This structure controls what enters or leaves the cell.
cell membrane
Does not require ATP
passive transport
Define Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration
List three basic structures that are common to ALL types of cells.
All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane.
All cells have cytoplasm.
All cells have DNA.
Paramecium use what structures to move around and sweep food toward their "mouth"?
cilia
Gel-like fluid that fills the space inside the cell and surrounds the organelles.
cytoplasm
Molecules moving from low concentration to high concentration across the cell membrane.
active transport
Diffusion of water is called?
Osmosis
Does not have a true nucleus or any membrane-bound organelles.
prokaryotic cell
Euglena use what structures to move around?
flagellum
Controls all the activities of the cell, including cell reproduction and protein synthesis.
Nucleus
Diffusion and osmosis are examples of which type of transport?
passive transport
Low solute and high water concentration outside the cell could cause cells to swell and burst.
Hypertonic solution
Has a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
eukaryotic cell
Amoeba use what structures to move around and catch prey to eat?
pseudopods
What is the difference between the rough ER and the smooth ER?
Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it. Smooth ER has no ribosomes.
When the cell needs to use energy to move things across the membrane.
Active transport
High solute and low water concentration outside the cell could cause cells to lose water and shrink.
Hypertonic solution
What organisms are prokaryotes
Bacteria are prokaryotes
What do Euglena use their eyespots for?
to find light
This organelle sorts and packages proteins and ships them to their final destinations.
Golgi apparatus
Movement across the membrane that does not need energy, but does need help from transport proteins.
Facilitated diffusion
Which way will the water molecules (small pink dots) diffuse? (right or left)

To the right
What organisms are eukaryotes?
animals, plants, fungi, and protists
Calculate the magnification for the highest-powered objective lens on the compound light microscopes we used in our lab.
10 x 40 = 400 X
This organelle converts glucose and other organic molecules into a form of usable cell energy called ATP.
Mitochondria
A type of active transport that keeps sodium from building up in the cell.
sodium-potassium pump
A solution with an equal solute concentration to the inside of the cell.
Isotonic solution
Which are the smallest types of cells?
prokaryotic cells
Which 2 structures do protists use to maintain the right balance of water and solutes inside their cell?
cell membrane and contractile vacuole
Name this organelle: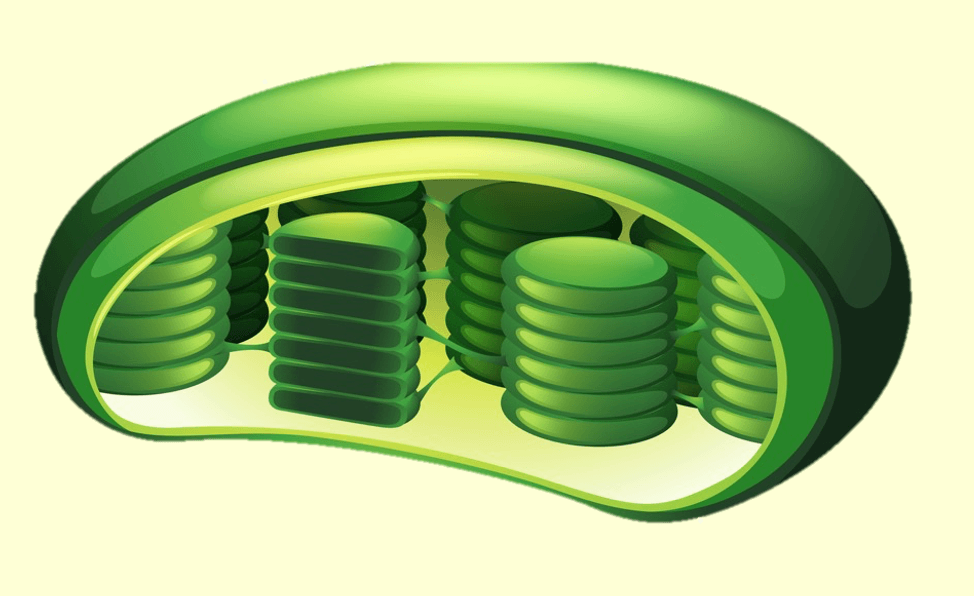
Chloroplast
When does diffusion of molecules stop?
when equilibrium is reached
If you have high amounts of glucose in the solution surrounding a cell and low amounts of glucose inside the cell, what would happen to the water molecules inside the cell?
The water molecules will move toward the outside of the cell.
In which type of cells does DNA coil up into chromosomes?
eukaryotic cells
What may happen to an amoeba if we placed it in saltwater?
it may shrink and shrivel up