What are the 3 risk factors for Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
Obesity
Type 2 Diabetes
Dyslipidemia
What does a portal triad consist of?
Hepatic artery, bile duct, portal vein
 Where are most gall bladder cancers first found:
Where are most gall bladder cancers first found:
The fundus
How much alcohol does one standard have and how much should you drink a day?
Adults
If you’re a healthy adult:
- on any day, you should not drink more than 2 standard drinks
- A standard drink contains 10g of alcohol. Many drinks have more than 1 standard drink in them.
What the three microscopic changes that you would find in Alcohol Liver Disease?
Mallory Hyaline Bodies, fatty change (steatosis)/Cloudy swelling, ballooning of the hepatocyte with necrosis
What are the contents of bile?
The composition of hepatic bile is 97% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats (cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin).
What is this? 
Mallory Hyaline bodies - ALD
Where are the stellate cells found?
In the peri-sinusodial space of the liver
What are the stages of Liver Disease?
1) Normal Liver
2) Steatosis
3) Steatohepatitis
4) Fibrosis
5) Cirrhosis
6)Hepatocellular Cancer
How is fat absorbed into the Small Intestines?

What does this show? 
Macro nodular Cirrhosis
What are the causes of Steatosis?
Enhanced lipogenesis
Arrested lipophagy
Diminished Fatty acid oxidation
Reduce adipokine production
What are the 5 types of Hepatitis and explain their causes?
Hepatitis A: Travelling, Fecal-oral route
Hepatitis B: Transplant, transfusion, sexual contact, perinatal (Blood Bourne)
Hepatitis C: Drug use, blood mixing etc (same as Hep B)
Hepatitis D: Requires Hepatitis B for infection
Hepatitis E: Contaminated food/water, Feco-oral route,
Explain the breakdown of Hemoglobin and the byproducts
- When RBC bursts, they are immediately phagocytosed by macrophages in spleen, bone marrow and liver
- Macrophages release iron from hemoglobin back into the blood – and transported by transferring to : bone marrow, liver (ferritin)
- Globin chains become amino acids
- Porphyrin is converted to unconjugated bilirubin and then transported to the liver (bound to albumin)
- Liver it is bound to glucuronic acid to become conjugated bilirubin, and excreted into the small intestine through liver-secreted bile.
- Small Intestine = Stercobilin (urobilinogen intermediate by bacteria)
- Kidney: Urobilin in urine
Name this pathology
Gall Stones
Cholecystitis
What is the proposed material principles of justice?
•Egalitarian principle: to each an equal share
•Merit principle: to each according to contribution or effort
•Need principle: to each according to need
•libertarian principle: to each according to the system of maximum libertyn
-often translates into “to each according to ability to pay”
•utilitarian principle: distribute according to the principle of maximum benefit (i.e. utility) for all members of society
Explain how alcohol damages the liver?
Alters fat metabolism : Oxidation of ethanol uses NAD. Lack of NAD inhibits oxidation of fat . Accumulation of NADH shunts normal substrates like glucose and alanine in lipid biosynthesis thus accumulation of fat within the hepatocytes (steatosis).
Microtubule disorganisation (Mallory hyaline bodies): Acetaldehyde causes aggregation of intermediate keratin filaments in the cell cytoplasm
Free radicals and oxidative injury: Free radicals, superoxide and hydroperoxides, are generated as by-products of ethanol metabolism via the microsomal and peroxisomal pathways.
Formation of acetaldehyde adducts: Toxic effects on cytoskeleton and cell membranes—hepatic cell injury
Cytokines: TNF-α, IL 6, 8,18 can induce programmed cellular death (apoptosis) in liver cells.
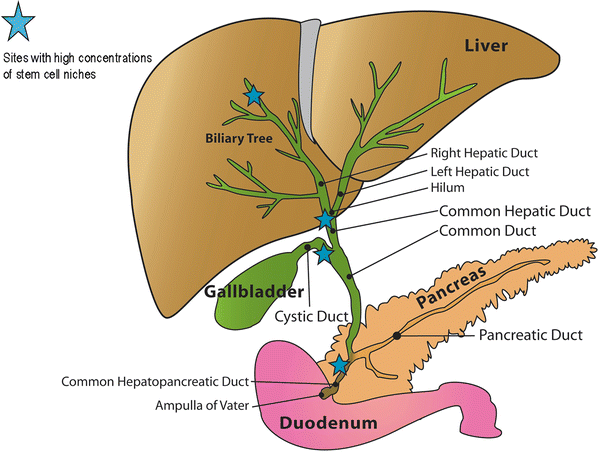
Draw the anatomy of the Billary Tree (including Liver, Gall Bladder and Pancreas)
Name this pathology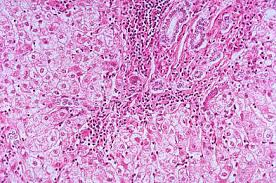
Chronic Hepatitis
What are important factors to consider when providing an organ transplant?
Decision-making regarding allocation must involve explicit evaluation of the risk and benefits to the potential recipient as well as the need to ensure the appropriate use of scarce health resources.
There must be no unlawful or unreasonable discrimination against potential recipients on the basis of: • Race, religious belief, gender, marital status, sexual orientation, social or other status, disability or age •
The need for a transplant arising from the medical consequences of past lifestyle • Capacity to pay for treatment • Location of residence (e.g. remote, rural, regional or metropolitan)