The 4 types of macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids (in any order)
All cells have ______.
Any of these:
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA
Ribosomes
The powerhouse of the cell is this organelle
Mitochondria
This is what allows things in and out of the cell
Cell membrane
Enzymes attach to these
Substrates
This macromolecule is the main source of energy for living things
Carbohydrates
All cells are surrounded by a _________.
This is the control center of eukaryotic cells
Nucleus
Name 1 type of passive transport
Osmosis
Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Fats, oils, and cholesterol are all types of these
Lipids
Proteins are made of these
Amino Acids
The image shows which type of cell
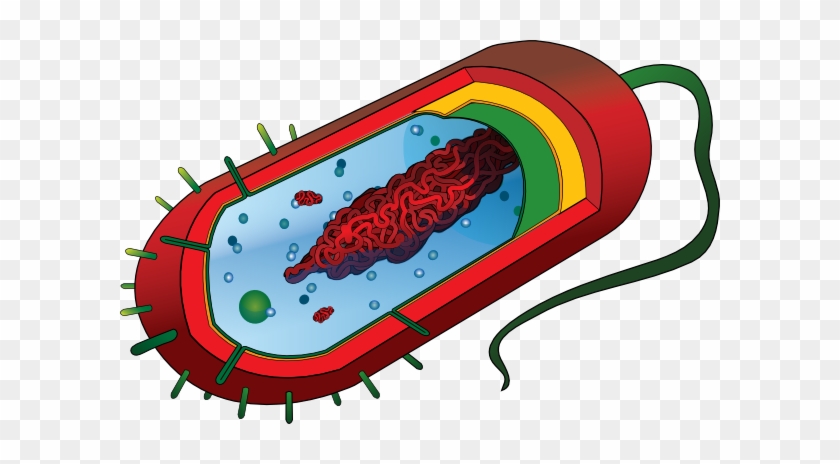
Prokaryote (or bacteria)
This part of the cell makes proteins for cells to use
Ribosome
This is the movement of water across a membrane from high to low concentration
Osmosis
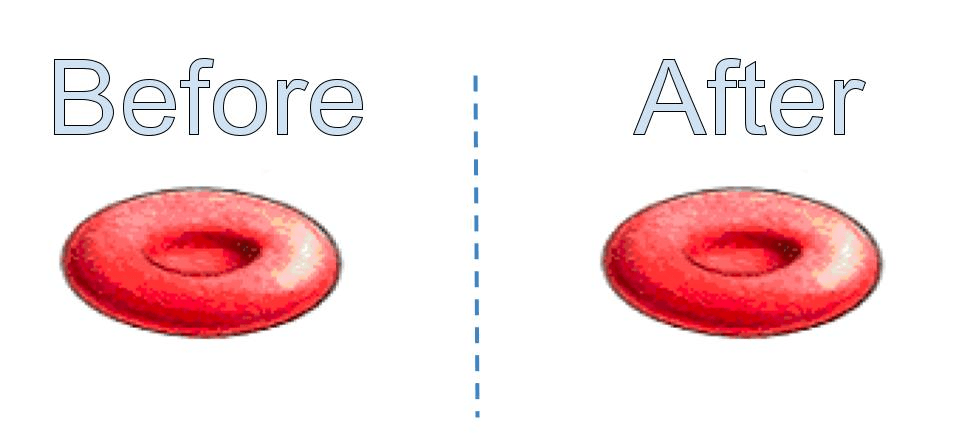 A blood cell was placed into an IV solution. The results are shown. What type of solution was it?
A blood cell was placed into an IV solution. The results are shown. What type of solution was it?
Isotonic
Enzymes are this type of molecule
Protein
The image shows what type of cell

Animal cell
OR
Eukaroytic cell
This organelle makes sugar during photosynthesis for plant cells
Chloroplast
In active transport, molecules go from low to high concentration, which requires this
Energy
One
Enzymes work by changing this part of chemical reactions
Speed (speed of the reaction)
These are 2 of the 3 parts of Cell Theory.
All cells come from existing cells.
All living things are made of cells.
The cell is the smallest living unit.
This is the gel-like fluid inside of cells
Cytoplasm
The process of keeping internal conditions fairly constant is known as this
Homeostasis
A red blood cell was placed in a beaker of ocean water. The cell shriveled up. What type of solution is ocean water?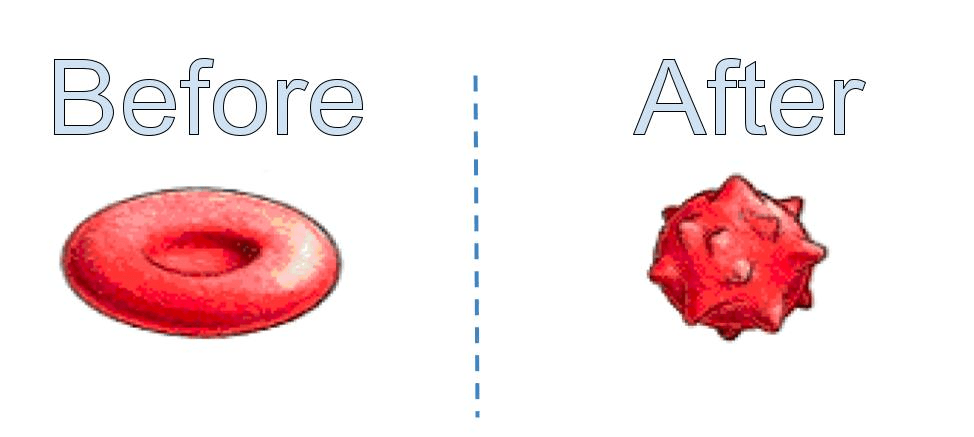
Hypertonic