Which of the following is true about the cell membrane?
- it is mostly made of proteins
- it is rigid
- it is selectively permeable
- it is only present in plant cells
it is selectively permeable
What are the three types of passive transport?
Diffusion
Osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
In a hypertonic solution, does the solution have more water or less water than the cell?
HYPER has more solute than the cell and less water, so water leaves the cell.
Cells spend most of their life cycle in what phase?

Interphase
What type of cells undergo mitosis?
Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells, or both?
Eukaryotic cells only
(because nucleus!!!)
What are the two functions of the cell membrane?
Protection -- from the outside environment
Regulation -- controlling what enters & exits the cell
1. Passive Transport ____________ energy and transports substances from _________ concentration to _________ concentration
2. Active Transport ____________ energy and transports substances from _________ concentration to _________ concentration
1. Passive Transport DOES NOT NEED energy and transports substances from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration
2. Active Transport NEEDS energy and transports substances from LOW concentration to HIGH concentration
In roots of plants, water enters cells because the outside environment is ________________.
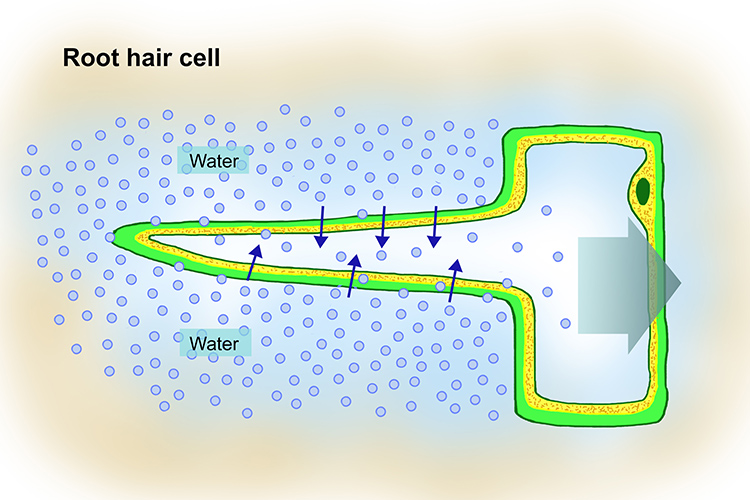
Hypotonic! Water moves from high to low concentration
During interphase, the DNA exists in which form?
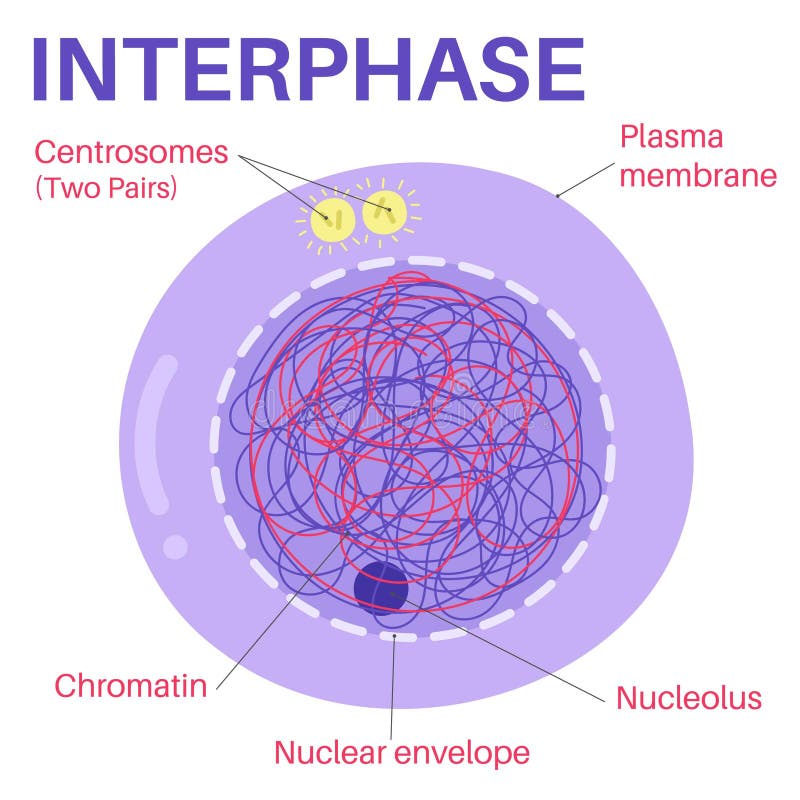
ChromatiN
What protein coded by a specific gene is called the "guardian of the genome" because of its specific tumor suppressing properties?

p53
What part of the phospholipid bilayer is hydrophobic and what part is hydrophilic?
Phosphate Heads facing outside of cell and inside of cell are hydrophilic.
Fatty Acid Tails in the inside of the membrane are hydrophobic
Glucose is a large molecule that needs the help of a protein to enter the cell, though it does not need energy to do so. What type of transport is this? Be specific
Facilitated Diffusion
In what type of solution does water both enter and leave the cell? When water does this, how do we describe this equal balance of concentration?
1. _______________ solution
2. ________________ __________________

Isotonic Solution
Dynamic Equilibrium
During anaphase, what exactly is separating?
________________ __________________
Sister chromatids
During what phase is there a critical checkpoint that double-checks DNA before determining if the cell will continue on to cell division or not.

G2 phase
What macromolecule is not present in the cell membrane?
Where is it actually found?
Nucleic Acids
DNA in nucleus
List the three types of active transport and explain what they are.
Protein Pump - protein pushes substances across the cell membrane from low to high concentration
Endocytosis - substances outside of cell are brought into cell by forming a vacuole around them (like pac-man)
Exocytosis - substances leave the cell when a vacuole in the cell fuses to the cell membrane to release material
What is plasmolysis?
Must explain fully (what type of solution, what direction water moves, what type of cell, and what happens to the cell)
Plasmolysis is when a plant cell is in a hypertonic solution, so the water leaves the cell into the solution, causing the plasma membrane to detach from the cell wall and the plant to die
Does mitosis occur so that cells can:
- reproduce a new organism
- grow & repair
- both?
ONLY growth and repair
(reproduction occurs by meiosis and binary fission only)
When a cell's DNA gets double-checked but the DNA is deemed to have too many errors, the cell decides not to continue to cell division.
Instead, it will decide to self-destruct. What is this programmed cell death called?
You must either spell it exactly right or pronounce it exactly right to get the points.

Apoptosis
What part of the cell membrane is responsible for "sensing" things outside of the cell?
Carbohydrate chains
1. Define Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis
2. Active or Passive Transport?
Must get both right.
1. Phagocytosis is "cellular eating" -- when the cell engulfs solid substances like food or bacteria. Pinocytosis is "cellular drinking" -- when the cell engulfs extracellular fluid/liquids
2. Active Transport
What happens to a red blood cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution?
What happens to a plant cell when placed in a hypotonic solution?
Must explain which direction the water moves, what happens to each cell, and the vocabulary word/term that corresponds to your explanation of what happens to the cell.
In both, water leaves solution and enters cell.
Red blood cell fills with so much water it bursts = cytolysis
Plant cell wall is able to resist the turgor pressure, so it becomes turgid
List the 4 phases of mitosis in order and explain what happens in each step.
I will give you three tries to get it all right but will not tell you what is wrong.
You have 2 minutes for the first try, then 30 additional seconds for each try after.

Prophase -- nuclear envelope disappears, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrioles form spindle fibers
Metaphase -- chromosomes line up at middle of cell and spindle fibers attach to centromeres (center of chromosomes)
Anaphase -- spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart to the sides of the cell
Telophase -- spindle fibers disassemble, chromosomes uncoil back to chromatids, nuclear envelopes reform around the chromatids
What happens during G1, S, and G2 phase? What phase are these three phases a part of?

G1 phase -- cell grows and makes copies of organelles
S phase -- DNA synthesis (DNA makes copy of itself)
G2 phase -- cell continues to grow, making organelles and proteins preparing for cell division
INTERPHASE

