What type of cell transport is represented by a high to low concentration gradient?
Passive Transport
What is the name of this structure?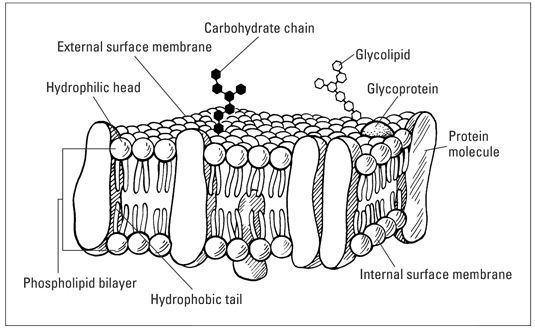
Cell membrane
The air freshener your teacher sprayed is an example of diffusion. This was an example of what type of transport?
What is passive transport?
The molecule that active transport uses to move large molecules against the concentration gradient
What is ATP?
The type of transport is shown in the picture
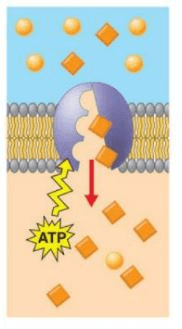
What is Active Transport?
Name the two structural components of the cell membrane.
What are Phospholipids and Protein Channel or Surface Proteins?
What is the function of the cell membrane?
to control what exits/enters the cells
The main function of the cell membrane
What is to control what substances enter and exit the cell?
What type of transport is osmosis?
Passive Transport
Water moves into a cell when the solution surrounding the cell is
What is Hypotonic?
The sodium-potassium pump is a form of active transport that moves sodium ions outside the cell and potassium ions inside the cell. Why is energy needed for active transport?
2. Ions are moving Low to High (against the concentration gradient)
What does the term semi-permeable mean?
Some materials are allowed in the cell, while others are blocked.
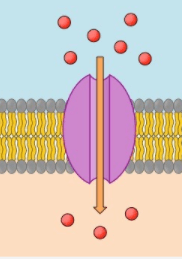
The type of transport is shown in the diagram
What is Facilitated Diffusion?
__________ is the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
What is Osmosis?
Water will move OUT of a cell when the surrounding solution is______________
What is HYPERTONIC?
What cellular transport did this cell model demonstrate?
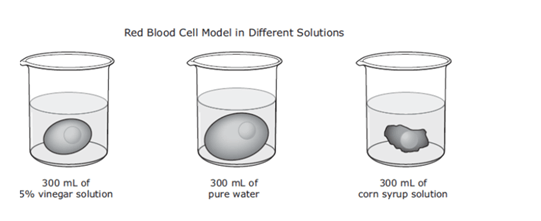
What is Osmosis (movement of water in/out of cell)?
The reason cells move substances in and out
What is maintain homeostasis, release waste, and/or transmit molecules to other parts of the body?
What is 2 differences between active and passive transport?
One uses energy on does not
The direction substances move during active transport
What is AGAINST the CONCENTRATION GRADIENT?
What type of cell or how will the water move?

hypotonic; water will move into the cell.
What is a CHANNEL PROTEIN?
Which picture represents endocytosis and exocytosis.
Explain.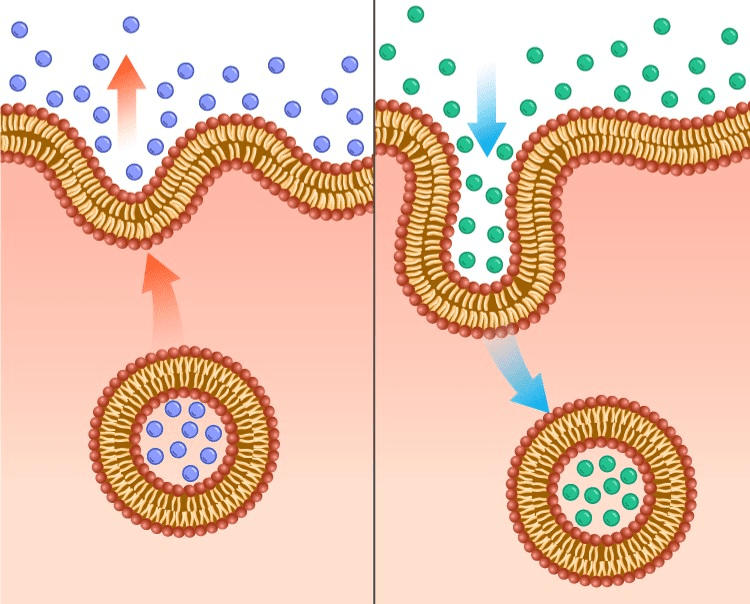
1st-exocytosis (goes OUT)
2nd-endocyctosis ( INTO)
If a freshwater fish was moved from a freshwater aquarium to a saltwater aquarium, what will occur?
The fish cells will shrink, saltwater will pull the water out of the cells.
During transport water will move in what direction?
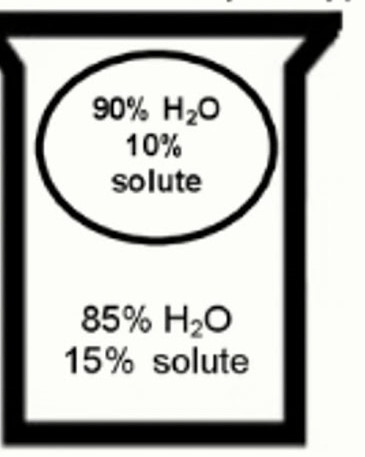
out of the cell; hypertonic
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level. Name the term?
Homeostasis