Which characteristic is not common to both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
A. Genetic Material
B. Cell Membrane
C. Cytoplasm
D. Multicellular Organisms
D. Multicellular Organisms
If a cell were lacking lysosomes, what would the cell not be able to do?
effectively digest and remove waste products, worn-out cell parts, and foreign materials
What type of cellular transport requires a cell to use energy?
A. Facilitated Diffusion
B. Active Transport
C. Diffusion
D. Osmosis
B. Active Transport
Explain the role of the cell membrane in maintaining homeostasis on a cellular level
provide protection to the cell- and prohibits the entry of toxic or unwanted substances.
Research has shown that uncontrolled cell growth and development can lead to which of these diseases?
A. AIDS
B. Cancer
C. Hemophilia
D. Down Syndrome
B. Cancer
Which of the following is found in a eukaryotic cell, but is not found in a prokaryotic cell?
A. Cytoplasm
B. Cell Membrane
C. Nucleus
D. Flagella
C. Nucleus
What part of the cell controls the passage of materials into and out of a cell?
Cell Membrane
In a hypotonic solution, water will move Into the cell, causing the cell to __________
A. Shrivel
B. Swell
C. Do nothing
B. Swell
Describe an example of a positive feedback mechanism
Fruit ripening- leads to more and more fruit ripening
If a cell has 8 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each of its daughter cells have after mitosis?
8
Cells often store materials like water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates in sac-like structures called
A. Chloroplasts
B. Lysosomes
C. Mitochondria
D. Vacuoles
D. Vacuoles
Energy is produced in the form of ATP. What part of the cell is involved?
Mitochondria
Fruit Ripening is an example of what
A. Positive Feedback Loop
B. Negative Feedback Loop
A. Positive Feedback Loop
what type of transport transports O2 and CO2?
Diffusion
What makes stem cells different from other cells in the body?
A. They are larger than other cells, and can absorb broken cells to repair them.
B. They repair cells by breaking open and making their cell parts available for absorption into other cells.
C. They are undifferentiated cells that can turn into a number of different kinds of cells as needed.
D. They are cells that grow uncontrollably
C. They are undifferentiated cells that can turn into a number of different kinds of cells as needed.
Which of the following serves as the cell’s boundary from its environment and controls what goes in and out of the cell?
A. Mitochondria
B. Cell Membrane
C. Chloroplast
D. Golgi Apparatus
B. Cell Membrane
What is the Cilia?
Structures shaped like small oars that beat in unison to move the cell or the liquid around it.
The need for an organism to stay stable by regulating internal conditions is called what?
A. Concentration
B. Life
C. Homeostasis
C. Homeostasis
What type of transport transports water?
Osmosis
What are The two purposes of the cell cycle?
Grow and Repair!
Which principle of cell theory best supports the idea that new cells will replace damaged cells in a scraped knee?
A. All living things are made of one or more cells
B. Cells are the basic unit of life
C. All cells come from other cells
D. The Nucleus of cells in animals reproduces when exposed to air
C. All cells come from other cells
what does the Flagella do?
Acts as a whipping propeller, moving a cell through its environment.
What is this an example of?
A. Hypertonic
B. Hypotonic
C. Isotonic 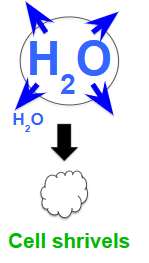
A. Hypertonic
What type of transport happens when a white blood cell captures bacteria?
Endocytosis
Beginning with prophase, list the parts of mitosis in order
Prophase, metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis.