What are the functions of carbohydrates?
There are 2
Quick Energy and Structure
Prokaryote or Eukaryote?
Large, Complex, Multicellular, Has Nucleus
Eukaryote
Which biomolecules can you find in the cell membrane?
Lipids and Proteins
What is the function of the Vacoule?
(VASO)
Store water
What is the anther used for?

contains pollen
What is the function of the digestive system?

Absorb nutrients from food
Are viruses living or non-living?
Non-living
Which biomolecule produces enzymes?
Proteins
What are the functions of the lipids?
There are 2
Transport molecules
Long term Energy

1. Prokaryote or Eukaryote?
2. How do you know? (what is it missing)
1. Prokaryote
2. No Nucleus
What does homeostasis mean?
Balance
What is the function of the nucleus?
1.
2.
1. Has genetic material (DNA/RNA)
2. Control everything.
What do the petals of a flower do?

Attract pollinators.
1. What is the main organ of the nervous system?
2. What is the function of the nervous system?
1. Brain
2. Controls everything
What does a capsid do?
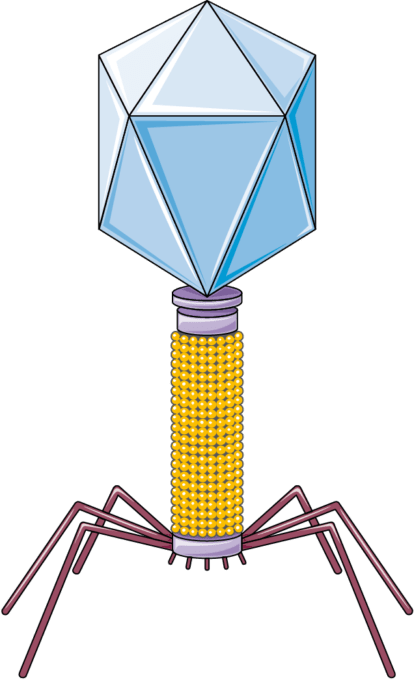
Protects the genetic material
How do we name enzymes?
(think of the last 3 letters)
-ase
What is the function of Nucleic Acids?
There are 2
DNA - Genetic Information
RNA - Build Protein
What is an example of a Prokaryote?
Bacteria
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Control what enters and leaves the cell.
What is the function of the ribosome?
Makes protein.
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
_____ + _____ + ______ -> ________ + _________
1 2 3 4 5
1. water
2. light
3. carbon dioxide
4. glucose/sugar
5. oxygen
How does the muscular system help us move?
C__________
Contractions
What type of genetic material can a virus have?

DNA OR RNA
What does DEnature mean?
DEstroy
What do lipids and carbohydrates have in common?
Provide Energy
What do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in common?
1.
2.
3.
4.
1. Cytoplasm
2. DNA and RNA
3. Ribosome
4. Cell Membrane
With or against?
Needs ATP or no ATP?
High to low or Low to high?
Against
Needs ATP
Low to High
2. What does it do?
1. Plants.
2. Give shape/structure
1. What does the xylem transport?
2. What direction does the xylem travel in?
3. What does the Phloem transport?
4. What direction does the Phloem travel in?
1. water
2. up
3. food/nutrients
4. up and down
What is the function of the respiratory system?

Gas exchange
Inhale: Oxygen
Exhale: Carbon Dioxide
What is the function of the tail fibers?

Attach to host cell
The lock and key model tells us that
Each substrate has a ___________ enzyme
Specific
What is the function of the protein?
There are 4
Enzymes
Build Muscle
Transport Molecules
Provide Structure
What do prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and viruses all have in common?
Genetic material
What are the examples of passive transport?
1.
2.
3.
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
1. What is this a picture of?
2. Who has it?
3. What is the function?
1. Chloroplast
2. Plants
3. Photosynthesis
What is the purpose of the root system?

1.
2.
1. Absorb water
2. Absorb nutrients
What is the function of the circulatory system?

Transport nutrients/gases through the blood
How can we prevent the spread of viruses?
Vaccines
What does an inhibitor do?
Stops the enzyme from working by blocking or changing the shape of the active site.
What do lipids and proteins have in common?
Transport molecules
What organelles make a plant cell unique?
1.
2.
3.
1. cell wall
2. chloroplast
3. large vacoule
1. Which type of osmosis will cause a cell to grOw larger from water entering it?
2. What is it called when a cell bursts?
1. hypOtonic
2. Lysed
1. What is this a picture of?
2. What is the function?
1. Mitochondria
2. Makes ATP/Cellular respiration
What is the purpose of the shoot system?
1.
2.
3.
4.
1. Photosynthesis
2. Reproduce
3. Transport food, water, and nutrients
4. Store glucose
What is the function of the endocrine system?

Glands that produce hormones/chemicals to maintain homeostasis.
How does a vaccine help our body?
What is the function of an enzyme?

Speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy.

