For this Rhythm what is the first action and medication treatment?
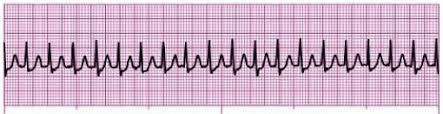
SVT
Vagal First
Medication: Adenosine
Why are Beta Blockers contraindicated in decompensated heart failure?

They have a negative inotrope which can worsen hemodynamics of ADHF. At this point the client can no longer tolerate a beta blocker.
After any type of neurosurgery and invasive procedure what is the most important assessments to obtain?

LOC
Can they follow commands!!!!
What is your evidence a client has had carbon monoxide poisoning?

Flu like symptoms
Severe Neuro concerns: vertigo, confusion
Such as loss of consciousness or even death.
How do we know that vasopressors such as dopamine and Levophed (norepinephrine) are actually effective?

Evaluating the MEAN ARTERIAL PRESSURE (MAP) is the gold standard always!
65-100
You are in a code and assigned to record. What actions would be your role?
Keep track of when meds are given.
Document team members names & tasks
Record accurate time of each intervention done.
Define Negligent Supervision
Patient Abandonment
Being expected to take a patient case that you have no training taking especially when floating in the hospital
Failure to provide safe and appropriate care.
What is the best pain assessment tool to use for a patient that is intubated on a mechanical vent?
CPOT

If your patient has a burn of over 70% of their body what route of pain medication would be the best?
1. SubQ
2. Topical
2. IV
Please IV!!!!
Think that their body is burned so SUB Q, topical and intradermal are not safe or useful routes at this point.
If a client is placed in CPAP or PSV mode what is the nurse's priority for both of these modes?
To ensure that the client can breathe independently and spontaneously from the ventilator!!!!!
A client has recently had a myocardial infarction MI what does the nurse understand is the cause for PVC premature ventricular contractions found on the monitor.
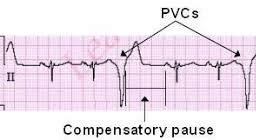
Ventricular irritability
Myocardial ischemia
Electrical instability from injured myocardium
Name Transplant Discharge instructions to a client.
1. Only bottled water or filtered water ice.
2. Only hot or cold foods
3. Strick medication regimen
4. Check-up appointments for life.
What is one type of care that causes DOUBLE EFFECT in ICU the most ?

Life Support
Mostly Ventilators
They are good for a time but can cause pneumothorax and barotrauma!
Why do patients need to understand what vessel is harvested during a CABG?
They need to know how to care for a midline incision from a LIMA or RIMA or leg incision from a great saphenous vein!
Which medication can increase the risk of Peptic ulcer disease PUD and then cause GI bleed.
Also which type of GI bleed is more common by 70-80%?
NAIDS
Upper GI bleeds
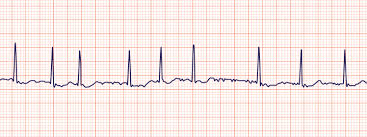
A client is in the ER and reports vertigo with heart skipping beats vitals stable. The nurse observes this rhythm. What should the nurse do?
Get an EKG (ECG) for further data analysis.
Define Pleural Effusion
Define Pulmonary Edema
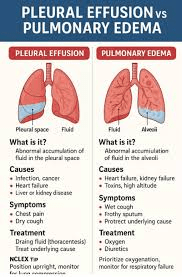
Water on the lung accumulating in the parietal space!
Water in the lung presenting as drowning and ventilation gets harder and harder.
What can cause ICP to increase past 0-15?
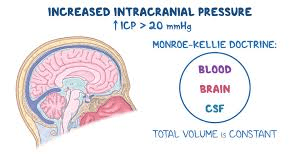
Elevated levels of CO2 (hypercapnia)
Anything that causes cerebral edema
Mnemonic: “B-B-C-C” causes of high ICP
Brain swelling
Blood (too much)
CSF (too much)
Compartment mass
Even jerky positions like neck or hip flexions!
If the patient is in Respiratory alkalosis and on a ventilator what must the nurse recommend changing on the settings?
Decrease the Rate
Think: If they are staying in acidosis then more than likely we need to increase the rate.
If alkalosis then more than likely decrease the rate.
A patient with severe vomiting from a gastroparesis and upper GI bleed comes into the ER. What does the nurse suspect with the ABG readings?

Metabolic alkalosis
A patient in SVT has not responded to vagal maneuvers or to adenosine. What would the nurse suspect next?
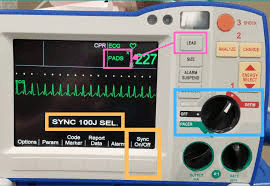
Synchronized cardioversion
How would we know that our patient that was in septic shock is now in MODS?
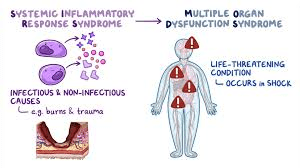
Multiple organ problems with labs would usually indicate!
Example Creatinine 5 Kidney
Ammonia level 70 Liver
Troponin 3 Heart
You walk in during a CODE BLUE As the ICU nurse called to the scene and high quality CPR is being done AED is hooked up, what do you need to be sure of that the patient has that is working?
A WIDE OPEN IV LARGE BORE
IV IV IV
During DKA which order is most important to implement first and why?
1. Insulin drip
2. IV fluids 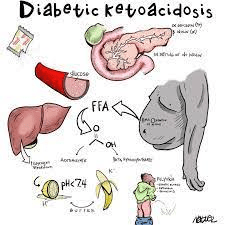
IV fluids Why SEVERE DEHYDRATION
Because of the osmotic diuresis and the patient clearing out fluid and electrolytes at a fast pace
NOW 0.9% NS
LATER 0.45% NS
Early DKA = intravascular problem → isotonic fluid
Later DKA = osmotic/free water deficit → hypotonic fluid
What type of Shock am I?
B/P 80/50 pulse 122, Lactic 5, Temp is 102 and patient is lethargic report was from the nursing home with a week long cough.

SEPTIC
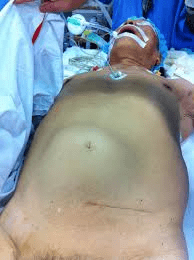
A client presents to ER with major HTN HX but complains of severe, tearing back pain. The nurses notes a bruit mass felt over abdomen. What conclusion does the nurse make?
Triple AAA
Abdominal aortic aneurysm dissection.
Identify the signs of Infective Endocarditis ?

Heart Murmur
Positive Blood Cultures
(So many things can cause this like IV drug use, rheumatic heart disease, immunosuppressive so our patients over time on immunosuppressive drugs.)
Name the intervention for a Biological agent?
Decontamination
Pt is experiencing a Non-Stemi with chest pain 8/10 with troponin 5. What should the nurse plan for?
Think: PAN
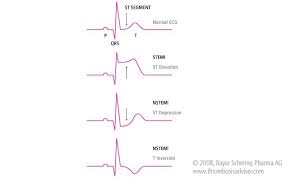
Do we give thrombolytics to non-stemi and the answer is heck no!!!
So, we proceed with:
P: percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
A: Aspirin
N: Nitro
What is the difference in aortic and mitral stenosis?

Aortic: Chest pain, dyspnea upon exertion, when lying flat relieved by sitting up.
Mitral: Unable to lay flat due to orthopnea, dyspnea and cannot even lay flat for short periods.