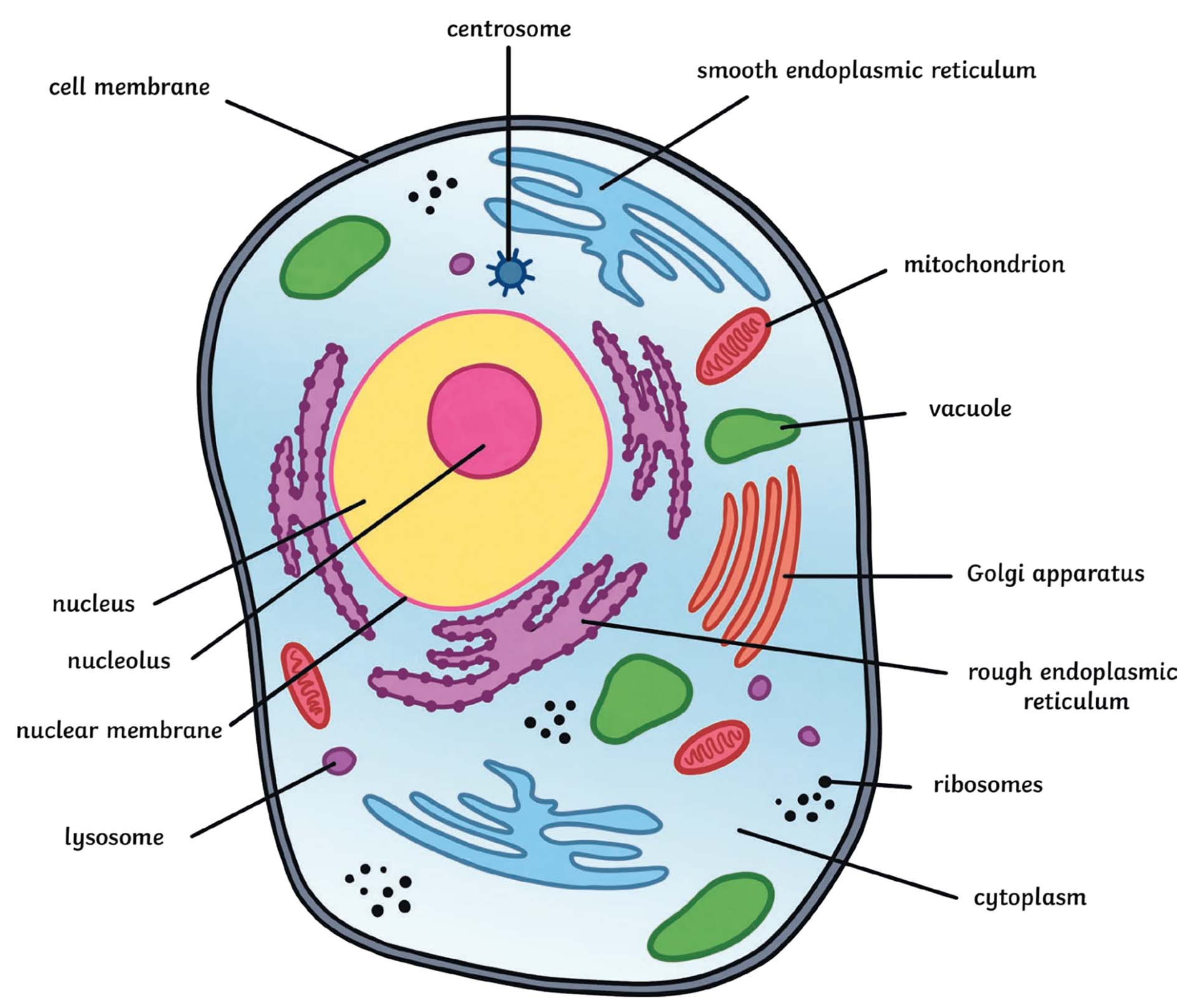
This organelle controls what enters or leaves the cell (gate keeper)
cell membrane
The rigid structure surrounding the plant cell that provides protection
Cell wall
2nd principle:Cells are the _____ unit of life.
basic
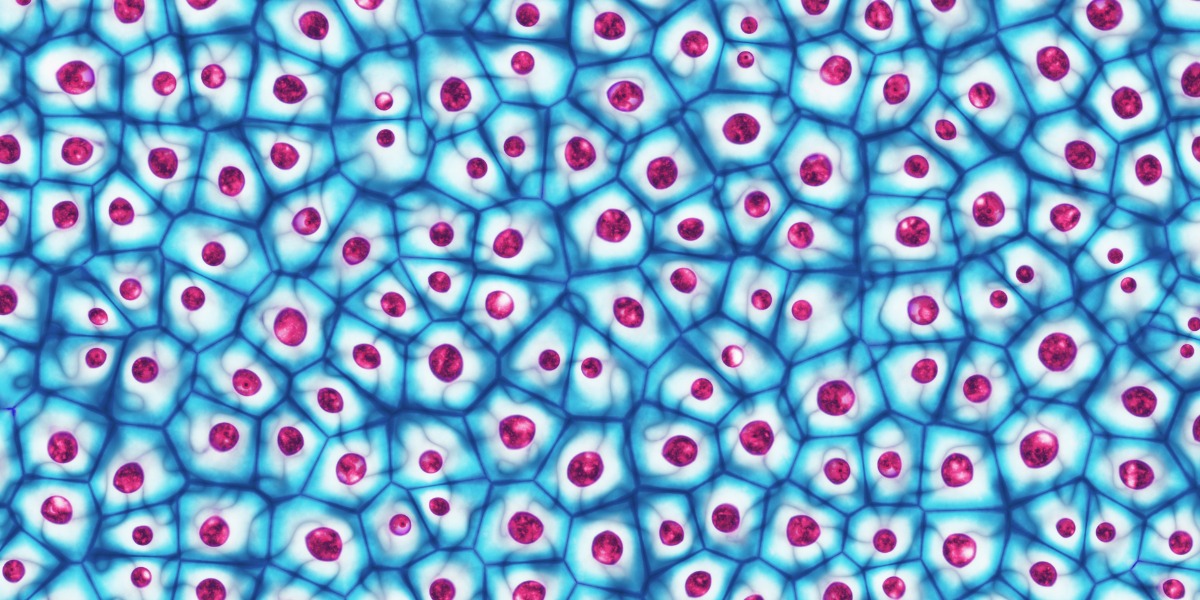 What level of organization is this?
What level of organization is this?
Tissue
What type of cell is this? (animal or plant)
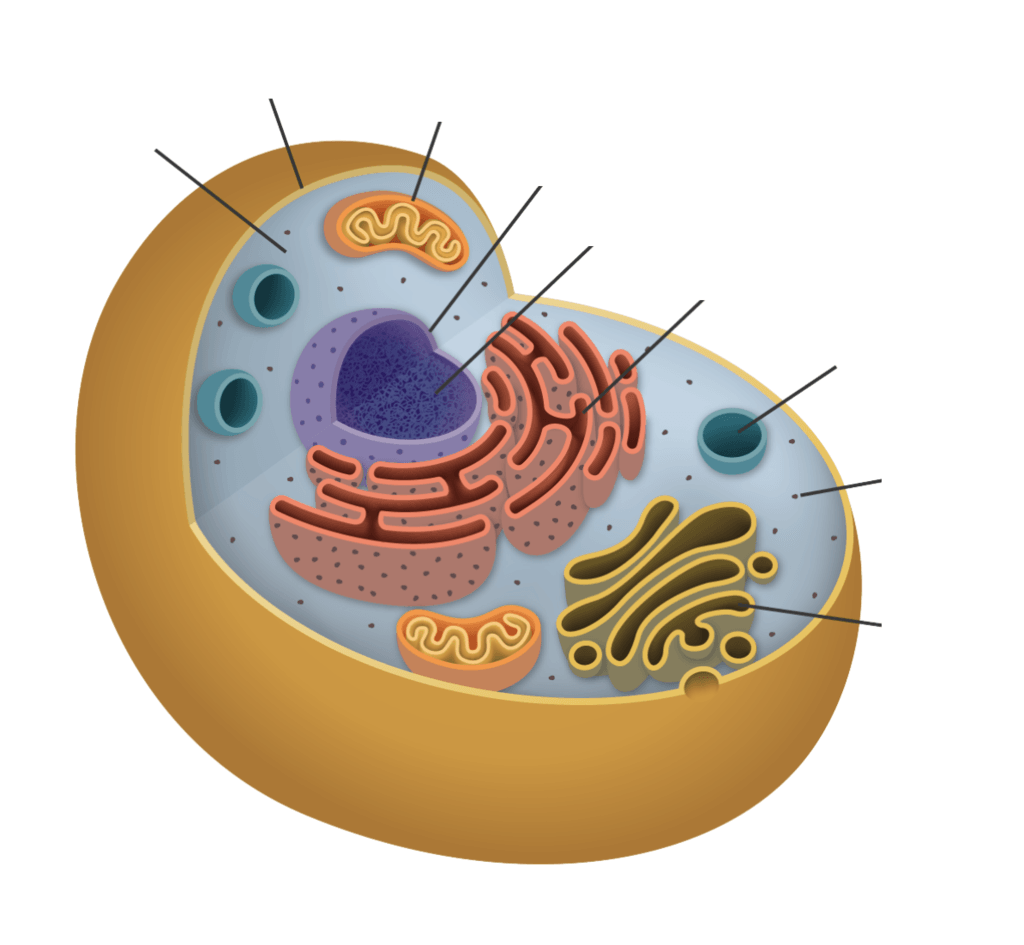
Animal Cell
What is an organism with only one cell called?
Unicellular
What is the function of the mitochondria
Uses food (sugar) to create energy for the cell
This is the site of photosynthesis (converting sunlight into energy)
the chloroplast
All ____________things are made of cells
Living
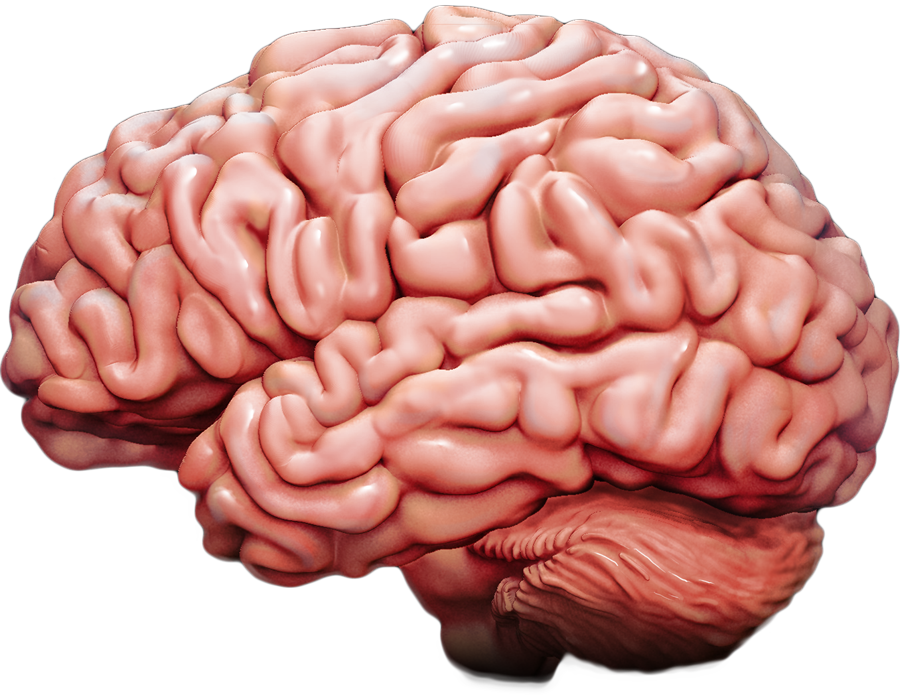
Organ
What type of cell is this? (animal or plant)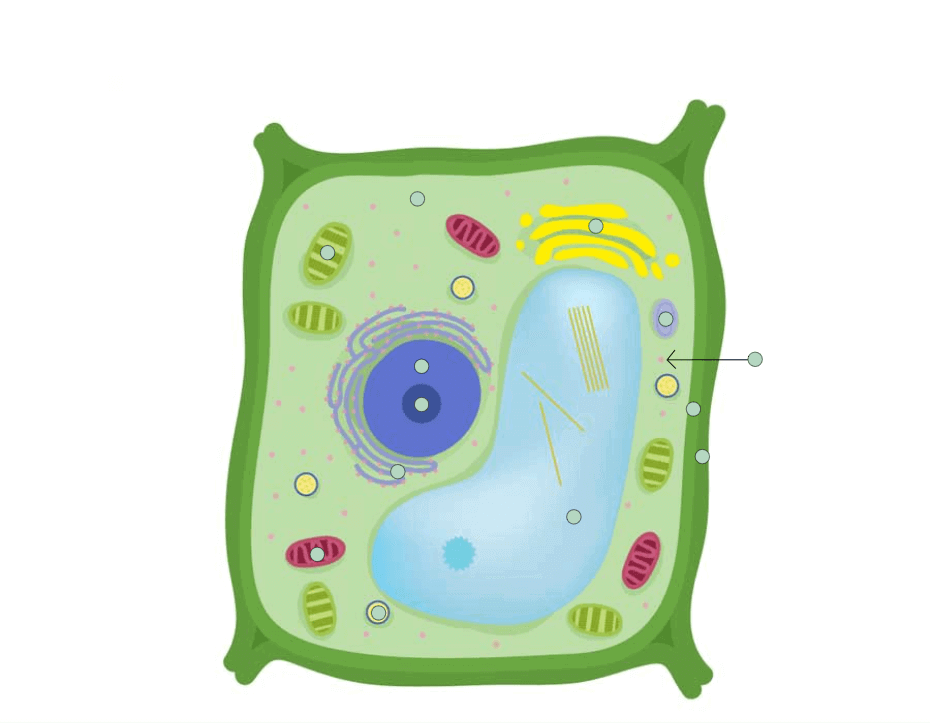
Plant cell
What is an organism with more than one cell called?
Multicellular
What is the jelly-like substance inside the cell in which other organelles are suspended?
Cytoplasm
Where is DNA mainly found in a cell?
The nucleus
3rd principle: All new cells are made up from ______________ cells
Preexisting
Cell
What is an example of a multicellular organism?
Animal or plant
What are cells with a nucleus called?
Eukaryotic
The control center of the cell
Nucleus
Which organelles are found in plant cells but not animal cells
Large central vacuole, chloroplast and cell wall
1st principle: All organisms are composed of ______________ cells
one or more

Organism
What is an example of a unicellular organism?
Amoeba or Bacteria
What is a simple cell without a nucleus called?
Prokaryotic
What does the vacuole do for the cell?
Stores food and water
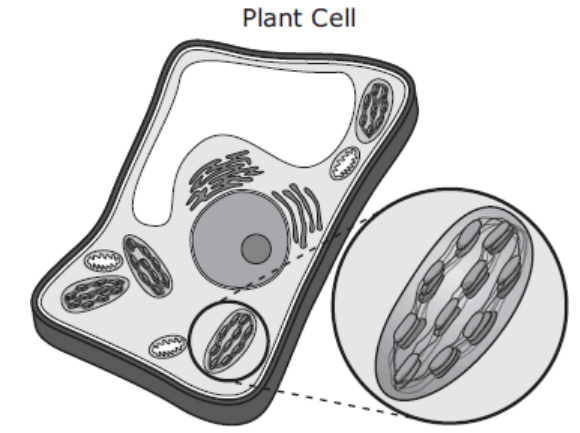 What is this organelle and it's function?
What is this organelle and it's function?
Chloroplast, uses energy from sunlight to make sugar.
Who discovered and named the cell?
Robert Hooke

Organ system
What is an example of a prokaryote?
Bacteria
What type of cells are plant and animal cells?
Eukaryotic cells