What is Chargaff's rule?
The amount of A and T bases in DNA will be similar to each other, and the amount of G and C bases will be similar to each other
A=T
G=C
What three enzyme activities are required for primer removal?
Nuclease
Polymerase
Ligase
What are the four types of RNA discussed so far?
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and snRNA
What are the three phases of translation?
Initiation, elongation, termination
What is an operator?
DNA Sequence where the repressor binds
How does DNA pack to fit in the nucleus?
DNA wraps around Histones to form nucleosomes which continue to pack on themselves to form chromatin and eventually chromosomes
What problem does topoisomerase solve, and how does it do it?
Topoisomerase relieves the overwinding of DNA caused by helicase opening the ds DNA, cuts one strand of DNA ahead of replication fork allowing it to untwist
What transcription factor binds to the promoter first and where does it bind?
TFIID at the TATA box
Explain the three ways we describe the genetic code
triplet, redundant, degenerate
Difference between a constitutive and inducible gene?
constitutive genes are constantly expressed whereas the expression of inducible genes are controlled dependent on cellular conditions or needs
What experimental methods did Hershey and Chase use to help discover what molecule carriers heritable material?

Which three key players are needed more often on the lagging strand than the leading strand?
primase, single-stranded binding proteins, primer removal
What are the functions of the 5’ cap and Poly A tail?
cap: protection, RBS, and identification for export out of nucleus
Poly a tail: protection and identification for export
How does termination occur?
release factor binds to A site, tRNA and polypeptide chain are released and complex comes apart
What occurs in the lac operon when there is low levels of glucose and low levels of lactose? Is the operon on or off?
in low levels of glucose, cAMP levels will be high and form an active complex with CAP that will bind to the CAP site
In low lactose - lactose will not be readily available to bind and turn off the repressor such that the repressor will be active, and bind to the operator which turns the operator off
How would you repair a thymine dimer?

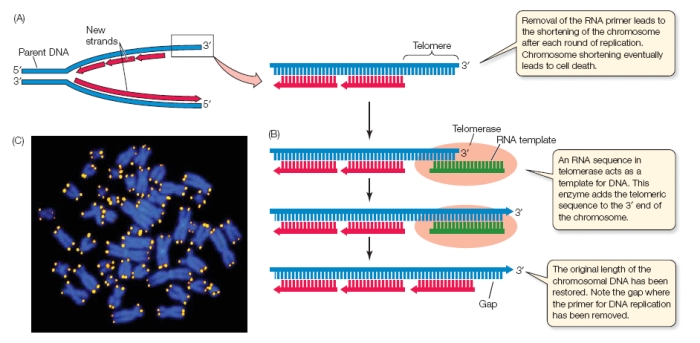
Why is telomerase needed in DNA replication?
allows for completion of DNA synthesis ong lagging strand, without it part of the gene would be degraded
Name two differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription
sigma factor versus transcription factors
Prokaryotic mRNA can be polyscitronic
Prokaryotic have -10 and -35 box vs eukaryotic TATA box
Eukaryotic occurs in nucleus vs prokaryotic in cytoplasm (same time as translation)
Describe the structure of tRNA
3 loops that form due to hair pinning of RNA, amino acid attached to 3’ end and anticodon arm/loop
Name two differences between lac operon and trp operon?
trp operon is an example of negative control as trp levels act to turn the operon off, whereas high lactose will turn the operon on
Trp operon is anabolic - pathway in synthesizing tryptophan
Lac operon is catabolic- breaks down lactose to use for metabolism
Lac operon is controlled by two different conditions (glucose and lactose levels) whereas trp is only controlled by one (trp levels)
How are histones modified and why is this modification important?
R,K,S residues on H3 tail can be modified through reversible covalent modification. By modifying histone structure and moving nucleosomes, you can change access to DNA regions and influence gene expression
What is the difference between mismatch repair and DNA damage repair such as base excision repair?
mismatch repair occurs in conjunction with DNA replication one the newly synthesized strand of DNA due to mistakes from DNA polymerase. DNA damage repair does not have to do with replication and occurs any time there is damage and can deal with either or both strands of DNA
What process explains why the human genome project found less genes than expected in human DNA? Why is this significant?
Alternative splicing -alternate ways of processing an mRNA which produces variability, can have different protein products from one gene that can be specialized for certain cell types or environments
What is the difference between pro and eukaryotic initiation?
prokaryotes-ribosomes bind specific RBS, polycistronic eukaryotes-ribosomes identify and bind to 5’ cap, mRNA codes for single gene
Why might the CAP binding sites be found in bacteria on different sugar operons other than lactose, such as arabinose?
CAP protein is controlled by glucose levels such that the same mechanism can be used to activate other sugar breakdown pathways to use alternate sugar sources in the absence of glucose which is the main sugar source for bacteria