Two layers of phospholipids with tails pointing inward is known as the...
phospholipid bilayer
Osmosis is a form of...
Passive transport
Which kind of cells (somatic or germ cells) undergo meiosis?
germ cells
When do chromatids line up at the equator of the cell?

True or false? Symporters are proteins that transports molecules in the opposite direction
False! Antiporters do this. Symporters transport molecules in the same direction
The two kinds of lipid that make up the bilayer are the...
hydrophobic (phosphorus) and hydrophilic (non polar fatty acid tails) lipids
The sodium-potassium pump is utilized in what kind of cell transport
True or False: Meiosis occurs in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms?
False, meiosis occurs only in eukaryotic organisms
What steps make up the mitosis (M) phase?

Microtubules are part of the ___
...cytoskeleton
Name the principal components of the phospholipid bilayer
cholesterol, phospholipid, and protein
What difference is there between active and passive transport?
Active transport: ATP provides energy for transport; transportation of molecules against electrochemical gradient
Passive transport: no ATP needed for transport across gradient; movement of molecules from a high to low concentration
Do sister chromatids separate and assort during meiosis I or meiosis II?
Sister chromatids separate and assort into 4 cells during meiosis II
During interphase there are ___ phases of growth?
G1, G2, and S phase (DNA replication)
Prokaryotic cell division is known as?
binary fission
Membranes can actively determine what materials are allowed into the cell. This is called?
Selective permeability
What difference is there between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions?
Hypertonic: net flow of water out of the cell
Hypotonic: net flow of water into the cell
What (three things) does meiosis have in common with mitosis?
Both mitosis and meiosis:
1) produce new cell
2) have similar basic steps
3) start with a single parent cell
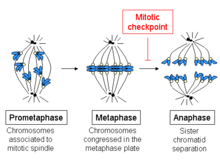
In mitosis, a spindle checkpoint ensures that sister chromatids will split evenly between the two daughter cells. Lack of proper alignment or attachment will halt cell division. When do we reach this checkpoint?
Before anaphase (after metaphase)
Name the three types of cell junctions
tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions
Plasma membrane thickness ranges from ___ to ___ nm in thickness?
5 to 10
Give two differences between diffusion and osmosis?
Osmosis: it is limited only to the liquid medium; it requires a semipermeable membrane; depends on the number of solute particles dissolved in the solvent; requires water for the movement of particles; only the solvent molecules can diffuse
Diffusion: occurs in all mediums; does not require semipermeable membrane; depends on the presence of other particles; does not require water for movement of particles; both solvent and solute can diffuse
Define crossing over? Does it happen at specific points of the chromosome?
The physical exchange of chromosomal parts between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. Crossing over occurs at random points on the chromosome, meaning that sister chromatics are no longer equal.
True or false: Mitosis produces 4 diploid daughter cells?
False: 2 diploid daughter cells are produced
What's the difference between pinocytosis and phagocytosis?
In phagocytosis, cells engulf a large, solid material. In pinocytosis, cells ingest the surrounding fluid.