What technology was essential for the development of the Cell Theory?
Compound light microscope
True or False: All eukaryotes are multicellular
False
Which organelle contains digestive enzymes to help break down things in the cell
Lysosome
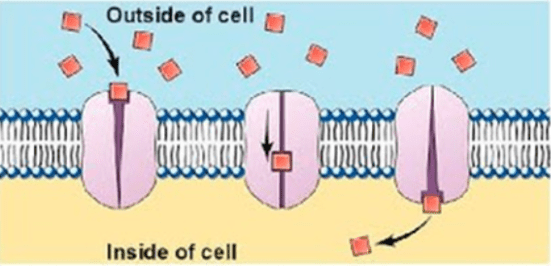
What type of transport is shown?
Facilitated diffusion
True or False: Osmosis can be simple or facilitated diffusion
True
Who was the first scientist to observe and name cells?
Robert Hooke
True or False: Protists are prokaryotic
(Mostly aquatic - amoeba, paramecium, algae, slime mold)
False
What is number 1 pointing to and what is made there?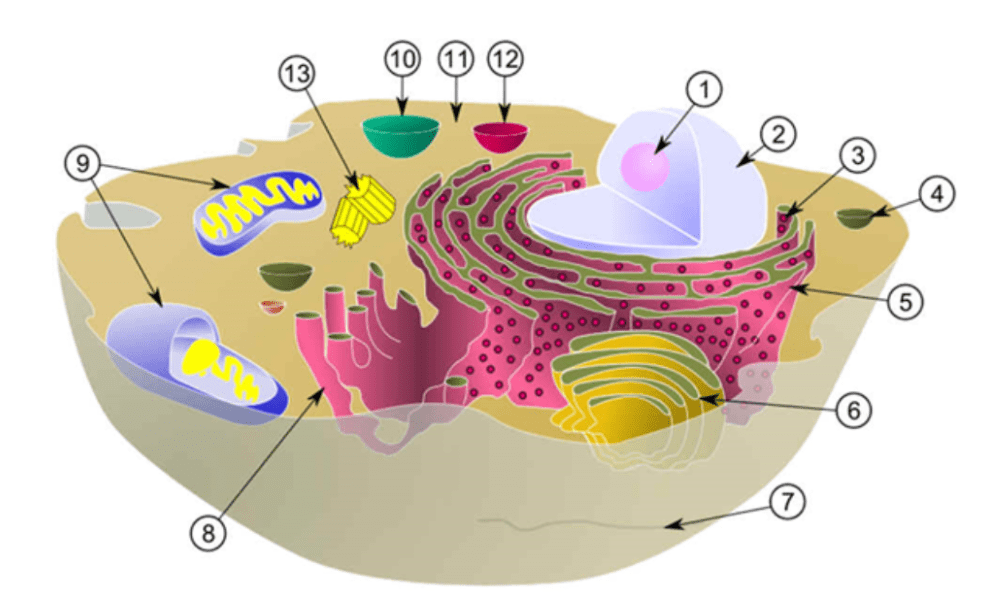
Nucleolus, makes ribosomes
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
Fatty acid tails
Osmosis is the movement of water towards ____________ solute concentration. (Higher or Lower)
Higher
How many cells make up the average human body?
Which cell type is older (evolved first)
Prokaryote
What process occurs in mitochondria to make ATP?
Cellular Respiration
Which component of the cell membrane is important for maintaining a balance between stability and flexibility?
Cholesterol
What type of solution is shown here? (light blue)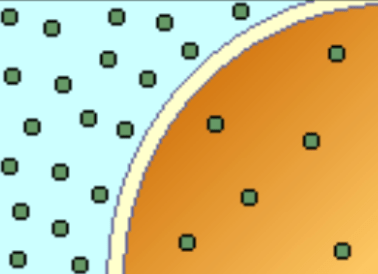
Hypertonic
Virchow's observation of cell division led to which part of the Cell Theory?
Part 3: All cells come from pre-existing cells
What are the small, circular, extra, non-essential chromosomes in prokaryotes called?
Name 3 organelles that a plant cell has that an animal cell does not have
Cell wall, chloroplast, large central vacuole
What is the function of carbohydrates on the surface of the plasma membrane?
Cell-to-cell recognition and communication
What will happen to the size of this cell?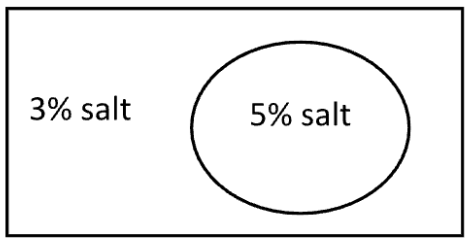
It will swell
What ratio in cells limits their size?
Surface Area : Volume Ratio
Name 3 cell structures that ALL cells have (both prokaryotic and eukaryotic)
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA
A protein has been synthesized and is now being exported out of the cell. What path will it take through the organelles, from production to export? (Include 5 different organelles, 1 will be repeated)
___ --> ___ --> ___ --> ___ --> ___ --> ___
Ribosome --> Rough ER --> Vesicle --> Golgi --> Vesicle --> Cell Membrane
What types of molecules are able to do simple diffusion? List 2 examples
Small non-polar molecules like O2 and CO2
You put a freshwater fish in the salty ocean. What will happen to the fish's cells?
They will shrink/shrivel