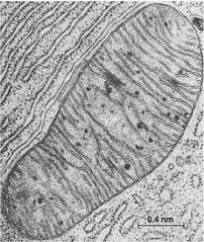
 Identify the function of this organelle.
Identify the function of this organelle.
What is the location of the reactions of aerobic respiration.
List three differences between passive and active transport.
What is:
Low to high (A) vs. high to low (A)
Uses energy (A) vs. No energy (P) (ATP)
Involves smaller molecules and substances (P) vs. Larger substances (A)
Could also list out the different types of transport and explain the examples.
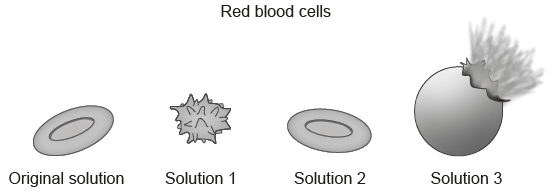
The images show samples of red blood cells that were placed in different concentrations of salt solutions.
Which solution has the highest salt concentration?
Why is the cell wall not considered to be an organelle?
A. It contains cellulose.
B. It is too big.
C. It is not surrounded by a membrane.
D. It contains DNA.
What is it is not surrounded by a membrane.
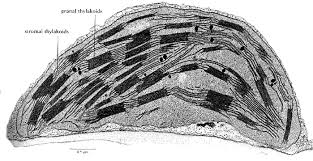 Identify the organelle and give a reason for your identification. (2 marks)
Identify the organelle and give a reason for your identification. (2 marks)
What is chloroplast.
Stacks of thylakoids
The diagram shows protein channels involved in the passive movement of a substance into the cell across the cell membrane.
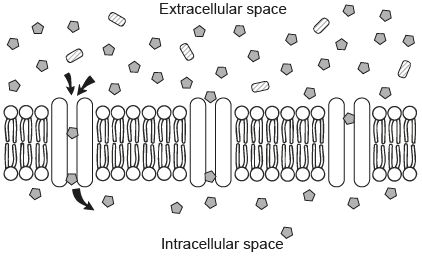
What is net movement occurs until the concentrations in and out of the cell are equal.
Predict what would happen if a eukaryotic animal cell was bathed in a hypotonic solution.
What is it will lyse (burst).
Which of the following are advantages of the presence of a nuclear membrane surrounding the nucleus of eukaryotic cells?
1. Separation of the DNA from the cytoplasm.
2. Separation of gene transcription from translation.
3. Concentration of enzymes for DNA replication and transcription.
4. Increased efficiency of nuclear division.
What is all of the above.
What is a difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
What is
Compartmentalization (organelles) is found only in eukaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells are smaller
Draw the cell membrane on a whiteboard and label at least 5 structures.
What is

• Channel/integral/pump protein
• Glycoprotein
• Phosphate/hydrophilic head
• Lipid/hydrophobic tail
• Extrinsic protein
• Phospholipid
• Phospholipid bilayer
Outline the movement of water between two cells with equal concentrations of solutes.
What is
Water will move between the cells.
The cells contain an equal concentration of solutes causing the water movement in each direction to be equal.
There will be no net gain or loss of water (mass) by the cells
List four organelles that would be found in a photosynthetic cell of a leaf.
What is
Nucleus.
Chloroplast.
Permanent vacuole.
Mitochondrion.
Ribosome.
Plasma/cell membrane
The image of a chloroplast on an electron micrograph is 21mm. The true size of the chloroplast is 4 µm What is the magnification of the image of the chloroplast?
What is 5250x
Outline why the process of osmosis across a cell membrane requires the membrane to maintain different solute concentrations on each side of the membrane.
What is
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules.
Water molecules move from a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution.
The membrane is needed to separate the two solutions with different solute concentrations.
If the membrane is impermeable to the solute this prevents it crossing the membrane.
A plant has not been watered for a few days. Explain the changes that occur in the water potential of one of its cells when it is bathed in distilled water.
Distilled water is hypotonic to cell sap. Water will enter the plant cells.
Water will enter the cell by osmosis.
Entry of water will cause the solute potential to rise/become slightly less negative.
Entry of water will cause the pressure potential to rise. Pressure potential is caused by (hydrostatic)/water pressure on the (inflexible) cell wall.
When the pressure potential equals the solute potential, the water potential will be zero.
Equilibrium is established/there will be no net gain or loss of water.
Water will enter and leave the cell at the same rate/equilibrium is established.
Explain the advantage to cellular function of organelles being surrounded by a membrane. Illustrate your answer with an example. List three.
What is
Compartmentalisation by organelles in a cell creates several separate parts each with its own solution. (Because of compartmentalisation) the cell can maintain conditions in an organelle different to the cytoplasm.
Organelles can contain high concentrations of enzymes.
Organelles can contain high concentrations of substrate molecules (or other metabolites.)
Organelles permit the separation of (incompatible) functions.
What is evidence for the endosymbiotic theory?
What is:
Eukaryote mitochondria contain DNA.
Mitochondria have 70S ribosomes.
Chloroplasts have their DNA.
Animals are adapted to different habitats and different ambient and internal temperatures. Explain how the composition of the cell membrane can be one form of adaptation to temperature.
Fatty acid layer of membrane can have unsaturated and saturated fatty acids (in the lipid bilayer).
Unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting points/converse.
Saturated fatty acids make the membrane more stable at high temperatures/converse.
Cholesterol increases membrane fluidity/decreases the effect of cold temperatures.
Fish living in cold waters have a high proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in their membranes/other relevant example.
Red blood cells from a small mammal were immersed in NaCl (sodium chloride) solutions of different concentrations for 2 hours. The graph shows the percentage of hemolysed (ruptured) red blood cells at each concentration.
What can be deduced from the graph?
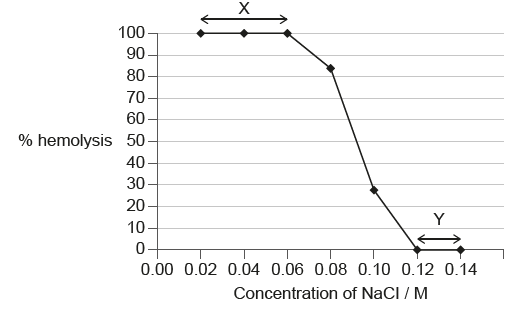
What is at X, water has moved by osmosis into the red blood cells.
Outline 3 ways in which a mitochondrion is adapted to its function.
What is
The folded inner membrane (Cristae) provides a large surface area to hold more enzymes for respiration.
They have a high concentrations of molecules/enzymes for the Krebs cycle in the matrix to speed up this process.
They have an intermembrane space / double membrane which makes a narrow space helping to form a high proton concentrations.
Mitochondria contain DNA and ribosomes which enable them to replicate themselves.
(Any three statements which must link structure to its function)