBBB morphology, QRS 120 to 149ms, NYHA III or IV on optimal medical therapy
Class IIB: EF < 36%,undergoing device placement for other indications and expected to have >40% ventricular pacing
This test is the preferred modality to evaluate for structural heart disease in VTach.
What is Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR)?
VT most commonly occurs in the setting of structural heart disease (RV cardiomyopathy, myocardial fibrosis/scarring [post-ACS], cardiac sarcoid, or other cardiomyopathies)
Based on the 2020 AHA/ACC guidelines on aortic stenosis, give two of the three measurements that would qualify a patient's aortic stenosis as severe.
V > 4m/s, mean gradient >40mmHg, AVA <1.0cm2
Ms Smith presents with chest pain two weeks after an uncomplicated delivery. She had an uncomplicated pregnancy, had no previous medical history, no cardiac risk factors, and no family history of atherosclerotic disease. Her troponins are elevated and ECG demonstrates ST segment elevation in the inferior leads. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD)?
According to the 2025 ACC/AHA Guideline update, there is a new Grade I recommendation that in patients with STEMI undergoing PCI, ______ is useful as an alternative to Unfractionated Heparin to reduce mortality and bleeding.
What is bivalirudin?

The EPHESUS trial demonstrated that the addition of this drug to optimal medical therapy reduces morbidity and mortality among patients with acute MI complicated by LV dysfunction and heart failure.
What is eplerenone?
What is the name of the 2020 trial demonstrating a reduction in MACE in patient who underwent rhythm control strategies as compared to rate control strategies?
What is the EAST-AFNET 4 trial?
Ms Smith presented to the hospital in cardiac tamponade. After emergent pericardiocentesis, she was found to have a mass arising from the lateral wall of the right atrium. Echo results are shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is cardiac angiosarcoma?
Myxomas most commonly arise in the left atrium and are more likely to present with constitutional symptoms. Rarely do they cause effusions/tamponade, which is much more common in angiosarcoma.
Updated in 2023, this calculator has replaced previous calculators to estimate the 10-year and 30-year total CVD risk, including ASCVD risk and heart failure.
What is the PREVENT Online Calculator?
https://professional.heart.org/en/guidelines-and-statements/prevent-calculator