The correct order of the four phases of mitosis
What is prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
The process by which cells become specialized
What is differentiation
The structure across which nutrients and waste move in and out of a cell
What is the cell membrane
The in-between period of growth between cell divisions
What is interphase
A disorder in which body cells lose the ability to control growth
What is cancer
The genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the duplicated chromosomes become visible
What is prophase
Unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop
What are stem cells
The aspect of a cell that increases faster as the cell grows (hint: think surface area or volume)
What is volume
The phase in which a cell does most of its growing, increasing in size and making new proteins and organelles
What is G1 (phase)
Stimulate the growth and division of cells
What are growth factors
The area at which sister chromatids are attached to each other
What is the centromere
An example of a multipotent stem cell
What are adult stem cells (bone marrow, muscle, nervous, hair follicles, etc.)
As a cell grows, it places increasing demands on its own _______.
What is DNA
DNA is replicated during this phase in preparation for division
What is S Phase
The process that increases genetic diversity within a population
What is sexual reproduction
The phase of mitosis pictured here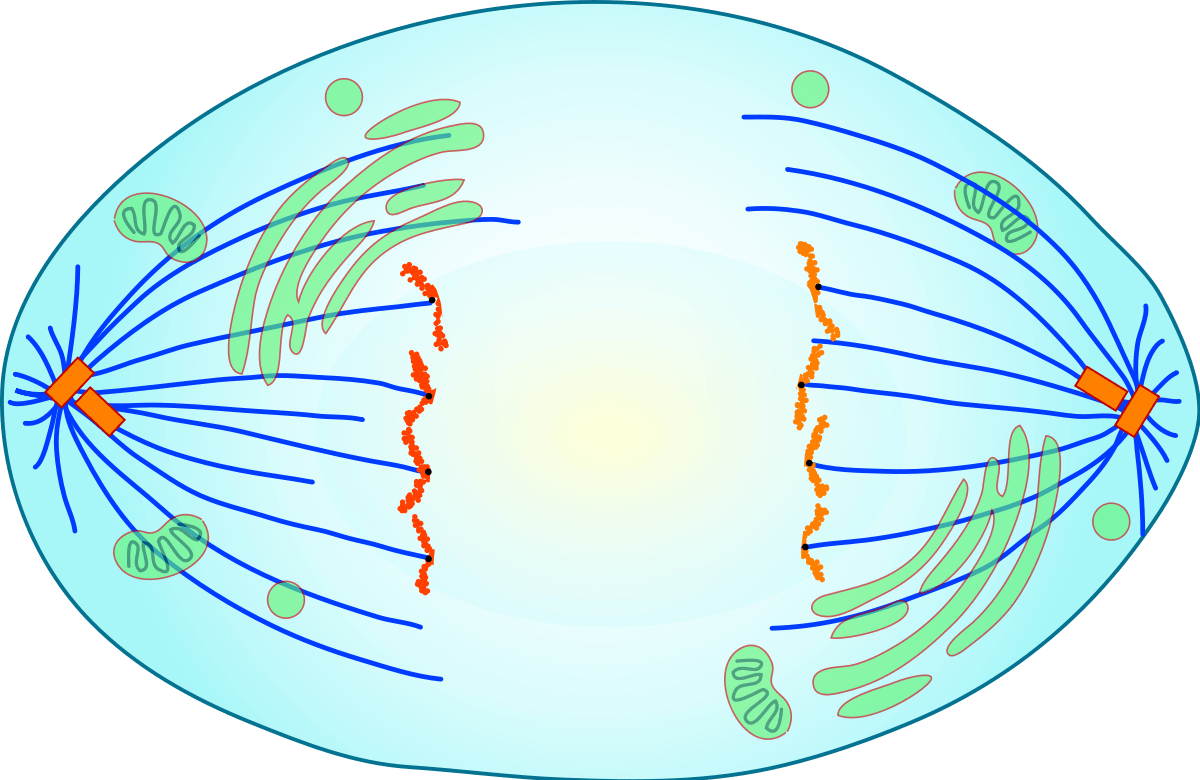
What is anaphase
Stem cells able to develop into any type of cell in the body (including the cells that make up the extra-embryonic membranes and placenta)
What are totipotent stem cells
The complex of DNA and protein (DNA tightly bound around histones)
What is chromatin
A description of what occurs during G2 phase of the cell cycle
What is the shortest phase of the cell cycle, during which many of the organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced
Programmed cell death
What is apoptosis
Two often simultaneous processes: Chromosomes return to a tangle of chromatin and one cell is divided into two.
What are telophase and cytokinesis
Adult stem cells reprogrammed to function as embryonic stem cells
What are induced pluripotent stem cells
The production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent
What is asexual reproduction
The process of cell division in prokaryotes, which is also a form of asexual reproduction
What is binary fission
A structure forming halfway between two nuclei during cytokinesis of plant cells
What is a cell plate