What is one difference between mitosis and meiosis?
1 division vs 2
2 genetically identical cells vs 4 unique cells
2 diploid vs 4 haploid
What is an allele?
A variation of a gene
Draw a punnett square for the cross between AA and aa.
See whiteboard
What does a circle in a pedigree mean?
Female
What is a mutation?
A change in the bases of DNA
A change in DNA
What is the structure/shape of DNA called?
Double Helix
What type of cells does mitosis produce?
body cells
Let's say the dominant trait in fur colour for rabbits is brown (B), and the recessive trait is white fur (b). What would be the phenotype of a rabbit with the genotype Bb?
In rabbits, brown fur is dominant (B) over white fur (b). Draw the punnet square for a cross between a rabbit that is Homozygous for brown fur and a rabbit that is heterozygous
BB x Bb
See whiteboard
What does it mean if a shape is shaded in?
The person has the trait/is affected
True or false: a mutation cannot cause a new phenotype
In the nucleus of the cell
Why must the daughter cells of meiosis be haploid?
So that when the haploid sperm cell meets with the haploid egg cell, they can make one diploid fertilized egg
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
genotype is the combination of alleles (ex. Aa), and phenotype is the physical trait (ex. blue eyes)
Write the genotype ratio for the cross between Aa and aa.
1Aa : 1aa
MUST BE SIMPLIFIED FOR POINTS!
What is David's relationship to Ruth?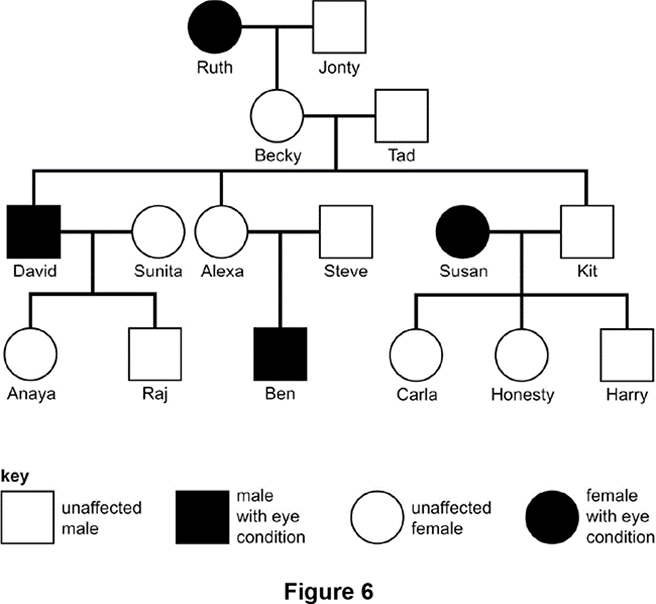
He is her grandson.
What is an example of environmental variation?
Twins having different weights from diet
A and T
G and C
What does haploid mean?
one copy of each chromosome
A gene in a mouse's genome codes for ear shape. The dominant trait is round ears (R), while the recessive trait is pointy ears (r). If one of their parents is homozygous dominant, what is their genotype and phenotype?
G: RR
P: round ears
In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue eyes (b) draw the punnet square for a cross between 2 heterozygous parents and give me the phenotype ratio.
Bb x Bb
Punnett square -- see whiteboard
Ratio: 3 brown : 1 blue
Which of Ruth's granddaughters is affected?
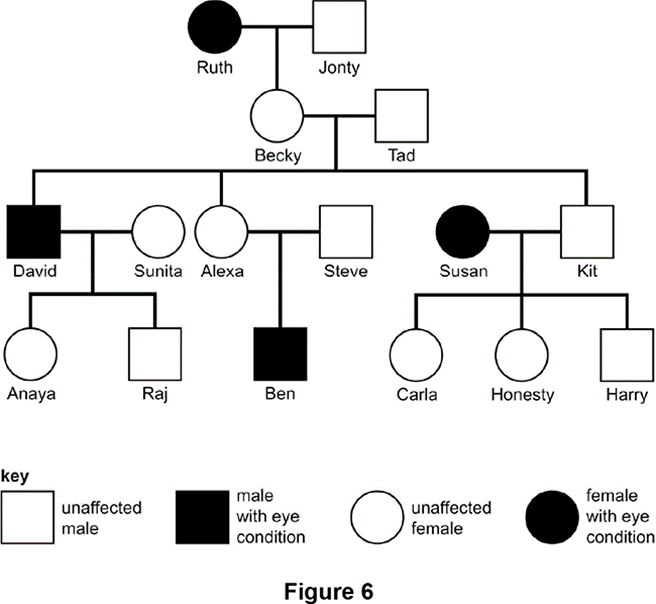
Susan
Would height be an example of continuous variation or discontinuous variation?
Continuous -- no distinct categories
hydrogen bonds
What are the phases of meiosis?
Prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1, cytokinesis 1, prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2, cytokinesis 2
Without doing a punnett square, figure out the percentage of children that would be heterozygous if one parent is homozygous dominant and the other parent is homozygous recessive.
100% -- only possible combo of parent alleles is heterozygous
A certain disease is dominant. Draw a punnet square for the cross between a parent who is homozygous for the disease and a parent that does not have the disease.
if they had 4 children, how many of them would have the disease?
DOUBLE POINTS
AA x aa
They would all have it because the dominant allele is present in each child
How many children did Becky and Tad have?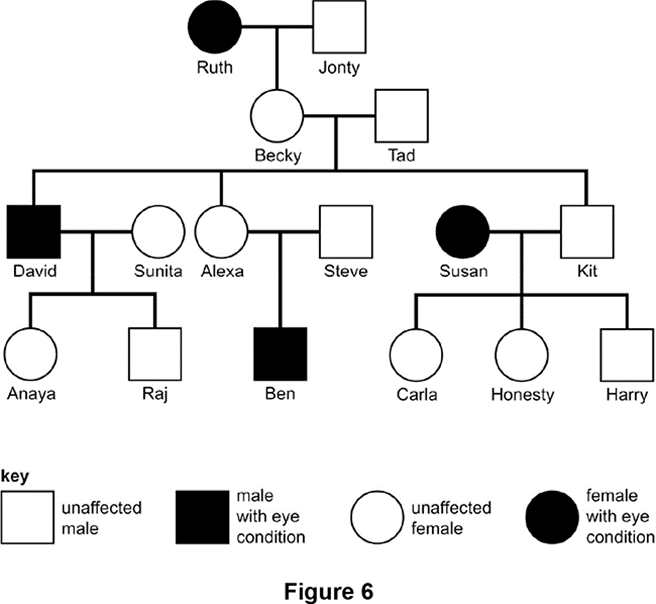
3 children
Double points!
what are 2 processes in sexual reproduction that cause genetic variation?
Random mating
chromosomes line up randomly
Recombination
random fusion of gametes
How does detergent help extract DNA?
It breaks down membranes in the cell