Membrane Basics
Fluid Mosaic Model
Membrane Formation
Membrane Proteins
Membrane Carbohydrates
100
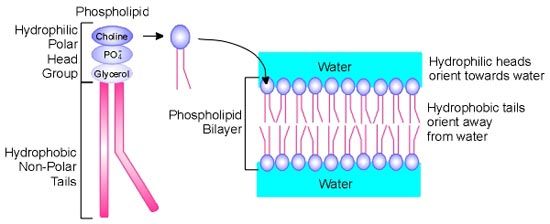
This is where the "fluid" part of the fluid mosaic model comes from.
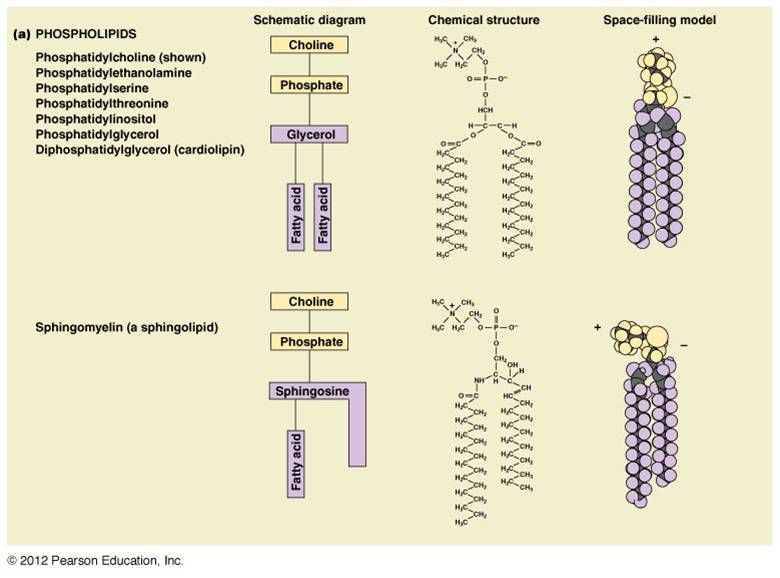
Phospholipids - membrane is fluid because the phospholipids are noncovalently (weakly) bonded to one another.
100
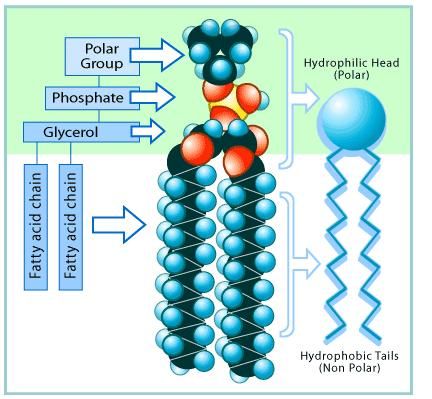
How is a single phospholipid made?
Made from components in the cytoplasm - some components come from diet, some components transported by mitochondria, some components come from Golgi.
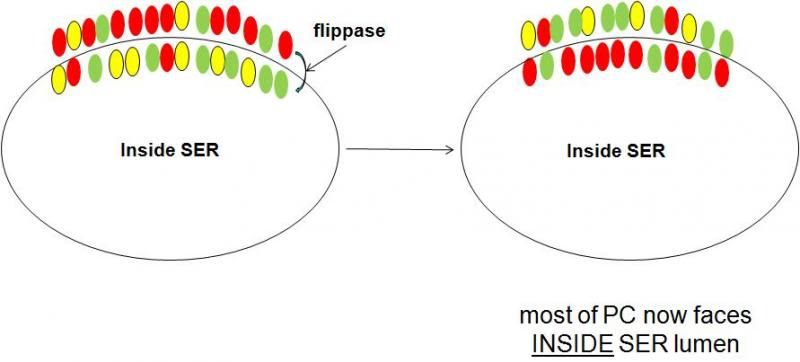
Phospholipids made on the smooth ER
Phospholipids made on the smooth ER
100
Do the carbohydrates of the plasma membrane face outward toward the extracellular space, or inward toward the cytoplasmic space?
Outward to the extracellular space.
200
These are the four main functions of the cell membrane.
1. barrier
2.movement of substances across the membrane
3. communication
4. micro-environment (hydrophobic)
2.movement of substances across the membrane
3. communication
4. micro-environment (hydrophobic)
200
How do we make the actual membrane?
Phospholipids are inserted one by one into the smooth ER membrane. Eventually, a vesicle from the ER will travel to the plasma membrane.
200
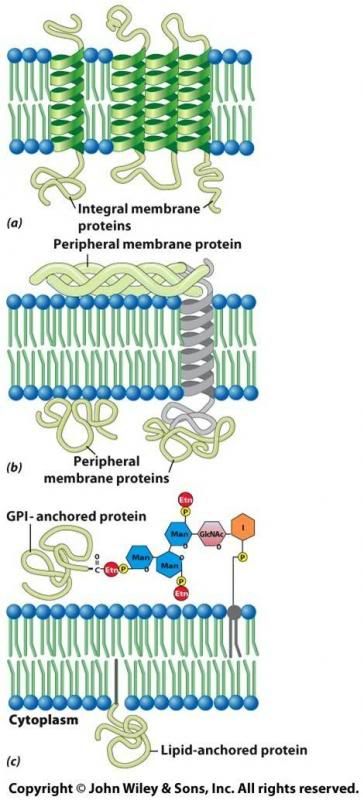
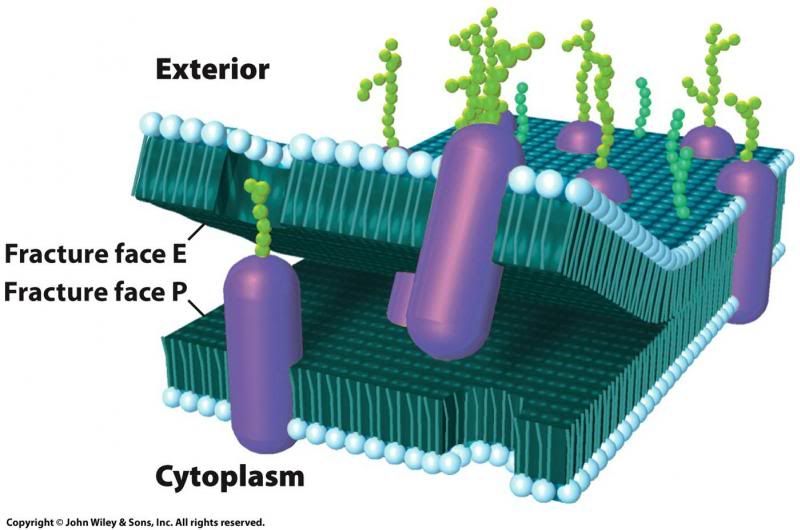
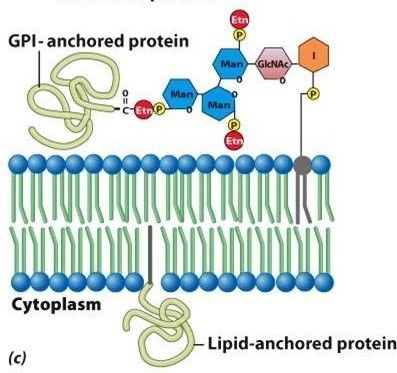
What are integral proteins?
Penetrate the lipid bilayer
"Membrane-spanning domain" - are transmembrane proteins, meaning they pass entirely through the lipid bilayer and have parts that protrude from both the extracellular and cytoplasmic sides of the membrane.
alpha helix = single mem.-spanning domain
beta-helix = multiple mem.-spanning domain
Interact with polar groups and tails (these are amphiopathic).
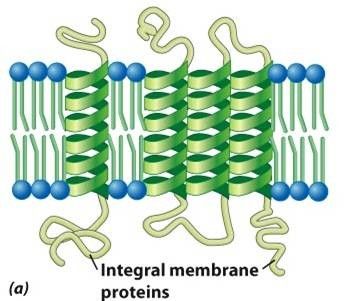
"Membrane-spanning domain" - are transmembrane proteins, meaning they pass entirely through the lipid bilayer and have parts that protrude from both the extracellular and cytoplasmic sides of the membrane.
alpha helix = single mem.-spanning domain
beta-helix = multiple mem.-spanning domain
Interact with polar groups and tails (these are amphiopathic).

300
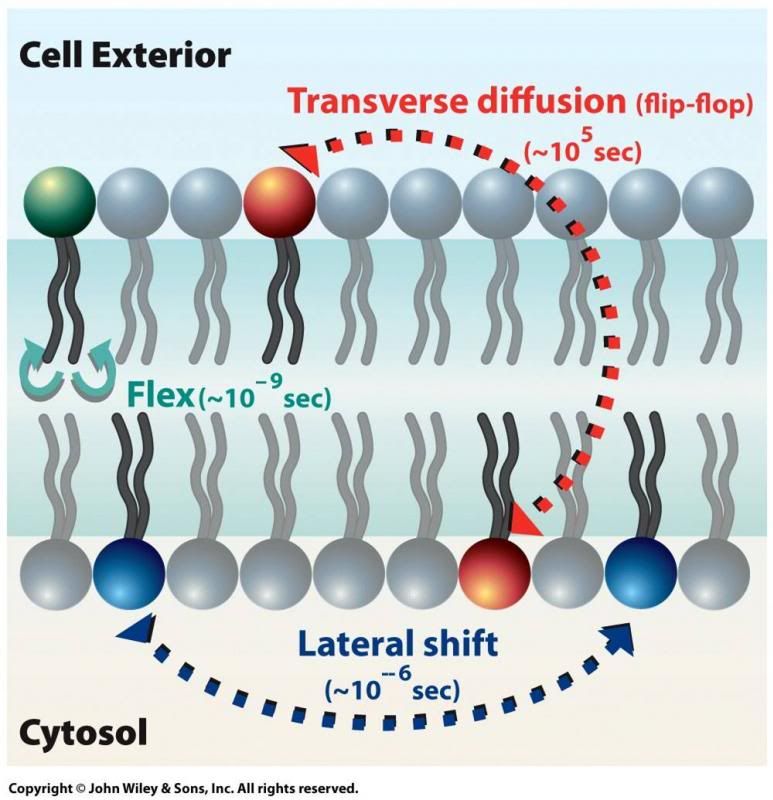
Describe transverse diffusion versus lateral shift, and state which is more likely.
300
What are peripheral proteins?
Located entirely outside of the lipid bilayer, on either the cytoplasmic or extracellular side.
Standard proteins in terms of structure.
Globular, hydrophobic surfaces.
Associate with either phospholipids or with transmembrane proteins.
Associated with the surface of the membrane by noncovalent bonds.
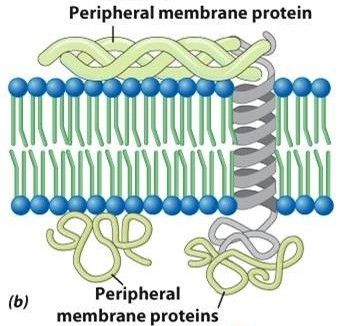
Standard proteins in terms of structure.
Globular, hydrophobic surfaces.
Associate with either phospholipids or with transmembrane proteins.
Associated with the surface of the membrane by noncovalent bonds.

300
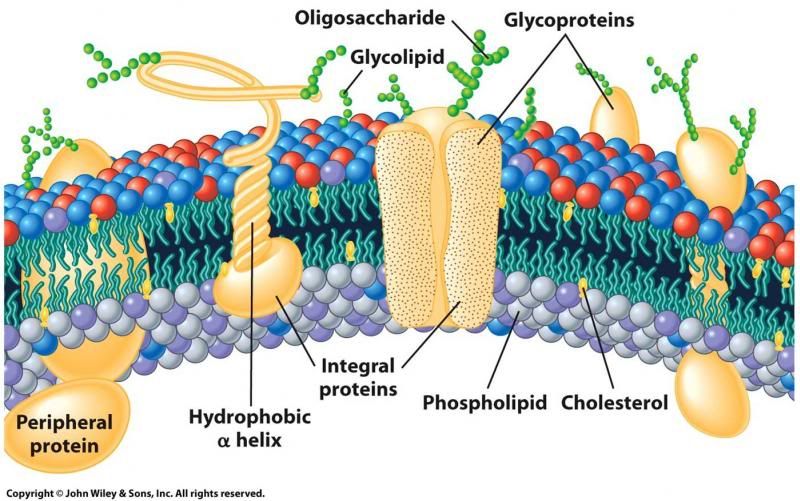
The addition of carbohydrates to membrane proteins is called _________.
Glycosylation.
400
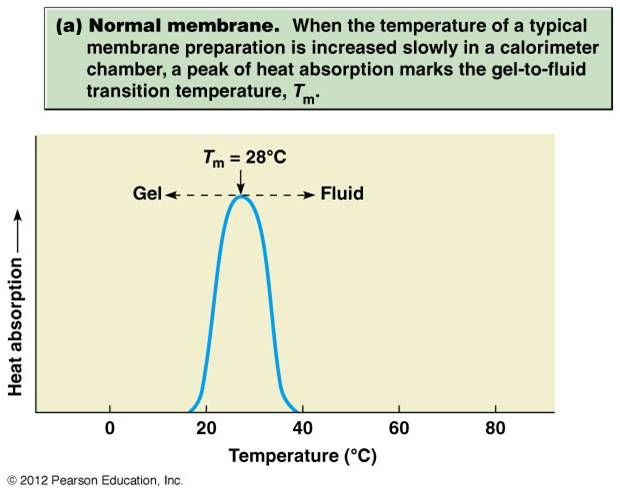
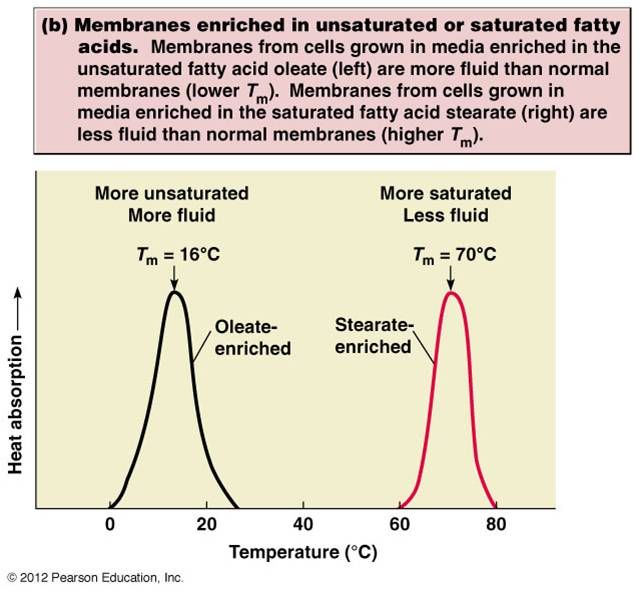
1. This is the temperature above which a particular liquid is fluid and below which it is solid.
2. Is oleate or stearate more unsaturated?
2. Is oleate or stearate more unsaturated?
400
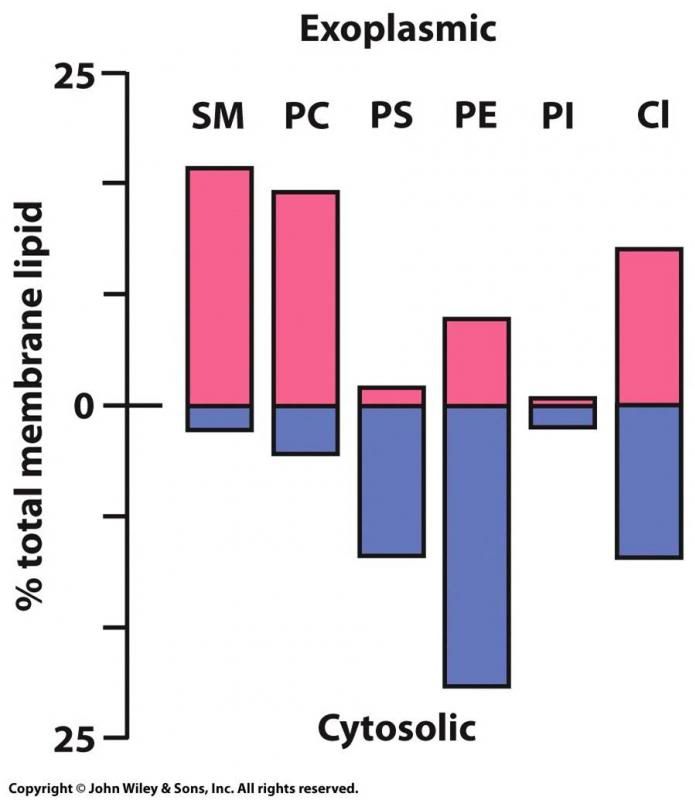
Why is the phospholipid bilayer assymetric?
Flippase is an enzyme, and enzymes are specific. So filppase will only flip a certain type of phopholipid.
400
What are oligosaccharides?
The carbohydrate of glycoproteins - they are short, branched, and hydrophilic, typically having fewer than about 15 sugars per chain.
Oligosaccharides may be attached to several different amino acids by two major types of linkages: N-glycosidic link between asparagine and N-acetylglucosamine, or the less common O-glycosidic linkage between serine or threonine and N-acetylgalactosamine.
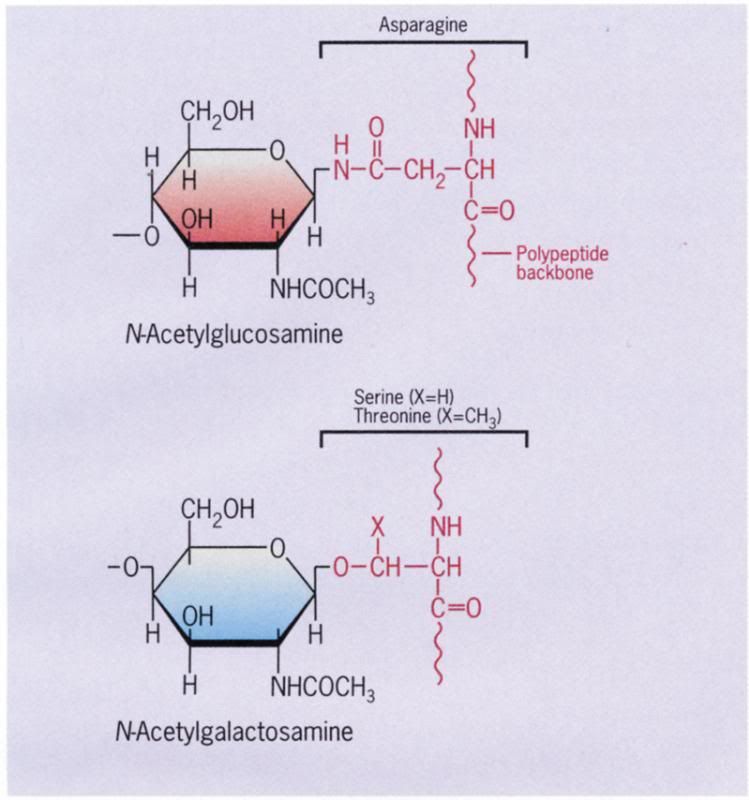
Oligosaccharides may be attached to several different amino acids by two major types of linkages: N-glycosidic link between asparagine and N-acetylglucosamine, or the less common O-glycosidic linkage between serine or threonine and N-acetylgalactosamine.

500
These three things influence the fluidity of the phospholipid membrane.
1. Number of double bonds - the more unstaurated, the more fluid. (Ex. Oleate is more unsaturated than stereate, since it has a lower trans. temp. and more double bonds).
2. Length of the fatty acid tail - the longer the tail, the better they stach together bc there are more interactions to hold them together. So the longer the tail, the less fluid.
3. Cholesterol - stabilizes fluidity. If the temperature is high, less fluid. If the temperature is low, more fluid.
2. Length of the fatty acid tail - the longer the tail, the better they stach together bc there are more interactions to hold them together. So the longer the tail, the less fluid.
3. Cholesterol - stabilizes fluidity. If the temperature is high, less fluid. If the temperature is low, more fluid.
500
What are the four main functions of membrane proteins?
1. Transport
2. Receptors
3. Structural (Anchor) - hold the shape of the cell.
4. Enzymes - live in the membrane, reaction carried out in membrane and not inside the cell.
2. Receptors
3. Structural (Anchor) - hold the shape of the cell.
4. Enzymes - live in the membrane, reaction carried out in membrane and not inside the cell.
500
What are the three main functions of the carbohydrate layer of the cell membrane (glycocalyx) ?
1. Protective coating - slimy, smooth texture on outside of cells.
2. Attracts H2O
3. Cell-cell communication
2. Attracts H2O
3. Cell-cell communication