When the amount of outgoing infrared radiation leaving the Earth's atmosphere is greater than the amount of incoming solar radiation, the Earth's atmosphere does this:
What is cool down?
An example of “weather” would be the temperature during this coming weekend. On the other hand, an example of “climate” would be the temperature averaged over at least ______ years:
What is 30?
This layer of gases within the Earth’s atmosphere protects us from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, but does *not* play a significant role in global warming or the greenhouse effect.
What is the ozone layer?
Contrary to the common misconception, this type of ice does not meaningfully raise sea levels.
What is sea ice? (only land ice contributes to sea level rise)
Ice cores contain these, which allow scientists to determine the composition of the Earth's atmosphere (including the amount of greenhouse gases) thousands of years ago.
What are air bubbles?

Greenhouse gases absorb these wavelengths of radiation
What is infrared (longwave) radiation or heat?
(not incoming visible light from the Sun, not reflected visible light either)
DAILY DOUBLE!!!!!!!
Darker colored surfaces are warmer because they absorb more (and reflect less) of this type of radiation.
What is sunlight? (shortwave, sunlight, visible light all acceptable)
Permafrost contains large amounts of carbon stored in frozen soils. As permafrost thaws, it releases carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, accelerating the warming process. This is an example of a ________ feedback loop.
What is a positive (amplifying) feedback?
Over the past century, the average temperature of land areas has been increasing (faster or slower?) than the oceans.
What is "faster than"? (Oceans warm slower due to its high heat capacity: It takes more energy to change its temperature)
The amount of these dark features on our nearest star rises and falls over 11 year cycles, but do not show any long term increase.
What are sunspots? (Note: Sunspots can be used to estimate the amount of radiation emitted from the Sun)
As the oceans warm, the evaporation of the water speeds up. Evaporation releases more of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere, which amplifies the warming:
What is water vapor?
The rotation of the Earth causes this effect, which deflects moving objects to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
What is the Coriolis Effect?
Globally, temperatures have been increasing slower during this part of the 24 hour day (daytime or nighttime):
What is daytime? (Note: Nighttime temps are increasing faster than daytime temps)
Coral bleaching is caused by this:
What is ocean warming (*not* ocean acidification)?
These cycles control the timing of the ice ages by changing the distribution of sunlight across the Earth over thousands of years
What are the Milankovitch cycles? (influenced by: precession, obliquity (tilt), eccentricity of Earth’s orbit)
Human activities currently emit ____ times as much carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as volcanoes do

What is 100? (Anywhere from 40 to 1000 also acceptable)
These tiny solid particles, emitted from volcanoes, coal-fired power plants, wildfires, and other such phenomena reduce the amount of sunlight that the Earth’s surface receives:
What are aerosols?

Over the past few decades, satellites in space have detected an imbalance between the net solar radiation coming into the atmosphere and the amount of this wavelength of radiation leaving the Earth's atmosphere.
What is infrared? (because of increased amount of greenhouse gases, more infrared is being trapped and less is escaping out into space)
The shells of marine organisms such as clams and oysters are made of this chemical compound, which is less abundant due to ocean acidification

What is calcium carbonate?
DAILY DOUBLE!!!!!!!
By analyzing isotopes of this element within ice cores, scientists can estimate the Earth’s past temperatures.
What is oxygen?
(compare oxygen-16 and oxygen-18 in ice cores, corals, etc. to get estimate of temperature)
(hydrogen/deuterium also acceptable)
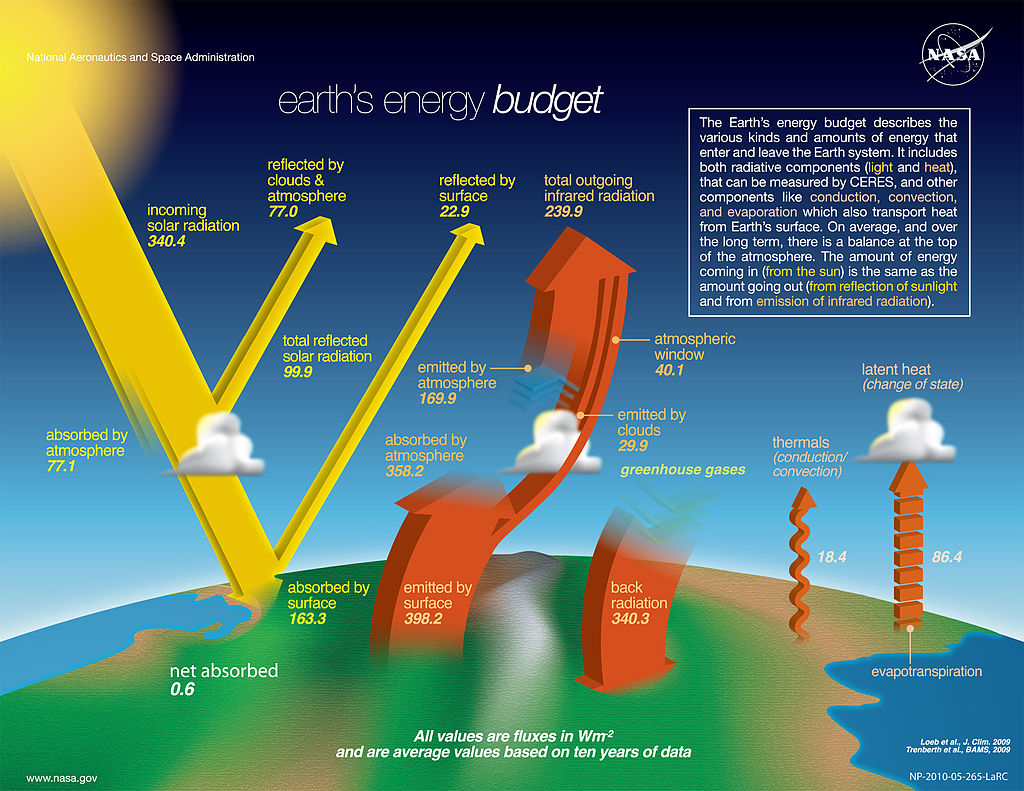
The largest proportion of radiation that the Earth’s surface absorbs is this type of radiation.
What is infrared (or longwave)? (Figure below from IPCC)
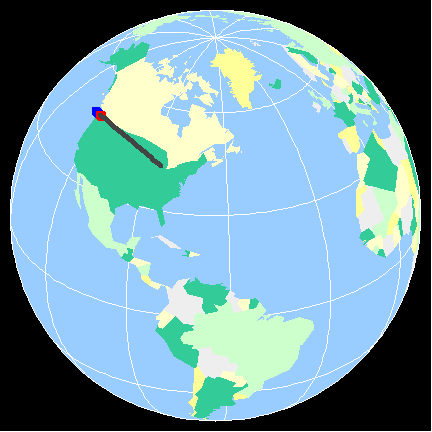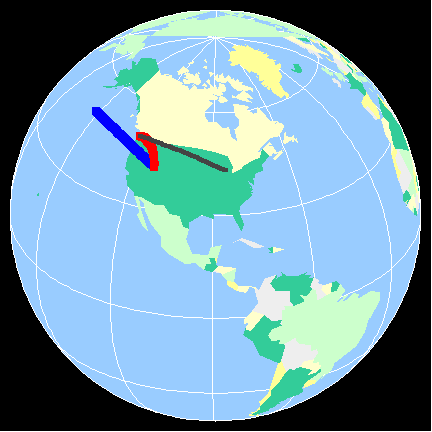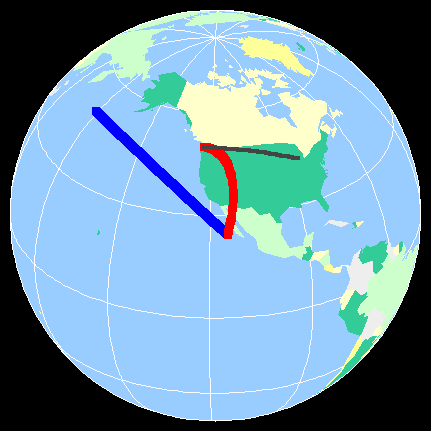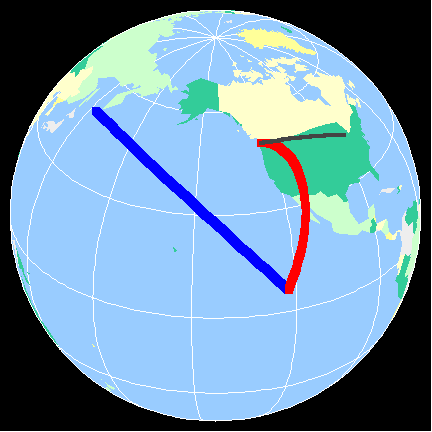
This side of a mountain range typically receives less precipitation due to the warming and drying that occurs as the air descends.
What is the leeward side (or rain shadow)?
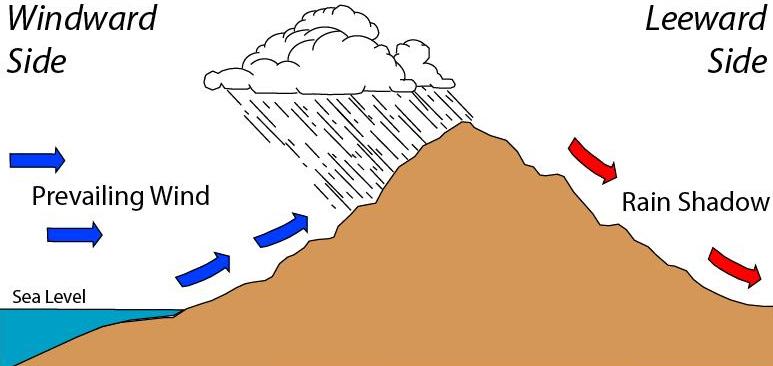
Image credit: Meg Stewart (https://www.flickr.com/photos/megstewart/8644087724/)
Temperatures are cooling in this layer of the atmosphere, indicating that it is the enhancement of the greenhouse effect (not the Sun) that is responsible for global warming.
What is the stratosphere? (mesosphere, thermosphere also acceptable)

These single-celled organisms are expelled from the coral tissue during the coral bleaching process, which results from warming ocean temperatures.
What are zooxanthellae (algae, phytoplankton, dinoflagellates also acceptable)?
This is the term for the wobbling of the Earth’s axial tilt (similar to the animation below), which is also one of the elements of the Milankovitch cycles
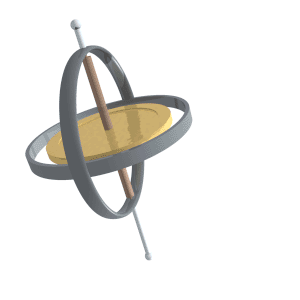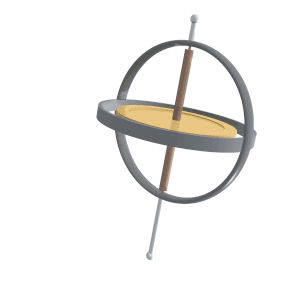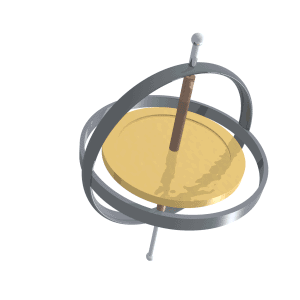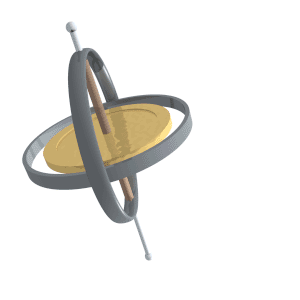
What is precession?