How many stages are there in PMAT?
Four
Interphase is which step of the cell cycle?
First
Meiosis results in the formation of how many gamete cells?
Four
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is cell division.
Anaphase.
What does PMAT stand for?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
How many stages are there in Interphase?
There are three stages to Interphase.
How many divisions of Meiosis are there?
Two: Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
What does Mitosis result in?
Two daughter cells.
Which phase is the division of the cytoplasms, and the last phase of mitosis?
Cytokinesis.
In which stage do chromosomes become visible, and nuclear envelope breaks down?
Prophase
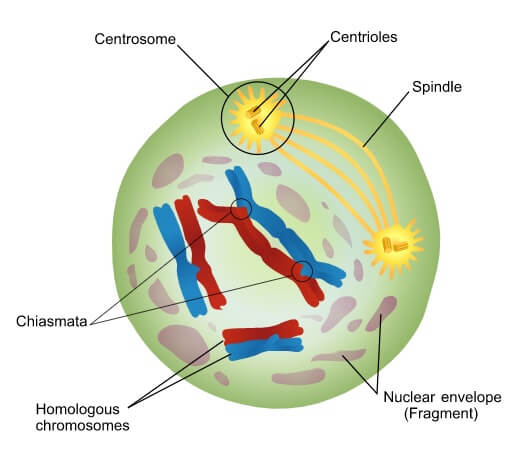
What is Interphase known as?
The rest and preparation stage.
What occurs in Meiosis 1?
Homologous pairs of chromosomes separate, and
two haploid cells are produced.
How do the two daughter cells produced compare?
The two daughter cells are identical.
What are genetic material attached to proteins, and look like spaghetti?
Chromatin.
In which stage do two cells start to form, ready to split?
Telophase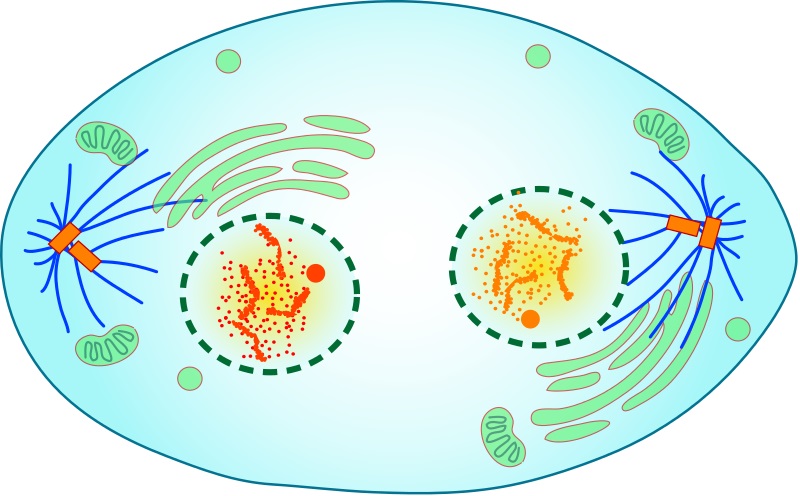
What are the three stages of Interphase?
G1, S, and G2.
What occurs in Meiosis 2?
Four gamete cells are formed, and chromosomes are separated to chromatids.
What releases fibers that help split the cell apart?
Centrioles.
What are chromosomes split in half?
Chromatid.
In which stage do cells line up in the middle of the cell, and spindles attach to centromere?
Metaphase

What occurs in the three stages of Interphase?
G1 is the phase of growth and development. S is the Synthesis of DNA, and G2 is the organelle replication/final preparation phase.
What are the cells in Meiosis?
The cells are haploid.
What are condensed chromatin?
Chromosomes.
What makes Meiosis different than Mitosis?
Mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, diploid daughter cells. Meiosis is the process by which gametes are produced. Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division and produces four non-identical haploid daughter cells.