What does CBT stand for?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
True or False: It is our interpretation of a situation not the situation itself that determines how we react?
TRUE: How we interpret or think about a situation determines how we feel about it, which then determines how we'll react.
True or False: We notice every thought that we have
False: Sometimes our thoughts happen so quickly we don’t notice them. Thoughts that a person has automatically in response to a trigger, often occur outside of that person's conscious awareness.
Why do we worry?
Worry is a type of vigilance for threat and an attempt to mentally deal with something that has not happened yet – the “What Ifs”.
True or False: Core Beliefs influence how we interpret our experiences
True: Our interpretations are based on the situation (what’s happening in the moment) and our understanding of the world based on our background and history (What’s happened in the past/our experiences).
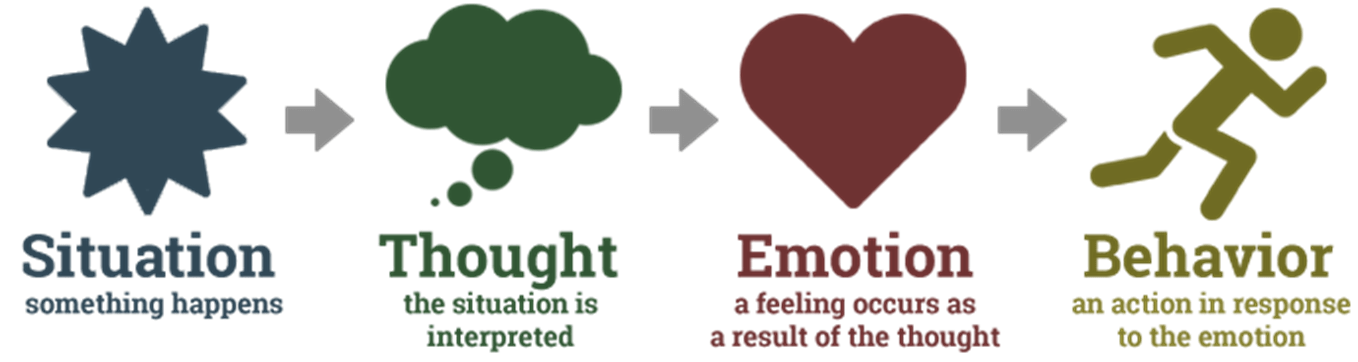
What are the three sides of the CBT triangle?
Thoughts - Emotions/Feelings - Behaviour/Actions
True or False: The cognitive model is made up of 4 parts. Situation - Interpretation/thought, Emotion, Behaviour/Action.
True
How do our negative thoughts and beliefs become automatic?
Through repetition, if you say something negative to yourself often enough you will start to believe it.
What triggers worry?
Many things can trigger worry
Things: Images – newspapers, T.V.’s
Audio – radios, conversations
Situations: Tasks, Activities, Making decisions
True or False: We cannot change our core beliefs
False: Core beliefs can be changed by challenging the evidence that underlies that belief. Repeat your revised belief over and over to yourself so it becomes automatic. Core beliefs can also change over time as we gain new experiences
In general what is the easiest point on the triangle to change? (i.e. Thoughts, Emotions, Behaviour)
In general, it is easiest to change your actions/behaviors; and thoughts are easier to change than emotions.
True or False: Our interpretations of a situation are always accurate
False: Interpretations are not always accurate. There are many ways to think about the same situation.
What is a strategy we can use to overcome our negative thinking patterns?
Simple Awareness - Mindfulness, Observe etc...
Thought Challenging - Check the Facts!, Take your thoughts to Court etc...
Reframing Unhelpful Thoughts - Coping statements etc...
What is worry?
Worry is a self-talk activity in which we overestimate the likelihood of something negative or terrible happening and underestimate our ability to cope.
Worry that is often repetitive and unproductive leaves people with a sense that their worries are uncontrollable, and that they cannot cope with the problem
What is the difference between a Fact and an Opinion?
Facts are verifiable statements. They are supported by evidence and can be agreed upon. Opinions are personal interpretations of facts, which differ from person to person.
What does CBT help with?
Through CBT we learn skills and techniques that will help us become aware of and change unhelpful thinking patterns and understand our emotions. Reduce or eliminate avoidance/unhelpful safety behaviours. Learn assertiveness, problem solving skills and grounding techniques. This is done through cognitive therapy, behavior therapy, learning interpersonal skills, and relaxation techniques.
What is a skill we can use to check if our interpretation is accurate?
Check the Facts!
Consider alternative interpretations!
How does the skill of awareness help us overcome negative automatic thoughts?
When we become aware of the automatic process it becomes less efficient. Increasing awareness of our most common negative thought patterns can help us examine our thoughts for errors, mistaken assumptions, and biases. We start to notice shifts in our mood and asking ourselves What was going through my mind just then? It becomes hard to believe in the negative thinking and then the negative emotions begin to fade as well.
What are some strategies to help us cope with worry?
Worrying Time - Set aside time to worry and make a worry list
Facing the Worst - What’s the worst thing that could happen? Could I survive that?
Worry to the End - Think about what comes next. The stressful event isn’t the end of the story, life continues
Worry Inflation - Exaggerate fears to become ridiculous
What are Core Beliefs?
These are beliefs that we hold at the center of who we are that describe the basic nature of the world.
Core beliefs are developed from a person's unique personal experiences. However, these beliefs aren't always accurate.
Why does CBT use a triangle?
All sides of the triangle are connected to each other and if one side changes the others will follow.
If you change your thinking, you will act and feel differently. Change your way of doing things and your thoughts and feelings will change. Change your feelings, your actions and thoughts will change.
What we THINK is going on in a situation influences what?
Our feelings and actions/behaviours
How you feel and act depends on what you THINK is going on, not what is really happening. Our brains use thought to interpret the world around us. We make assumptions about our surroundings which plays a part in our survival. However, in some situations these assumptions can be problematic
What is the distancing technique?
Talk to yourself as you would a friend
What is the difference between worry and problem solving?
Worry - Leaves us unprepared and without a plan even if the unlikely event occurred. People think more about how things can go wrong than how to solve problems.
Problem Solving - Tries to flexibly and effectively deal with a problem. Identify the problem, Brainstorm ideas of how to deal with the problem, Choose possible solutions, Examine the pros and cons for each solution, Develop a plan and put it into place, Evaluate the outcome
What are some examples of negative thinking patterns?
All-or-nothing thinking, Catastrophizing, Disqualifying the positive, Overgeneralization, Mental filter, "Should" statements, Mind Reading, Labelling, Personalization