What are cells?
The smallest units of life.
State the name of the level in the cell organisation flow chart that is made up of groups of specialised cells?
Tissue
What does this part of the microscope do?

These are the objectives lenses and they increase the magnification.
Which organ system is responsible for moving fresh air around the body and removing waste gases?
Respiratory system
What does Villi do as part of the digestive system?
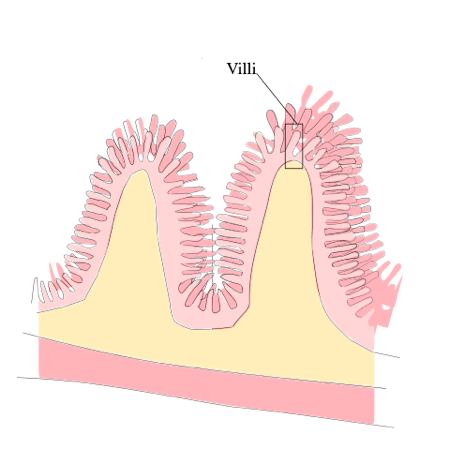
Lining the small intestine are villi. Villi increase the surface area of the small intestine allowing more nutrients to be absorbed in the circulatory system.
Which organelle is referred to as the brain of the cell?
Identify the highest level in the cell organisation structure and provide an example.
The highest level is the organism, for example a human or a zebra.
What are the three rules of cell theory?
All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells are the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
What are the 3 main roles of the digestive system?
The digestive system has three main functions relating to food: digestion of food, absorption of nutrients from food, and elimination of solid food waste.
What is the role of the diaphragm?
It is located below the lungs and helps you breath in and out by flattening down to allow air to be drawn in to the lungs and then returns to its original shape forcing the air out.
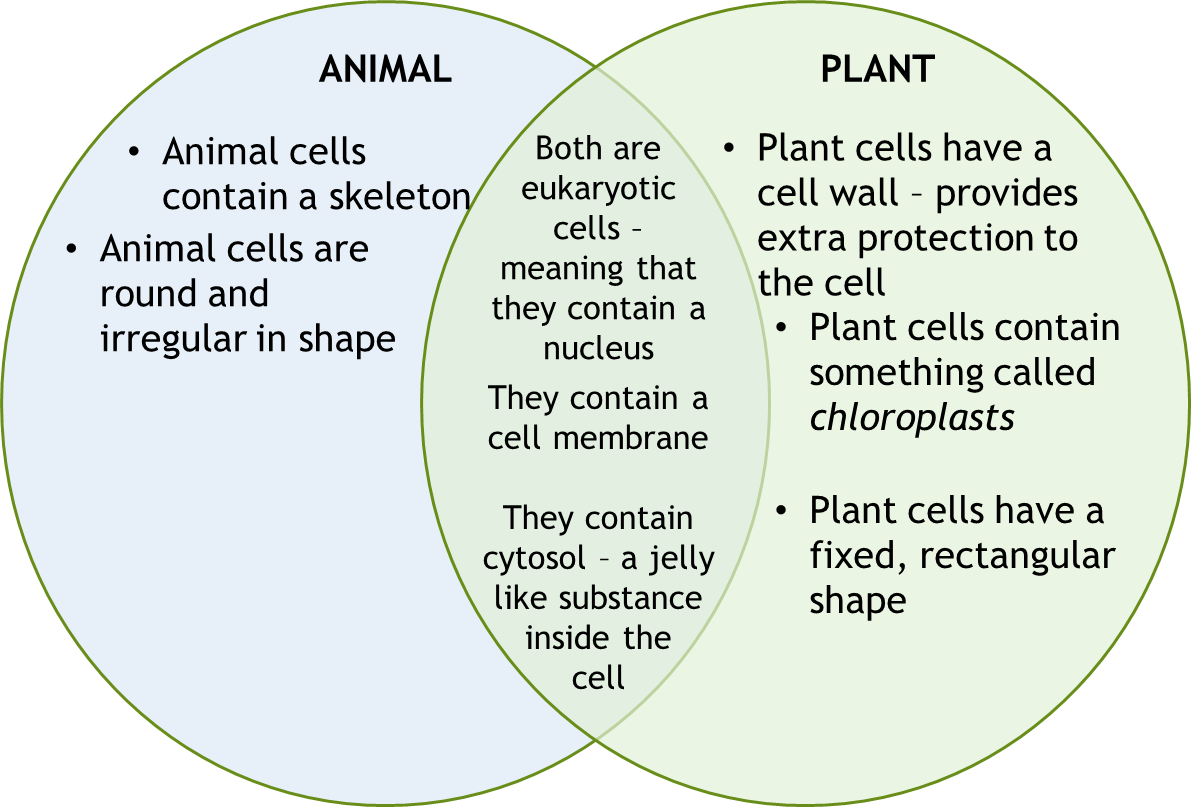
Complete the Venn Diagram -
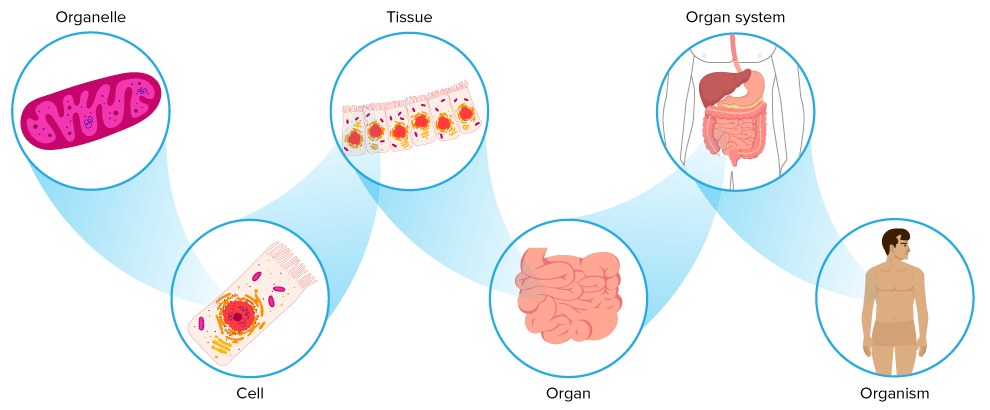
Create a flowchart of the levels of organisation in a human body.
What is Zacharias Janssen famous for?
He is credited, with the help of his father, of inventing the first compound microscope.
What is the difference between the role of bronchioles and alveoli in the lungs?
In your lungs, the main airways, called bronchi, branch off into smaller and smaller passageways. The smallest airways, called bronchioles, lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli. The bronchioles deliver air to and from the alveoli. Alveoli are where the lungs and the blood exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing, with their membrane preventing liquid entering into the lungs.
Describe three things that a cell needs to survive
To survive a cell needs to be able to extract energy, eliminate waste, and reproduce.
Identify two organelles that only appear in plant cells and explain what they do
Example response -
Two organelles that occur only in plant cells are the cell wall and chloroplasts. The cell wall has the role of giving the plant cell structure and assists the plant to have shape and strength. It sits outside the cell membrane and assists with regulating movement of materials in and out of the cell. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and this allows the plant to undertake the process of photosynthesis. This process is how the plant produces energy from sunlight to fuel the cell.
Explain why there are different sized and shaped cells within the body. Provide an example.
Each type of cell within the body is specialised to carry out a particular function, either solely, or as part of a particular tissue. The shape and size vary from cell to cell consistent with their functions and composition. For example, a neuron is long and branched to help with transmission of signals throughout our body, while a red blood cell is a small donut shaped cell that allows it to move through small spaces.
While working to improve the microscope in 1665, what did Robert Hooke discover?
Robert Hooke is credited with improving the microscope which led to discoveries that began Cell theory. He looked through a microscope at a piece of cork and he thought the cork looked as if it was made of tiny pores, which he came to call “cells” because they reminded him of the cells in a monastery.
The cardiovascular system: what are the key parts and what does it do?
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels (including veins, arteries and capillaries), and blood. Its primary function is to transport nutrients and oxygen-rich blood to all parts of the body and to carry deoxygenated blood back to the lungs. It also delivers hormones and other important substances to cells and organs in the body and helps maintain body temperature, among other things.
Identify the location and names of the two parts involved in the magnification of a specimen, and explain how they work together for magnification. 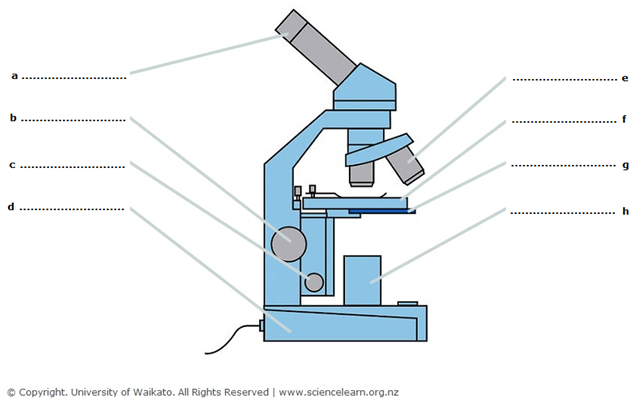
Part a, the eyepiece lens, and part e, the objective lens, combine to determine the amount of magnification being viewed between the two. For example, if the eyepiece has a magnification of x10 and the objective has a magnification of x40, then the total magnification is 10 x 40 = 400x.
Two of the main categories of cells are Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. How are they different? Provide an example of each.
Prokaryotic cells are single celled organisms that do not contain a nucleus, An example of a prokaryote is bacteria. Eukaryotic cells exist in multicellular organisms that contain a nucleus. An example of a eukaryotic cell is a plant cell.
Blood is made up four different types components.
What are they and what do they do? 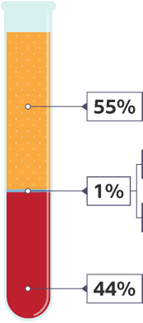
Plasma makes up about 55% of your blood and carries the blood cells and platelets around the body. Red blood cells make up approximately 45% of blood and carry oxygen from the lungs to every cell in the rest of the body. White blood cells combined with Platelets make up 1%. White blood cells fight infection and stop disease. Platelets are made up of broken down parts of cells that form scabs.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch biologist made famous by what?
He was the first person to see living cells under the microscope. He saw bacteria that he had scraped off his teeth and called them 'animalcules'. He did this with a microscope he invented that could magnify things 200 to 300 times their size.
How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work together?
The circulatory and respiratory systems get connected in the lungs. To pump the blood within the body, the circulatory system requires oxygen from the lungs and the respiratory system gives the oxygen that it takes from the air into your bloodstream.
Do you think that there are ethical issues with organ transplants?
Example responses might reference making sure it's fair, how do we make sure donors agree and how do we stop people trying to profit.