How a cell maintains a high surface area to volume ratio
What is dividing and remaining small?
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and prepares for division.
What is interphase?
These proteins, that regulate the cell cycle, were discovered in the 1980s.
What are cyclins?
Uncontrolled Cell Growth that occurs due to unregulated Cell Cycle.
What is Cancer?
The process through which unspecialized cells become specialized.
What is cell differentiation?
2 Purposes of Meiosis
What is ...1. produce Sex Cells / Gametes or
2. Reduce the total number of Chromosomes by 1/2 or
3. Increase genetic diversity
The sub-phase of interphase where a cell prepares for cell division
What is G2 Phase?
The type of reproduction, which includes budding, binary fission, or the release of spores, is where offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
What is asexual reproduction?
These enzymes that partners with cyclins to form MPFs (Mitotic Promoting Factors) and advance the cell cycle.
What is cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)?
The term for a mass of cells caused by uncontrolled cell growth.
What is a tumor?
The subphase of interphase where cells stop or delay the cell cycle and perform specialized roles after differentiation. Cells may also go into this subphrase when nutrients are low or when the cell will not divide again.
What is G0 phase?
Occurs in Prophase I and results in the recombination of Genes
What is Crossing Over
The organelle that helps provide energy (by making ATP) for producing proteins for cell growth and division.
What is the mitochondria?
The phase of mitosis where chromosomes align on the equatorial plate of a cell.
What is metaphase?
A process of programmed cell death important in development.
What is apoptosis?
The ability of cancer cells to spread to other body parts.
What is metastasis?
The type of stem cell capable of developing into most (but not all) body cell types.
What are pluripotent stem cells?
The Result of the coming together (Synapsis) of replicated, homologous chromosomes.
What is a Tetrad
The synthesis of these macromolecules greatly increase during the G1 phase to support cell growth and maintenance.
What are proteins?
The phase of mitosis when nuclear envelopes re-form around the segregated chromosomes.
What is telophase?
These type of proteins ensure that each growth stage in the cell cycle is completed correctly before moving forward during the cell cycle.
What is the internal regulators?
The type of treatment that targets cancer cell DNA with high-energy waves.
What is radiation therapy?
The type of stem cells primarily found in bone marrow and hair follicles and can differentiate into a limited number of different cell types.
What are multipotent stem cells?
What Meiotic Phase is illustrated below:
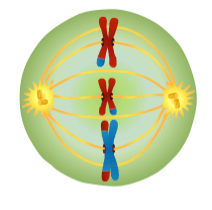
What is Metaphase 2
The 2 necessary functions that are efficiently maintained due to the cell keeping a high surface-area-to-volume ratio in cells.
What is nutrient uptake and waste removal?
The difference between cytokinesis in plant and animal cells.
What is the formation of a cell plate in plants and a cleavage furrow in animals?
These external regulating proteins help in wound healing and embryonic development.
What are growth factors?
Cancer results from a defect in _____, sometimes caused by oncoviruses, that control cell growth and division by coding for regulating proteins.
What are genes?
This research is controversial because arguments for and against involve ethical issues of life and death.
What is human embryonic stem cell research?
What Meiotic Phase is illustrated below:
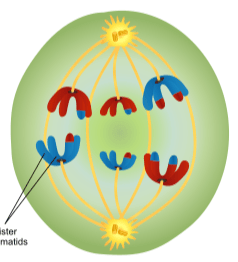
Anaphase 1