The heart rate doesn't have a typical response because it has undergone this.
What is denervation
You’re going to want to stay out of the pool with most brands to prevent one of these
What is an infection
It’s the lines shown here
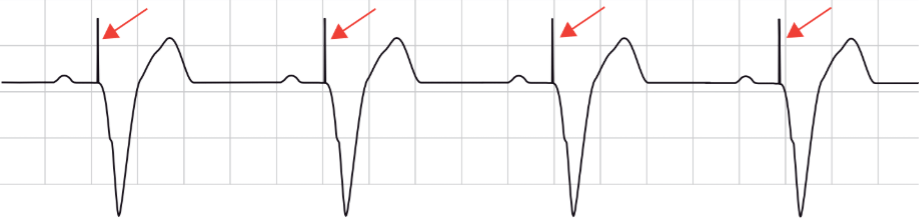
What are pacemaker spikes/ discharge
Surgical complications, low EF, instability, ≥ 2 mm ST-depression, CRF ≤ 3 METs, or major sxs at < 5 METs. THey would be this AACVPR Risk level
High-risk (AACVPR)
Chest pain with activity and recovers with rest. Score it on a 5-point scale
What is stable angina
Keep your patient at least 10 beats below this chest pain level
What is anginal or ischemic threshold
To prevent transplant rejection, folks take medications that put them in this immune state, or lack thereof
What is immunocompromised
This special cable shown here (image below) should be treated with utmost respect
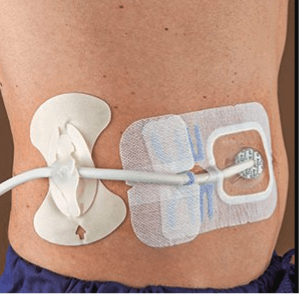
What is the driveline
You’ll basically leave these people alone with this emergently anchored pacing method
What is the transvenous pacing
This person looked good at the start, but then developed angina at high workloads. They would be this risk level (AACVPR).
What is moderate risk (AACVPR)
We expect to see this product rise over time with exercise. It means the heart is improving
What is ischemic threshold / rate pressure product
Based on consensus without an exercise test, taking resting HR +20 bpm for (blank) & +30 bpm for (blank)
What are MI and cardiac surgeries
You’ll want to prolong the (blank) and (blank) at the start and end of exercise based on their heart’s slow adaptability
What are the warm-up & cool-down?
The LVAD is (blank) dependent & (blank) sensitive
What are preload & afterload
4 weeks of these movement restrictions are usually surgeon dependent
What are pacemaker precautions
You may want to include more or less of this depending on their risk
What is continuous telemetry OR supervision
Pop 1, wait 5, pop 1, wait 5, pop 1, call 911 (and say a prayer)
What are nitroglycerine instructions
This tends to be overreported in deconditioned patients and underreported in aggressive personalities
What is RPE
This tends to be the range of bpm at rest for a transplanted heart
What is 100+ bpm
There certain skills becomes a set of new ADLs. They need to do it every day!
What is general LVAD management
Keep it 10 bpm below this… Otherwise, zap!
What is the ICD discharge rate
2+ major risk factors without signs or symptoms would be what ACSMG risk level
What is a moderate-risk patient
Prinzmetal, variant, and (blank)
It’ll improve insulin sensitivity, body composition, VO2max, and lower BP faster, among others
What is HIIT
This describes a heart rate’s failure to rise, usually staying blunted throughout and possibly higher at rest
What is chronotropic incompetence
The first Korotkoff sound heard in a LVAD with a doppler US during blood pressure
What is the MAP
This term is used when pacer spikes are present, but fails to cause a contraction like seen here (image 2 below)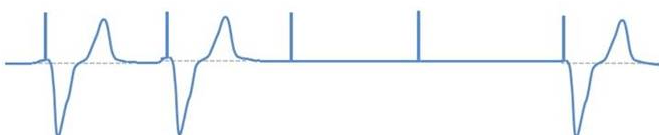
What is failure to capture
1st stage (2 METs), 5 PVCs. 3rd stage (5 METs), 26 PVCs with 2 couplets. No symptoms.The patient would be this risk factor (AACVPR)
What is mod or high risk depending on hemodynamic stability
Be careful with nitro use for the patient with ischemia in this area
What is Right Coronary Artery Disease
This intensity of exercise may increase collateral circulation over HIIT. Who knew?
What is moderate continuous training?