These types of cells do not have a nucleus or organelles
prokaryotic cells
The control center of the cell
nucleus
Triple points
The rigid structure surrounding the plant cell that provides protection and support
Cell wall
Triple points and point donation
Which two levels of biological organization did we look at using the microscopes?
tissue and organ
Quadruple points
How does the DNA in all of your cells compare?
It's all the same
Triple points
Which type of gene mutation is most likely to be neutral or lead to a new beneficial trait for an organism?
substitution
These types of cells are large, complex and contain organelles
eukaryotic cells
What is the function of the mitochondria
Generates energy (ATP)
This is the site of photosynthesis
the chloroplast
About how many cells does each human have?
trillions
What type of cell is this?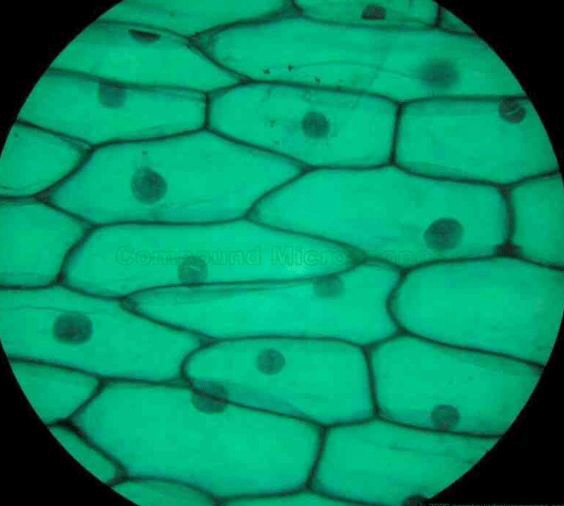
Plant cell
What type of mutations affect many genes and usually cause serious problems for the organism?
chromosome mutations
Double points
What is the name of the type of cell division that somatic/body cells, such as skin, pancreas and liver cells go through?
mitosis

Chloroplast
Where is DNA mainly found in a eukaryotic cell?
The nucleus
Double points
Name three characteristics of life that apply to cells.
*energy use
*reproduction
*heredity
*evolution
*responsive to the environment
*maintain homeostasis
What type of cell is this?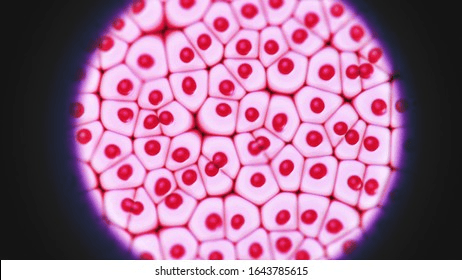
Animal Cell
This type of gene mutation occurs when the order of DNA bases is reversed
inversion
Which type of cell evolved first on Earth?
prokaryotic cells
This organelle controls what enters and leaves the cell
cell membrane
Which two organelles are found in plant cells but not animal cells
chloroplast and cell wall
Point donation
What is the name of the special type of cell that can give rise to specialized cells?
stem cells
Double points
Name the three main things that happen during interphase for most cells.
1. Cells grow
2. Cells replicate their DNA
3. Cells perform their specific functions
What type of gene mutations lead to frameshifts in which everything after the initial mutation gets messed up?
deletions and insertions
List three structures that are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
DNA, cell membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm
This organelle breaks down cellular waste and recycles it
lysosome
This organelle makes proteins
ribosome
_________ means a one-celled organism. An example is a _______
_________ means a many-celled organism. An example is a __________.
unicellular, bacterium/archaean
multicellular, any animal, plant or fungi
Point donation
What are the two parts of cell division and what occurs in each?
Mitosis = when the nucleus divides in two
Cytokinesis = when the cytoplasm divides in two
Gene mutations are only damaging to the organism if they result in what?
a messed up protein