This cranial nerve allows us to move our muscles for facial expressions.
What is the facial nerve?
The psychological sensation of frequency.
What is pitch?
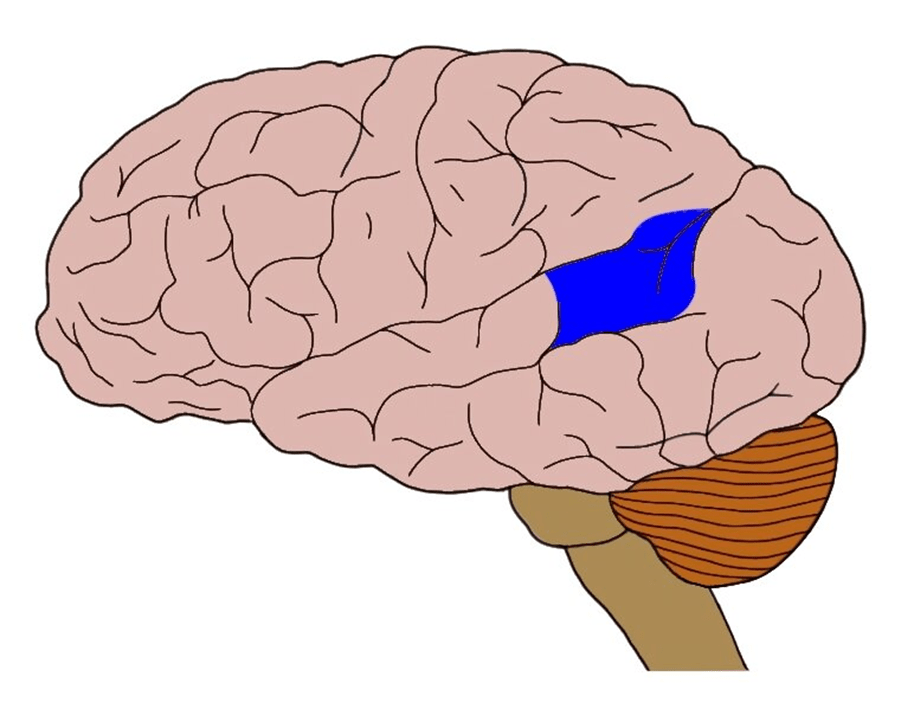
This area of the brain is important for the comprehension and processing of speech.
What is Wernicke's area?
A graphic representation of sound over time.
What is a waveform
This model oversimplifies how we plan for speech.
What is the Wernicke-Geschwind Model?
This cranial nerve is important for moving our larynx, pharynx, lungs, and abdominal muscles.
What is the vagus nerve.
A combination of multiple frequencies.
What is a complex tone?
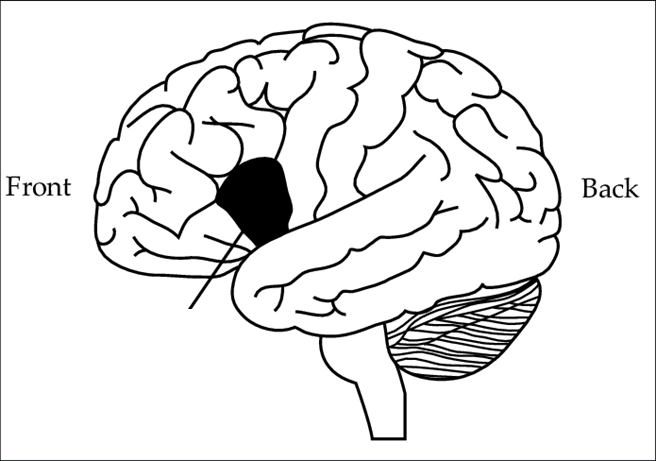
This area is associated with speech production and articulation.
What is Broca's area?
The shaping of the vocal tract to create speech sounds.
What is articulation?
This model states that processing happens simultaneously in many areas of the brain.
What is the parallel model?
This cranial nerve moves the muscles of the tongue.
What is the hypoglossal nerve?
A type of waveform repeats at regular intervals over time.
What is a periodic waveform?
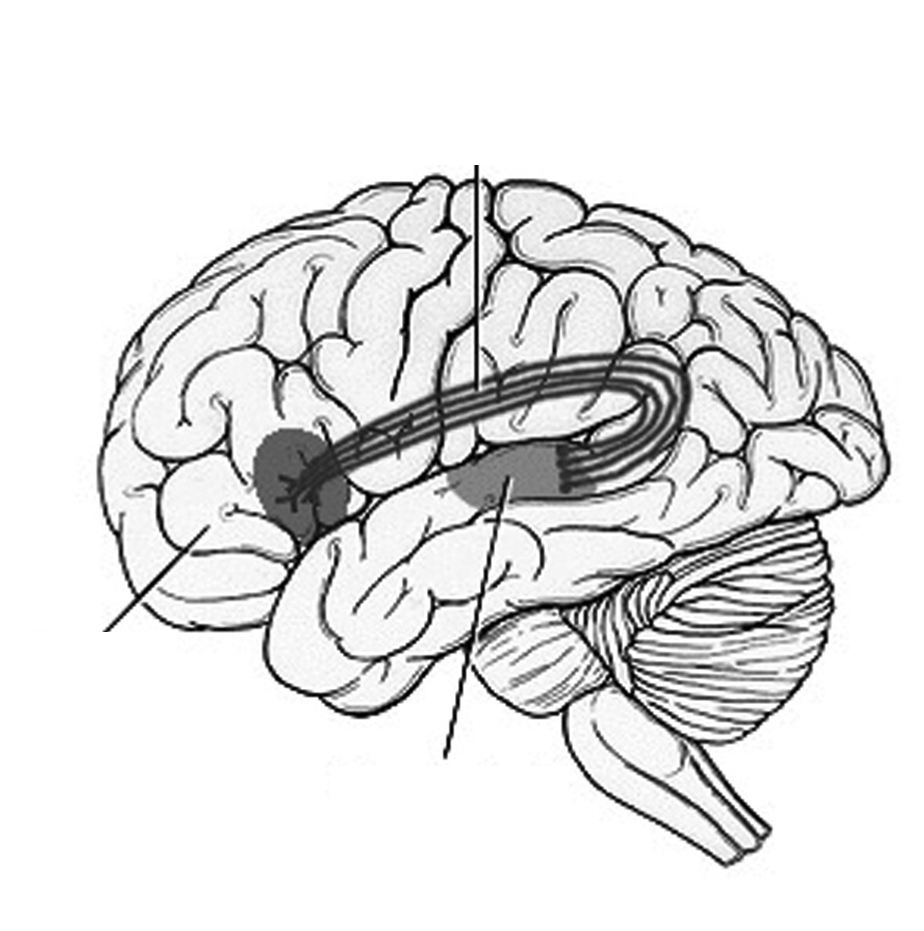
Band of nerves that connects Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area.
What is the arcuate fasciculus?
The quality of a sound that distinguishes one voice or musical instrument from another.
What is timbre?
This neuron provides information to the central nervous system.
What is afferent neurons?
These two cranial nerves we talked about are only motor.
What are the accessory and hypoglossal nerves?
This is the psychological sensation of amplitude.
What is loudness?
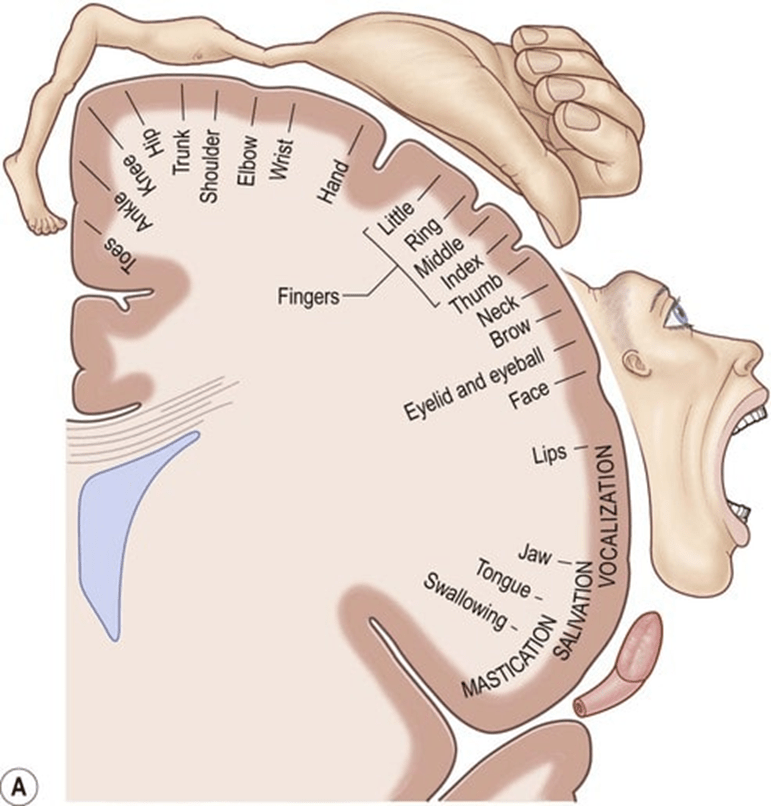
This area encodes the movements and provides the execution and voluntary control of motor planning for speech.
What is the primary motor cortex?
The vibrating response of an object to an applied force.
What is resonance?
The description of the rhythm and tonal patterns of speech.
What is prosody?
This cranial nerve that we discussed is only sensory.
What is the vestibulocochlear nerve?
The amount of time it takes to complete one cycle.
What is the period of a waveform?
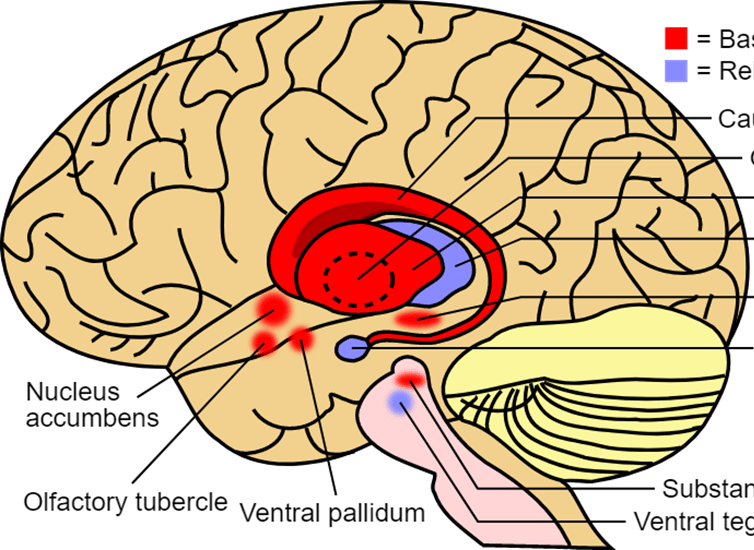
This part of the brain is important for smooth motor control.
What is the basal ganglia?
The lowest frequency of a vibrating object, which determines the pitch of the voice.
What is the fundamental frequency (F0)?
A method used to analyze the individual frequency components of a sound
What is Fourier analysis?