Name 3 characteristics of life
-Made of cells
-Grows and develops
-Maintains homeostasis
-Reproduces
-Responds to a stimulus
-Displays organization
-Requires energy
This organelle controls everything that happens in the cell
Nucleus
Cells following different DNA instructions in order to have different structures and functions
Define homeostasis in scientific terms
The process by which organisms regulate and maintain stable internal conditions
Why do we always start on the lowest magnification when using microscopes?
It allows you to see more of the specimen which helps you to find it!
Which characteristic of life explains why babies and adults do not look the same?
Growth and development
Name 3 organelles not found in animal cells
Cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplasts
List the following in order from smallest to biggest
Cell, Organelle, Tissue, Molecule, Atom, Organism, Organ, Organ System
Atom, Molecule, Organelle, Cell, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism
Why is it important for our bodies to maintain homeostasis?
If homeostasis is not maintained, it can affect every process in our bodies. Some body functions need to happen within certain temperature ranges, and homeostasis helps us maintain a stable temperature (among other things).
This organelle is the most numerous in the cell and helps make proteins
Ribosomes
Give an example of a stimulus and response
-Sweating in response to hot weather
-A touch-me-not plant recoiling from someone poking it
-Heart rate increasing as a result of exercise
What organelle is this an analogy for?

Ribosomes - make proteins
Why do scientists study stem cells?
Stem cells have the potential to treat diseases like diabetes - if stem cells can be turned into new pancreatic cells, they could potentially be injected into someone with diabetes and help them start producing insulin again.
How does sweating help us maintain homeostasis?
Sweating happens when the body overheats. The brain tells the body to sweat, and the sweat evaporates off our skin which cools us down and lowers our body temperature.
 Why are plants green?
Why are plants green?
They contain chlorophyll (which is green)
What are two of the characteristics of life a car shows?
Responds to a stimulus
Displays organization
What is the function of the central vacuole?
Stores water for the plant and applies pressure to the cells (turgor pressure)
Do all cells have the same DNA?
Yes - they all have the same DNA, they just follow different instructions based on their job
What is glucagon and how is related to maintaining blood sugar?
Glucagon is released from the pancreas when blood sugar levels are too LOW. Glucagon makes the liver release some stored glucose, which raises blood sugar levels.
Is this a prokaryotic cell or a eukaryotic cell? How do you know?
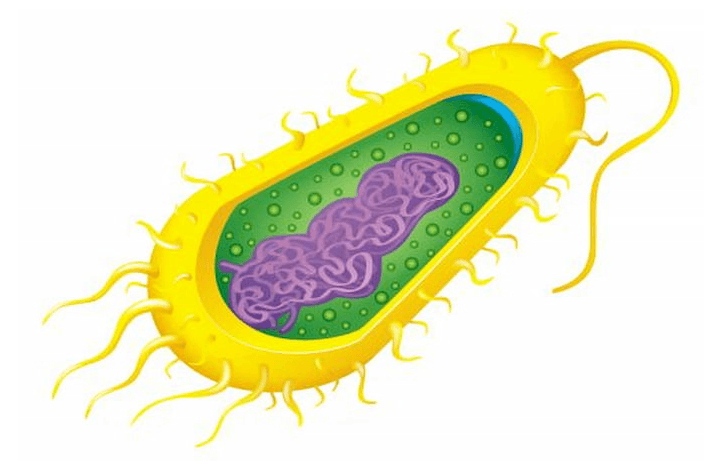
Prokaryotic - has a tail, no organelles, DNA is just floating in the middle
Some of the characteristics of life apply to water but water is not a living thing - why?
Not made of cells
Can't reproduce
Not organized
Doesn't maintain homeostasis
Why is the inner membrane of mitochondria folded?
Describe a specific type of cell and discuss what makes it specialized.
(answers will vary - look back at the extra credit assignment we did)
How does this graph show negative feedback?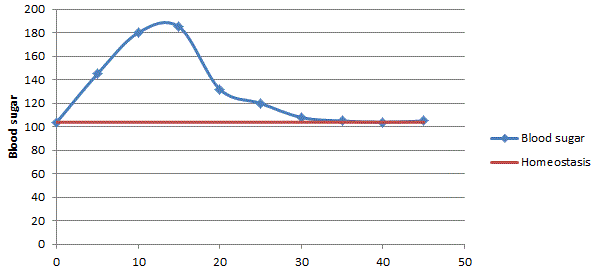
Is this a plant cell or an animal cell? How do you know?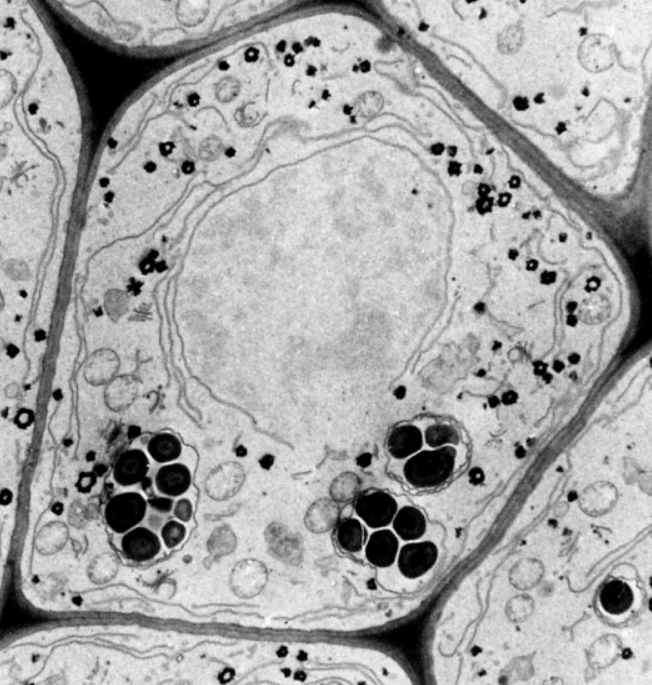
Plant cell: cell wall visible, well defined square-ish shape, large central vacuole