What does the term geocentric mean?
Earth-centered model
How does a planet’s distance from the Sun affect its speed of orbit?
The closer a planet is to the Sun, the faster it moves in its orbit.
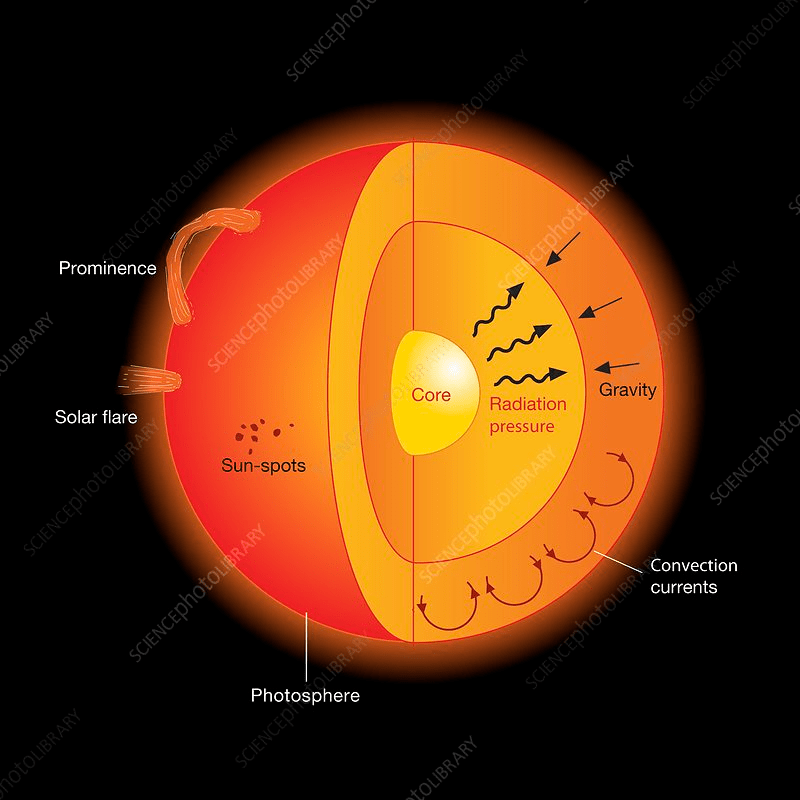 Which layer of the Sun gives off visible light?Hint: it is the lowest layer of the sun's atmosphere)
Which layer of the Sun gives off visible light?Hint: it is the lowest layer of the sun's atmosphere)
Photosphere
What force keeps all the planets in orbit around the Sun?
Gravity
Orbit
A curved path followed by a satellite as it revolves around an object.
What technology helped scientists move from the geocentric model to the heliocentric model?
The invention of the telescope gave scientists a more accurate view of space
Which category of planets is located nearest to the Sun? And what is the typical composition of these planets?
The inner planets. They are rocky planets/terrestrial planets
What is the Sun made of?
(If you are going to say specific elements, you must name both to earn the points.)
Hot gases or hydrogen and helium
How does a planet's distance from the Sun affect a planet’s gravitational pull from the Sun?
The farther a planet is from the Sun, the weaker the gravitational pull.
Gravity
The force that causes objects with mass to attract one another.
What evidence led early astronomers to believe in the geocentric model?
The Sun and stars appeared to move across the sky each day, making it seem like Earth was at the center
Why are outer planets much colder than inner planets?
They are farther from the Sun and receive less solar energy.
What process occurs in the Sun’s core to produce energy?
Nuclear fusion
How does a planet's distance from the sun affect a planet’s speed in orbit?
Planets closer to the Sun move faster because the Sun’s gravity pulls on them more strongly.
Prominence
A large, bright, gaseous feature extending outward from the Sun’s surface, often in a loop shape.
What observations made by Galileo provided evidence that not everything revolved around Earth?
He saw moons orbiting Jupiter, proving not all objects revolve around Earth
Compare the atmospheric conditions of the inner and outer planets.
Inner planets have thinner or minimal atmospheres; outer planets have thick, gaseous atmospheres made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
How does convection work in the Sun’s inner layers?
Hot gases rise, cool, and sink back down
With respect to mass, how does Earth’s gravitational pull compare to Jupiter’s?
Jupiter’s gravitational force is stronger because it has much more mass.
Inner Planets
The rocky, terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, whose orbits are inside the asteroid belt.
Why is the heliocentric model accepted today?
It explains planetary motion accurately—planets orbit the Sun in predictable paths supported by evidence from telescopes and space exploration
Describe two ways the movements of the inner planets differ from those of the outer planets.
Inner planets orbit faster and in smaller paths around the Sun, while outer planets move more slowly and follow larger orbits.
Name three solar activities that happen in the sun's atmosphere and describe what happens in each one.
Sunspots – Cooler, darker areas on the Sun’s surface caused by strong magnetic fields.
Solar flares – Sudden bursts of energy and light released from the Sun’s surface.
Prominences – Large, bright loops of gas that extend outward from the Sun’s surface.
Compare the Sun’s gravitational pull on the inner planets to its pull on the outer planets.
The Sun’s gravitational pull on the inner planets is stronger because they are closer to the Sun, while its pull on the outer planets is weaker because they are farther away.
Outer Planets
The planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, whose orbits lie beyond the asteroid belt.