Grass is a decomposer
a.True
b. false
a. false
Which category has the most population?
Producers!!!!!
The kelp level is called... 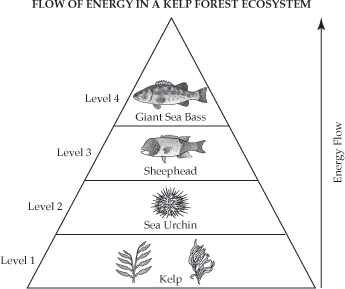
Producers
What is the producer in this food chain?
grass
Which of the following is a symbiosis?
a. a sheep eating grass
b. a wolf chasing a coyote away from a dead elk
c. a fungus living partially inside the roots of a plant
c. a fungus living partially inside the roots of a plant
because it is a long-term relationship between 2 species
A secondary consumer is on the top of a trophic pyramid
a. true
b. false
b. false
What is the approximate carrying capacity for rabbits in this ecosystem?
65 rabbits

If there are 1,000 sea urchins, there should be about how many sheephead?
100
What are3 primary consumers?
any 3 of: deer, rabbit, caterpillar, grasshopper
In which kind of symbiotic relationship do both species benefit?
mutualism
Theres the most energy at the top of a trophic pyramid.
a. true
b.false
b.false
What is the carrying capacity for rabbits in *this* ecosystem?
6,000 rabbits
Where are the least amount of organisms in a trophic pyramid? (lowest level, middle, or top?)
At the top
In parasitism, the parasite benefits. If the parasite were to go extinct, what would you expect to happen to the population of the host? Why?
The host population might increase because parasites benefit while the host is harmed. However, hosts do not immediately die because of the parasite, so the change in the host population might be small.
True or false? Mushrooms are decomposers.
true
 During what years was the population of meerkats stable?
During what years was the population of meerkats stable?
years 2-3 and years 4-7
Which level of a trophic pyramid has the most amount of energy?
a. Tertiary consumers
b. Secondary Consumers
c. Producers
d. Primary Consumers
c. Producers
Why in a stable ecosystem are there *more* producers than any other trophic level?
Only 10% of the energy and biomass at one level is passed to the level above. Therefore, since producers are the bottom of the pyramid, there must be more of them than any other level to support the levels above.
In a mutualism, what would happen to the other species if one species were to decrease in population? Why?
Give one example of this.
E.g. hummingbirds are pollinators for many species of flowers. If there are fewer hummingbirds, some of the plants might not be pollinated. Over time, this would decrease the population.
True or False: It is not unusual that we calculated primary consumers to have 24% of the population of producers in Yellowstone National Park.
200 pts: correct answer
300 pts: explanation of why this is or is not unusual
200 pts: false
300 pts: we would expect primary consumers to have 10% of the population of producers because only 10% of the biomass and energy from the producer level should be transferred to the primary consumer level
 What are the carrying capacities for meerkats in this ecosystem? List the years for each.
What are the carrying capacities for meerkats in this ecosystem? List the years for each.
BONUS 200 points: What could have caused the carrying capacity to change?
Years 2-3: 200 meerkats
Years 4-7: 100 meerkats
An ecosystem has organisms at 3 trophic levels (producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers)
The biomass of secondary consumers was calculated to be 750 kg. What is the expected biomass of producers? (100 pts)
Explain why. Don't just say the name of the rule. Actually explain why the rule is what it is.
The expected biomass of producers is 750 x 100 = 75000 kg.
Each time you drop down 1 trophic level, multiply the biomass by 10 because of the 10% rule. The 10% rule states that 10% of the energy and biomass at each level transfers up to the next one. The other 90% is used to keep the organisms at the lower level alive. Some energy is lost as heat or kinetic energy; some matter cycles down to decomposers. Also, some individuals must remain at their level to reproduce.
The snake COULD be which of the following? choose all that apply:
producer, primary (1) consumer, secondary (2) consumer, tertiary (3) consumer, quaternary (4) consumer
Explain why.
BONUS 100 pts: which ONE level do you think is most appropriate? Why?
200 pts: secondary OR tertiary consumer
300 pts: secondary because it eats grasshoppers, which are primary consumers; tertiary because it eats frogs and hawks, which are secondary consumers
BONUS: tertiary consumer because 2/3 of its prey species are secondary consumers, implying it eats *mostly* secondary consumers
Orchids and the trees they grow on are in a commensalism relationship. A student argues that, because trees are not affected by orchids, that the ecosystem will not be affected if orchids were to decrease in population. Are they correct? Explain your answer.
They are partially correct. The tree population will likely not be directly affected by a decline in the orchid population. However, there are other species that might depend on orchids to survive, or that might benefit from orchids. For example, there could be a species that pollinates or eats the orchids, or uses them for shelter.