What are the monomers of DNA? Describe the 3 parts of its structure.
Nucleotides
Structure:
1. Phosphate group
2. Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G)
3. Deoxyribose sugar
What does it mean that DNA replication is semi-conservative and bidirectional?
Semi-conservative: DNA replication involves using one old strand as a template and produces one new strand, resulting a product that conserved half / semi of the parent strand (half old half new)
Bidirectional: it occurs in both directions
T/F: Gametes (egg and sperm cells) go through mitosis.
False - only somatic cells go through mitosis
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose sugar?
Ribose has an additional oxygen on the 2' C, while deoxyribose is missing an oxygen on the same position (so only H instead of OH) 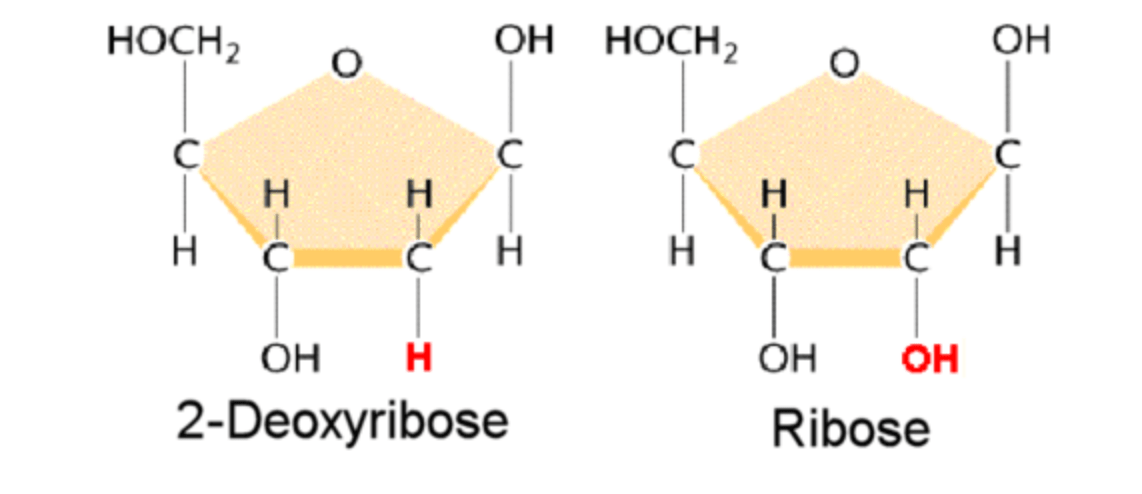
What is the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin? Which one is used for transcription?
Heterochromatin: highly compacted chromatin
Euchromatin: loosely coiled / compacted chromatin - used for transcription since the proteins have easier access to the DNA
What are the functions of DNA polymerase I and III?
DNA pol. III: adds nucleotides onto the 3' OH end of the strand
DNA pol. I: removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA nucleotides
What's the difference between mitosis in animal cells vs. plant cells?
Animal cells form a contractile ring that pinches the cytoplasm and cell into two.
Plant cells form a cell plate in the middle of the cell, which eventually fuses with the cell wall. This occurs since the cell wall is too rigid so it can't break.
What does it mean that DNA is "anti-parallel"?
The strands run in opposite directions; one from 5' -> 3' direction, the other from 3' -> 5' end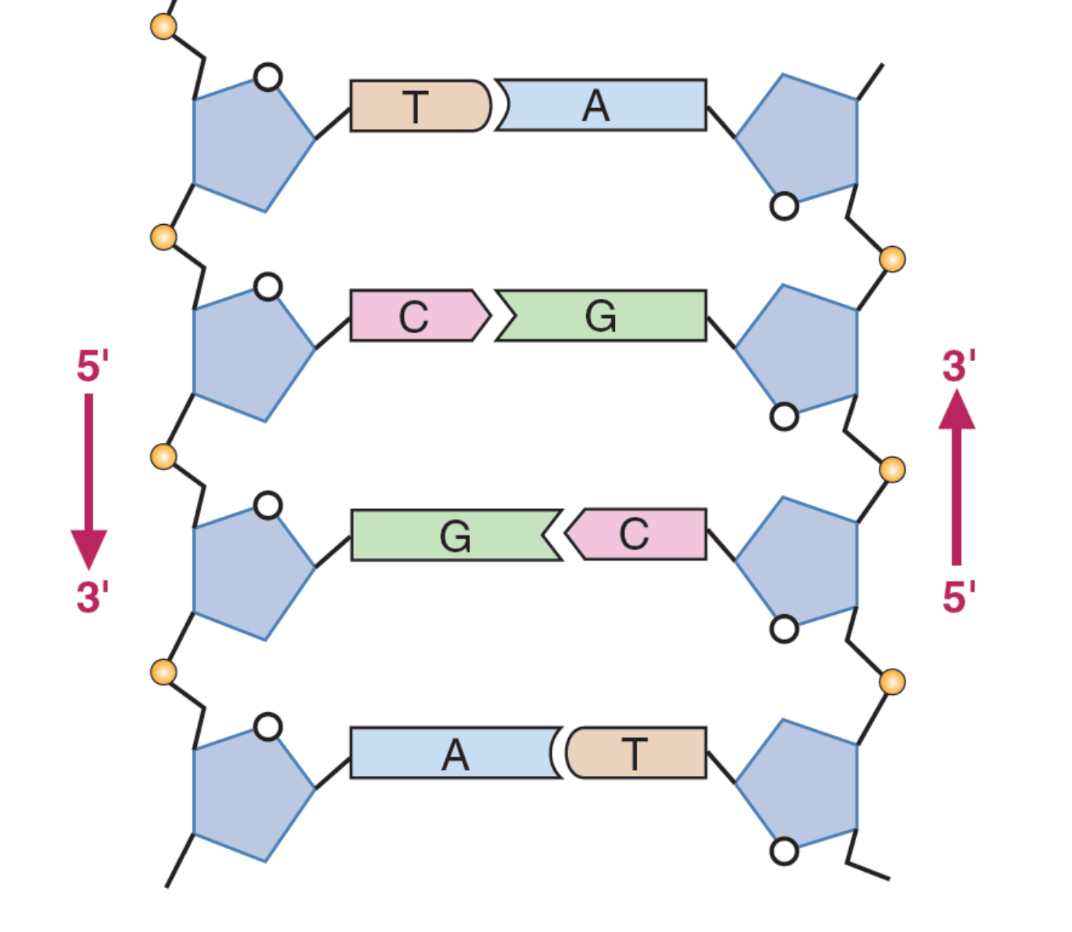
How does the amount of A-T and G-C pairs affect DNA melting temperature?
High amounts of G-C pairs results in a high DNA melting temperature given the 3 H bonds in between G and C bases, thus requiring more heat to break these bonds
(therefore, high amounts of A-T bonds means a lower DNA melting temp. since there's only 2 H bonds)
List 4 of the 6 proteins/enzymes involved in DNA replication.
1. DNA helicase
2. DNA gyrase / topoisomerase
3. Single Stranded Binding proteins (SSB)
4. Primase
5. DNA pol. I and III
6. DNA ligase
What are the three kinds of microtubules within the mitotic spindle and what do they each do?
Kinetochore microtubules: attach to the centromere and separate sister chromatids
Astral microtubules: short star-like microtubules that keep the centrosomes at the pole
Polar microtubules: extend from each pole and overlap with each other to lengthen the cell
What are histones? List all 5 of the histone proteins.
Histones: specialized proteins that DNA wrap around in order to compact/tighten itself
H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4
Describe at least 2 of the 3 bonds / interactions present within DNA (including those holding nucleotides together and the space in between).
- Phosphodiester bonds keep the deoxyribose sugar and phosphate group together within a nucleotide
- Nucleotides are held together via hydrogen bonds
- Van der Waals and hydrophobic interactions occur between stacked bases (known as base stacking - this keeps the DNA helix stable and protects it from degradation)
What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand? Why does the lagging strand take place at all?
Leading: continuous DNA synthesis with no gaps
Lagging: discontinuous DNA synthesis filled with Okazaki fragments and RNA primers
The lagging strand is usually going in the 3' to 5' direction, but DNA pol. III can only add nucleotides on the 3' OH end, which results in those Okazaki fragments.
(Double Jeopardy)
List the steps of mitosis and describes what happens in each step briefly.
Prophase: DNA condenses
Prometaphase: Nuclear envelope fragments, spindle attaches to chromosomes
Metaphase: Chromosomes align on metaphase plate
Anaphase: A) Chromatids separate and move to the poles B) Centrosomes move to the poles of the cell and cell elongates
Telophase: (Reverse prophase) Chromosomes decondense, nuclear envelope reforms
What are the 3 checkpoints in the mitotic cell cycle?
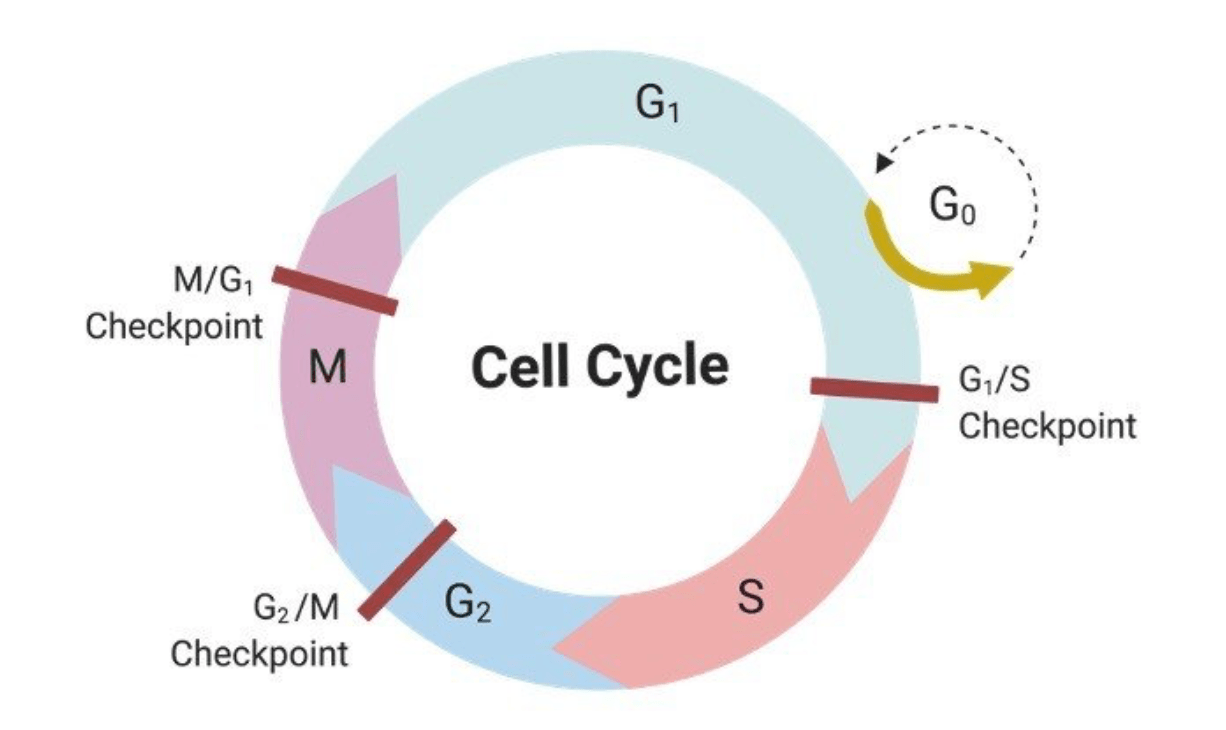
(Double Jeopardy)
Describe the steps or levels of DNA packaging.
hint: 6 levels
1. DNA wraps around histone proteins, making nucleosomes
2. Beads on a string/chromatin forms, so nucleosomes connect
3. 30 nm Chromatic fiber forms with the help of H1 histone
4. DNA loops
5. Heterochromatin
6. Chromosome
(Double Jeopardy)
What are the functions of DNA helicase, topoisomerase, single stranded binding proteins (SSB), primase, and DNA ligase?
1. DNA helicase: unwinds/separates the parent strands
2. Topoisomerase: relieves supercoiling ahead of the replication fork
3. SSB: bind to the unwound DNA strands to keep them stable
4. Primase: adds RNA primers
5. DNA ligase: seals Okazaki fragments together and links any remaining gaps
When is cyclin produced and is the most available? Which events in the mitotic cycle are regulated by cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk)?
Cyclin is produced throughout interphase and reaches a threshold at the end of G2. Since there's more cyclin, there is a higher chance it will bind to Cdks and allow mitosis to begin.
Cdks play a role in:
- Nuclear envelope breakdown
- Chromosome condensation
- Spindle formation
What is base excision repair in DNA?
Excision repair is when single abnormal nucleotides are removed and replaced by repair endonuclease enzymes.