This phase is when chromatin condenses and the nuclear membrane disappears.
What is prophase?
The enzyme that unwinds DNA strands.
What is helicase?
This is the sequence of cell growth and division.
What is the cell cycle?
The division of the cytoplasm and cell membrane is called this.
What is cytokinesis?
This process results in the division of the nucleus.
What is mitosis?
These keep DNA strands separated after unzipping.
What are binding proteins?
Unicellular organisms use cell division to produce this.
What are two separate organisms?
In plants, cytokinesis builds this structure that becomes the new cell wall.
What is a cell plate?
In this phase, spindle fibers disappear and the nuclear membrane reforms.
What is telophase?
The enzyme that bonds nucleotides together.
What is DNA polymerase?
Multicellular organisms use cell division for growth, maintenance, and this.
What is replacement?
What is the end result of cytokinesis?
What are 2 daughter cells.
Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell during this phase.
What is metaphase?
Short DNA fragments on the lagging strand are called this.
What are Okazaki fragments?
During this stage, DNA is copied.
What is S (synthesis) phase?
These structures are the poles of the cell.
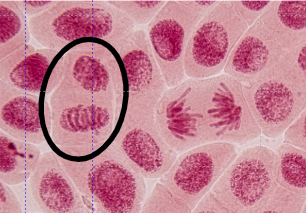
This cell is in the following stage of mitosis.
What is telophase?
DNA replication is described as this type of process because each strand is half new and half old.
What is semiconservative replication?
After G1, cells may enter this resting phase.
What is G0 phase?
Plant cells do not form these structures during mitosis.
What are centrioles?