First to observe/discover cells, named them after the rooms in a monastery. He was looking at cork under the microscope.
Who is Robert Hooke?
What is prokaryotic?
Where the DNA is found in a eukaryotic cell
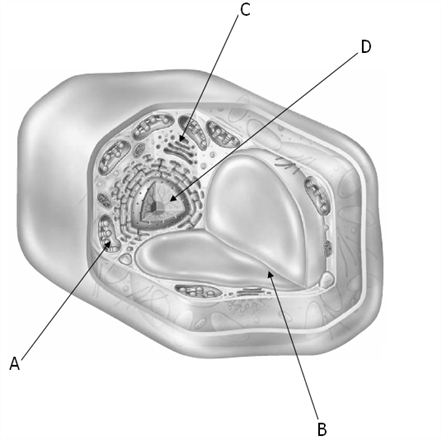
What is the nucleus? (Letter D in the diagram)
The passive transport of water across a permeable membrane
What is osmosis?
The subunits (building blocks) of carbohydrates that are produced during the process of photosynthesis
What is glucose sugar?
German scientists who proposed the original 2 statements of the cell theory; they studied plants and animals
Who are Schleiden & Schwann?
Type of cell that has no nucleus
What is a prokaryote?
Acts as a barrier to what can enter/exit the cell; offers protection from the outside environment; made of a phospholipid bilayer
What is the cell membrane?
Process that occurs in the mitochondria that breaks down food molecules in the presence of oxygen (O2) to release ATP energy
What is cellular respiration?
A byproduct (waste) of photosynthesis that is necessary for cellular respiration to occur
What is oxygen gas (O2)?
The three statements of the classical cell theory
What is
1. The cell is the most basic unit of life
2. All living things are made of cells
3. Cells come only from preexisting cells
Type of cell that has a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, is larger and more complex
What is a eukaryotic cell?
Prepares, packages, and transports proteins and other materials made by a cell from one area (or one cell) to another; Amazon of the cellular world
What is the Golgi apparatus/body?
Movement of substances across a cell membrane (either against the concentration gradient or substances that are too large for protein channels) that uses ATP energy
What is active transport?
Plant pigment that is necessary for photosynthesis to occur
What is chlorophyll?
Person(s) responsible for disproving spontaneous generation at the cell level by stating that cells only come from preexisting cells
Who is Rudolf Virchow? (and Robert Remak)
The Theory of Endosymbiosis explains the evolution of which type of cell?
What is eukaryotic?
Usually the largest organelle in most eukaryotic cells
What is the nucleus?
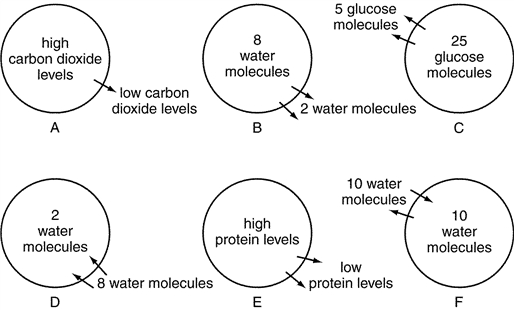
Which diagram represents equilibrium?
What is diagram F?
What is photosynthesis?
Person(s) responsible for stating that all animals are made of cells
Who is Theodor Schwann?
Site of photosynthesis in eukaryotic cells
What is the chloroplast?
Xylem and phloem are specialized transport tissues in plants. What do the transport?
What is food (glucose) and water?
Process that releases small amounts of energy without using oxygen (Averages 2 ATP instead of 36 ATP); occurs in the cytoplasm of cells; can result in the production of waste products such as ethanol and lactic acid
What is fermentation?
Person(s) who state all plants are made of cells?
Who is Matthias Schleiden?
Known as the "bag of death"; acts as cell's custodian cleaning up broken, worn-out parts of the cell
What is the lysosome?
Main difference between active and passive transport
What is passive transport does NOT use cell energy, while active transport uses the cell's energy
The green color of leaves is caused by light reflected from this
What is chlorophyll?
Person(s) who first saw living cells in a microscope, really discovering protists, but called them "animalcules"
Who is Anton Leeuwenhoek?
Difference between rough ER and smooth ER
What is the rough ER is covered in ribosomes?
Process where cell brings in very large substances by wrapping its membrane around it and pushing the substance inward
What is endocytosis?