How many phases make up mitosis and what are their names?
4 phases, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase/Cytokinesis
What are the 4 nucleotide bases and which are paired?
Adenine w/ Thymine
Guanine w/ Cytosine
What is the enzyme that unwinds the double helix of DNA and separates the DNA strands?
Helicase
What is the main purpose of meiosis?
To reduce diploids to haploids and create gametes.
True or False? The new DNA strand formed after DNA replication is an exact copy of its parent strand.
True
What occurs when a cell enters G0?
The cell leaves the cell cycle to perform a specific function for the rest of its life. It cannot reenter the cell cycle. Ex. heart cells, liver cells
Who were Watson and crick and what did they discover about the structure of DNA?
They were scientists who discovered the double helix shape of DNA with the help of Rosalind Franklin's x-ray diffraction image.
What do 5' and 3' prime mean and how are they different? Which direction does replication go?
They mean "five prime" and "three prime" and they indicate the carbon numbers in the sugar-phosphate backbone. The 5' carbon has a phosphate group attached to it and the 3' carbon a hydroxyl (-OH) group. Replication goes from 3' to 5'.
Why are tetrads formed in meiosis and not mitosis?
Tetrads are needed for crossing over so that there is variation in the chromosomes.
Why do cells divide when they get too large?
As a cell grows, the volume increases much faster than the surface area. Transportation of wastes and nutrients becomes difficult. Dividing increases the surface area and decreases the volume.
Explain the difference between telophase in plant cells and animal cells.
In plant cells, cell wall formation takes place in which a new cell wall is formed in the center of the cell and the cell is split apart.
In animal cells, a cleavage furrow is formed and the cell is pulled apart at the center.
What does it mean that DNA strands are antiparallel?
The nucleic acid sequences are complementary and parallel but go in opposite directions.
Which is the strand that grows continuously towards the replication fork?
Leading strand
What stage in meiosis is this?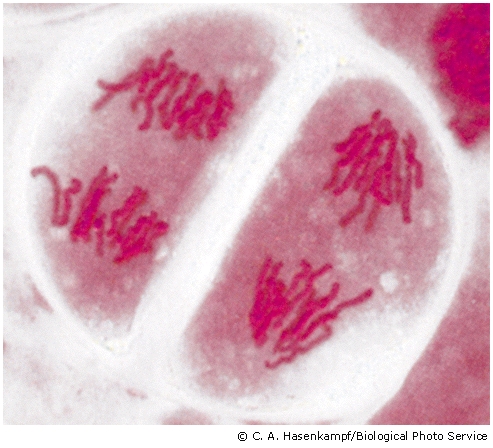
Anaphase II because the cell is split, indicating that telophase I has occurred, and the chromosomes are at the poles of each cell.
Spindle fibers and centrioles are made in which phases of the cell cycle?
G1
What are three checkpoint proteins and what do they do?
G1, G2, Spindle checkpoint (between metaphase and anaphase)
G1 - checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factors, DNA damage
G2 - DNA replication
Spindle checkpoint - checks for chromosome attachment to spindle at metaphase plate
How did the Hershey-Chase experiment prove that the DNA was the genetic material?
They took a virus that only has a protein shell and DNA inside and labeled each. The bacteriophages infected bacteria and the radioactively labeled DNA was inside the bacteria instead of the protein so they knew that it was the genetic material.
What is a step necessary to create the lagging strand, but not the leading strand?
DNA ligase must connect the Okazaki fragments.
Is there duplication of chromosomes between meiosis I and II?
No, there is no interphase II in meiosis
How does crossing over contribute to genetic variation?
Segments on nonsister chromatids switch places and the chromosomes have different combinations of genes in the gametes that are not found in either parent.
In which phases of mitosis does the cell have twice as much DNA than G1?
S, G2, Prophase, Anaphase, Metaphase, Telophase
This is because DNA is duplicated in the S phase of interphase and there is twice as much DNA in the cell until the cell divides during telophase.
Explain Frederich Griffith's experiment and what he discovered.
Transforming Principle
2 types of bacteria
R bacteria - rough coat does not give pneumonia
S bacteria - smooth coat gives pneumonia
The experiment shows that DNA can renature
He discovered evidence that bacteria are capable of transferring genetic information through a process known as transformation.
Why is antiparallel DNA important of replication?
An antiparallel arrangement allows base pairs to complement one another and form hydrogen bonds. Antiparallel DNA is structurally more stable than if DNA was parallel.
How does independent assortment affect genetic diversity?
When cells divide, chromosomes separate independently of each other which leads to a new combination of genes in the gametes.
What does it mean that DNA is semiconservative?
One half of the parent strand is used as a template for replication and is preserved in the daughter strand.